CCK2– Gastrin Antagonist: Development of PNB-001 (4-Chloro-5-Hydroxy-1-Phenylethyl-5-Phenyl-1, 5-Dihydro-Pyrrol-2-one) as Anti-Inflammatory Analgesic
Study aim: To prepare and evaluate CCK gastrin antagonists from readily available materials such as furfural and to focus on inflammatory pain management.
Methods: Receptor binding assays, isolated tissue preparations and selected animal models were applied to evaluate the lead molecule PNB-001.
Results: Arylated 5-hydroxy–pyrrol-2-ones were prepared in 3 synthetic steps from furfural and subsequently optimised as CCK2 selective ligands using radiolabelled binding assays. Originally a CCK1 selective lead structure was identified and from that lead, a potent and selective CCK2 ligand (PNB-001, IC50= 22 nM) was fully SAR optimised. The antagonism was confirmed for PNB-001 by using isolated tissue preparations with CCK5. Subsequent in vivo evaluation revealed analgesic activity for the gastrin CCK2 antagonist PNB-001, in the hotplate and tail immersion test at 0.5mg /kg by IP administration in mice. PNB-001 was superior in the formalin test to the morphine standard by oral administration and in the x-maze test the anxiolytic activity was greater in magnitude than diazepam.
Conclusion: The front runner PNB-001 completed preclinical development and will enter clinical phase 1.
Keywords: Phenyl-Pyrrolone; CCK antagonist; Cholecystokinin; Gastrin; Analgesic
In terms of cholecystokinin-physiology, CCK8 is the most common peptide hormone, which is extensively found throughout the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) and is also widely distributed through the nervous system [1,2]. Originally, cholecystokinin was discovered to cause contractions of the gallbladder [3]. It was then rediscovered as pancreozymin, triggering the release of pancreatic enzymes. Finally, it was confirmed that both peptides are identical [4]. Cholecystokinin acts as a neuromodulator as well as gut hormone. CCK-ligands, agonists and antagonists have been extensively investigated as potential drug molecules [5].
Cholecystokinin antagonists have been extensively investigated as potential drug targets [6]. They were studied as growth inhibitors in certain forms of cancer, as anxiolytics, in the treatment of schizophrenia and satiety [7-10]. An agonist, the shortened CCK4 was found to induce panic in patients and the CCK2 receptor is known to mediate anxiety and panic attacks [11-13]. Cholecystokinin does cause proliferation in colon- and pancreatic cancer cell lines and therefore, CCK-antagonists were studied as growth factor inhibitors in certain forms of cancer.
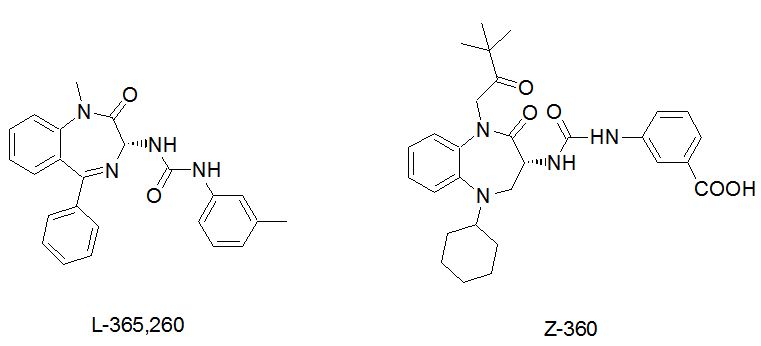
Asperlicin was the first non-peptidal lead structure from nature and analogues thereof were studied as CCK ligands [14,15]. Simplification of this lead structure by Merck led to Devazepide, a potent CCK1 selective cholecystokinin antagonist, containing a 1, 4-benzodiazepine template and an indole moiety [16]. Proglumide was the first glutamic acid based agent, marketed as Milid for the treatment of ulcer [17]. The indolyl amide of devazepide was replaced by a urea linkage and Merck’s L-365,260 resulted in a CCK2 selective antagonist [18]. Further subsequent SAR optimization led to Zeria’s improved Z-360, in which the N-alkyl side chain, the 5- position (cyclohexyl) was optimized for potency and a meta-carboxylic acid on the aryl urea linkage was introduced to enhance water solubility (Figure 1). Z-360 is a CCK2 –gastrin receptor antagonist and progressed into phase 2 trial with pancreatic cancer [19,20]. Z-360 is the most recent derivative derived from this original lead structure, with improved selectivity and bioavailability.
Molecular pain targets have been reviewed recently and the results are quite disappointing in terms of efficacy and FDA approval rate [21]. Even, this review missed out on CCK antagonists and most importantly on a very positive report, publicised only in form of an abstract [22,23]. In summary in this study, devazepide at 5 mg was found very efficient in pain management as adjunct to strong opiates in a phase 2 trial carried out at leading UK pain research centres [24].
Initial results for CCK antagonists of the pyrrolone scaffold were communicated in the area of cancer therapeutics and GI inflammation [25].
Here, a full biological evaluation with respect to inflammatory pain is reported in detail for the CCK2 - gastrin antagonist PNB-001[26].
The chemicals were obtained from Aldrich (Gillingham, UK) and Lancaster (Lancaster, UK). Atmospheric pressure chemical ionisation mass spectroscopy (APCI), negative or positive mode, was carried out using a Hewlett-Packard 5989b quadrupole instrument (Vienna, Austria). Proton and Carbon NMR spectra were obtained on a Bruker AC 250 instrument (Follanden, Switzerland), operating at 250 MHz, calibrated with the solvent reference peak or TMS. IR spectra were plotted from KBr discs on a Mattson 300 FTIR Spectrometer. Melting points were recorded using a Stuart Scientific (Coventry, UK) apparatus and are uncorrected.
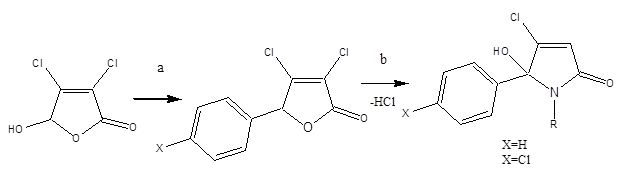
Dry and powdered aluminium chloride (20g, 0.15 mol) was added slowly to a mixture of mucochloric acid (16.9g, 0.1 mol) and benzene / chlorobenzene (250 ml). The reaction mixture was stirred overnight. It was then poured into a mixture of 100 g ice and 32 ml concentrated hydrochloric acid. The organic layer was separated by separating funnel and washed with 3 x 100 ml water. The combined organic layers were dried over magnesium sulphate and the solvent was removed under vacuum. The oily residue was crystallized in n-hexane.
Yield = 70%; mp: 78-79 oC; MS (APCI(+)): 195/197 (M+), 230/232 (M+1) m/z; 1H NMR (CDCl3) 250 MHz: δ = 7.22-7.51 (m, 5H), 5.81 (s, 1H); 13C NMR (CDCl3):165.3, 152.2, 139.8, 130.5, 129.3, 128.5, 127.4, 127.2, 121.2, 83.5; IR (KBr-disc) υ max: 3445, 3074, 3035, 2959, 2056, 1768, 1630, 1499, 1457 1294, 1224, 1028, 910, 772, 705 cm-1.
Yield = 69% mp: 76-78 oC; MS (APCI(+)): 227/229/231 (M+1), 262/263/265 (M+) m/z; 1H NMR (CDCl3) 250 MHz: δ = 7.48 (m, 2H), 7.35 (m, 2H), 5.91 (s, 1H); 13C NMR (CDCl3) 165.3, 152.0, 136.6, 130.1, 129.6, 128.7, 121.3, 82.9; IR (KBr-disc) υ max: 3451, 3075, 2952, 2051, 1769, 1636, 1497, 1419, 1289, 1231, 1027, 927, 826, 748, 720 cm-1.
Stage 2 products; general method
The relevant amine (2.3 times excess) was added to a solution of lactone A or B (0.7 mol) in ether (10 ml) and it was stirred on ice for 30 minutes, allowing to warm up to RT over time. The resultant mixture was poured into 5 ml of water and was separated by a separating funnel. The organic mixture was washed with water three times. The organic layer was dried over magnesium sulphate and the solvent was removed under vacuum. All compounds gave an oily solid, which were passed through a short silicagel column (80% ether, 20% petrol ether). The resulting fractions were dried from excess solvent under a stream of argon to yield crystals.
Yield = 85 %; mp: 167-169 oC; MS (APCI(+)): 266/268 (M+) m/z; 1H NMR (CDCl3) 250 MHz: 7.38-7.51 (m, 5H), 6.24 (s, 1H), 4.79 (bs, 1H), 3.23 & 2.18 (m, 2H), 1.71 (m, 1H), 0.76 (m, 6H) 13C NMR (CDCl3) 168.5, 155.7, 137.1, 129.2, 128.7, 126.2, 121.7, 93.1, 47.6, 27.5, 20.4 ppm. IR (KBr-disc) 3237, 3114, 2965, 2926, 2881, 2374, 2343, 1675, 1614, 1460, 1416, 1299, 1251, 1202, 1150, 1072, 1027, 878, 758, 696 cm-1.
Yield = 66%; mp: 155-158 °C; MS (APCI(+)): 300/302/304 (M+) m/z; 1H NMR (CDCl3) 250 MHz: 7.30 (m, 4H), 6.19 (s, 1H), 3.13 (m, 1H), 2.49 (m, 1H), 1.69 (m, 1H), 0.69 (t, J = 4.5 Hz, 6H) 13C NMR (CDCl3) 163.3, 156.3, 139.4, 134.8, 129.1, 127.7, 122.3, 95.0, 47.6, 27.6, 20.4 ppm. IR (KBr-disc) 3426, 3252, 2964, 2850, 1684, 1406, 1209, 1095, 817, 743, 703 cm-1.
Yield = 48 %; mp: 168-171 oC; MS (APCI(+)): 314/316 (M+) m/z; 1H NMR (CDCl3) 250 MHz: δ = 7.46 (m, 5H), 7.34 (m, 5H), 6.38 (s, 1H), 3.68 (bs, 1H); 13C NMR (CDCl3) 168.9, 159.7, 136.9, 135.1, 132.4, 129.9, 129.0, 126.9, 123.0, 122.3, 122.2, 93.5; IR (KBr-disc) 3517, 3357, 3114, 2840, 2674, 2361, 2342, 1678, 1607, 1464, 1412, 1361, 1208, 1138, 1071, 988, 755, 700 cm-1.
Yield = 71 %; mp: 165-167 oC; MS (APCI(+)): 300/302 (M+) m/z; 1H NMR (CDCl3) 250 MHz: 7.36 (m, 5H), 7.24 (m, 5H), 6.08 (s, 1H), 4.69 (m, 2H), 3.62 (bs, 1H); 13C NMR (CDCl3) 167.9, 155.9, 137.6, 134.4, 129.3, 128.7, 128.4, 128.4, 127.3, 127.1, 126.4, 93.2, 43.4; IR (KBr-disc) 3446, 3279, 3098, 2931, 2850, 2374, 2334, 1684, 1611, 1456, 1413, 1349, 1276, 1205, 1128, 1051, 696 cm-1.
Yield = 59 %; mp: 149-152 ºC; MS (APCI(+)): 334/336/338 (M+) m/z; 1H NMR (CDCl3) 250 MHz: δ = 7.33 (m, 4H), 7.16 (m, 5H), 6.09 (s, 1H), 4.60 (m, 2H), 13C NMR (CDCl3) 167.6, 155.4, 137.5, 135.3, 133.2, 129.1, 129.0, 128.9, 128.6, 128.4, 127.9, 127.4, 121.9, 92.6, 43.2; IR (KBr-disc) 3442, 2931, 2849, 2365, 2339, 1674, 1616, 1492, 1406, 1349 1272, 1199, 1094, 1018, 817, 699 cm-1.
Yield = 89 %; mp: 155-158 oC; MS (APCI(+)): 314/316 (M+) m/z; 1H NMR (CDCl3) 250 MHz: δ = 7.09-7.53 (m, 10H), 6.20 (s, 1H), 3.74 (m, 1H), 2.88-3.29 (m, 3H), 2.65 (m, 1H); 13C NMR (CDCl3) 168.0, 155.7, 139.0, 134.6, 129.4, 128.85, 128.84, 128.6, 126.6, 126.2 , 121.8, 92.7, 41.9 , 34.6 ppm. IR (KBr-disc) 3433, 3246, 2929, 2366, 2334, 1681, 1658, 1607, 1455, 1406, 1251, 1151, 1128, 1066, 931, 753, 699 cm-1.
Yield = 45 %, mp: 145-148 oC; MS (APCI(+)): 348/350/352 (M+) m/z; 1H NMR (CDCl3) 250 MHz: δ = 7.22-7.49 (m, 7H), 7.12-7.18 (m, 2H), 6.13 (s, 1H), 3.68 & 2.64 (m, 2H), 2.88 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (CDCl3) 250 MHz: 167.7, 155.5, 138.8, 135.5, 133.3, 129.1, 128.8, 128,7, 127.7, 126.7, 121.9, 92.3, 42.0, 34.5; IR (KBr-disc) 3421, 3228, 2925, 2848, 2370, 2338, 1684, 1658, 1606, 1461, 1406, 1248, 1190, 1097, 935, 806, 697 cm-1.
For target preparation the protein structures, pdb identifier 1HZN for the CCK1 and 1L4T for the CCK2 –gastrin receptor were downloaded from the protein data bank (www.rcs.org) and docking was performed using Autodock Vina and Hex. After several docking trials for the CCK1 / CCK2 receptor the results were analysed and visualized using Chimera and Designer studio 4.5. After visual inspection the results were presented to rationalize drug ligand interactions with the each CCK receptor subtype.
CCK2 and CCK1 receptor binding assays were performed, by using guinea pig cerebral cortex or rat pancreas. Male guinea pig brain tissues were prepared according to the modified method described by Saita, et al. [27]. Pancreatic membranes were prepared as described by Charpentier, et al. [28]. Tissues were homogenized in ice cold sucrose (0.32 M, 25 ml) for 15 strokes at 500 rpm and centrifuged at 13000 rpm for 10 minutes. The supernatant was re-centrifuged at 13000 rpm for 20 minutes. The resulting pellet was re-dispersed to the required volume of buffer at 500 rpm and stored in aliquots at 70 ºC.
Binding was achieved using radioligand 125I-Bolton-Hunter labeled CCK, NEN at 25 pM. The samples were incubated with membranes (0.1 mg/ml) in 20 mM Hepes, 1 mM EGTA, 5 mM MgCl2, 150 mM NaCl, at pH 6.5 for 2 hrs at RT and then centrifuged at 11000 rpm for 5 minutes. The membrane pellets were washed twice with water and the bound radioactivity was measured in a Packard Cobra Auto-gamma counter (B5005). Binding assays were carried out with L-363, 260 as control.
Male Sprague Dawley rats, weighing 200-250g were used and all animal care and experimental protocols adhered to the relevant laws and guidelines of the institution. The animals were housed under standard conditions of temperature (25 oC) with unrestricted access to food and water. The animals were sacrificed using cervical dislocation without anaesthesia. From the abdomen of the animals, the duodenum was carefully excised and washed with physiological solution. The mesentery of the tissue was removed and the lumen was gently flushed with Tyrode’s solution to clear luminal contents. The prepared isolated tissue was rapidly incubated in Tyrode’s solution maintained at 32 ºC and gassed with 95% O2 / 5% CO2. Tyrode’s solution was freshly prepared daily (g/l): NaCl, 8.0; KCl, 0.2; CaCl2, 0.2; MgSO4, 0.1; NaH2PO4, 0.05; NaHCO3, 1.0; Glucose, 1.0. The main equipment used was the Radnoti single unit tissue bath system with a chamber capacity of 35 ml. Bath aeration with carbogen (O2 95%, CO2 5%) was maintained at a constant temperature (32 °C). The force in grams was measured with an isometric transducer linked to a power lab data acquisition system.
From the isolated tissue preparation, strips of appropriate length were mounted vertically in organ bath containing Tyrode’s solution, under a tension of 1g and allowed to equilibrate for 30 minutes. Agonists, such as CCK5 and CCK8S were directly applied in the bath and antagonists were pre-incubated for 10 min. Stock solutions of all test compounds including the standard were prepared in DMSO.
CCK5, penta-gastrin preparations: CCK5 was dissolved in distilled water to prepare a stock solution of 500 μM solution, from which cumulative additions of increasing concentrations (0.1 nM, 1 nM, 5 nM, 10 nM, 20 nM, 30 nM, and 40 nM) were tested to plot a dose response curve. Test molecules and lorglumide were added to the organ bath 10 minutes before exposure to the next CCK5 serial concentrations.
DSS induced spontaneous muscle contractions in rat duodenum: A solution of 0.1% DSS dextrane sulfonic acid sodium was freshly prepared in Tyrode solution and it was added to the bath to give 100-300 microM final bath concentration. Within 30 min contractions were induced and stable. The amplitude of these contractions was measured for the test molecules.
Experiments were conducted in male standard IRC mice obtained from the animal house, Faculty of Medicine, Khon Kaen University. Each experimental group consisted of 6 animals and the treatment procedures were approved by the ethical committee, Faculty of Medicine, Khon Kaen University (BEA030699). Mice were intraperitoneal injected with test compound at the volume not more than 0.2 ml/animal. The test molecule was dissolved in DMSO and water was added to give a 5% solution for IP and PO administration. 30 min after drug administration, animals were tested as described in the following sections.
Nociception tests:
Formalin test: The rats were placed in a plastic behavior cage (30x30x30 cm) and a mirror was mounted at 45* angle below the transparent floor to allow an unobstructed view. 0.05 ml of 1% formalin was injected subcutaneously into the dorsal surface of the right hind paw. Subsequently behavior responses were recorded by the number of licks / bites in the early phase (0-5 min) and late phase (20-25 min) in all groups. PNB-001 was injected 30 min prior to the formalin injection.
The tail immersion test: The thermal response latency was measured by the tail immersion test. The animals were placed into individual restraining cages leaving the tail hanging freely. The tail was immersed into water at 50 oC. The response time, at which the animal reacted by withdrawing its tail from water, was recorded and the cut-off time was 10 sec in order to avoid tissue damage. The base line withdrawal thresholds (BT) were recorded prior to the first injection. Test thresholds (TT) were measured 60 min after the second injection. The test thresholds were expressed as a percentage of Maximal Possible Effect (% MPE) using the equation: % MPE = {(TT-BT) / (45-BT)} x 100 DMSO (5 %), pyrrolone (in 5 % DMSO) was intraperitoneally injected and morphine was administered subcutaneously.
The hot plate test: Mice were placed on a hot plate, that was thermostatically maintained at 50 °C. A plexiglass box was used to confine the animal to the hot plate. The reaction time of each animal (either paw licking or jumping) was considered a pain response. The latency to reaction was recorded. For prevention of heat injury, the cut-off time of the test was 30 sec.
Anxiolytic test
The elevated plus-maze: The wooden elevated plus-maze consisted of two open arms (30 × 10 cm) without any walls, two enclosed arms of the same size with 5-cm high side walls and end wall, and the central arena (10 × 10 cm) interconnecting all the arms. The maze was elevated approximately 30 cm from the floor. At the beginning of the experiment the mouse was placed in the central arena facing one of the enclosed arms. During a 5-min interval, the time animals spent in the open arms of the plus-maze was recorded. The mouse was considered to be in the open part when it had clearly crossed the line between the central arena and the open arm with its four legs.
Statistical methods: The data were expressed as mean + SD and one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and supplementary Tukey test for pairwise comparison were tested to determine for any significant difference at p< 0.05.
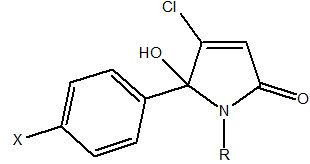
5-arylated dichloro-2(5H)-furanone intermediates were evaluated previously as anticancer agents [29]. Overall, the desired N-alkylated unsubstituted 5-phenyl pyrrolone PNB-001 was obtained in only a 2 stage process as white crystalline material. The molecule is not present in the ring opened keto form and fully occurred in the 5-membered ring form, as a hydroxy-pyrrolone. The analysis of PNB-001 by chiral HPLC showed a 50:50 racemic mixture of both enantiomers in solution in methanol. 5-arylated dichloro-2(5H)-furanones A and B were synthesised from mucochloric acid (Scheme 1), which is commercially available from furfural under oxidising conditions with hydrochloric acid. Mucochloric acid was reacted with benzene as reagent and solvent at RT under the development of hydrogen chloride gas. Depending on the scale of the reaction cooling with ice was required. For chlorobenzene / benzene the powdered or most preferred granulated aluminium chloride served as the best catalyst and during work up with hydrochloric acid on ice the inorganic salts were easily removed from the organic phase. For the small scale synthesis aluminium chloride worked well as Lewis acid. However, during scale up aluminium chloride was replaced by trifluoroborane in THF as the exothermic reaction become problematic on a kg scale. Subsequent reaction of the 5-arylated 3,4-dichloro-2(5H)-furanones A and B (Stage 1 intermediate) in diethylether with alkyl- and aryl alkyl amines furnished N-alkylated hydroxyl-pyrrolones 1-21 (Stage 2 products) in high yields under mild conditions. The general synthetic sequence is outlined in Scheme 1.
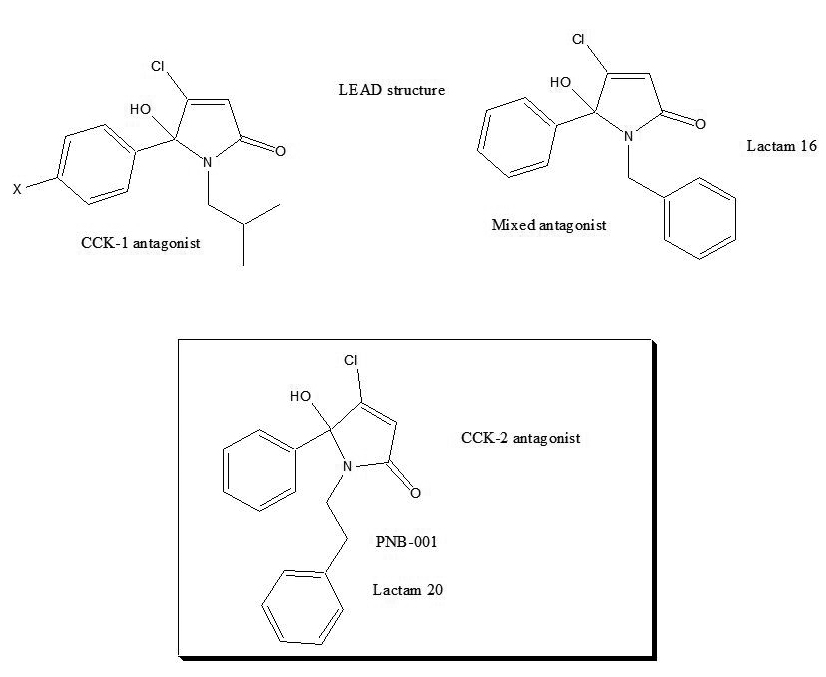
Only active lactams and relevant lactams for the understanding of a full structure activity relationship, SAR, are outlined in Table 1.
The first step was to screen for potent binding affinity and to identify a CCK1- or CCK2-selective ligand for subsequent in vitro and in vivo evaluation.
Using radiolabelled iodinated cholecystokinin, inhibition of binding was determined for all test molecules and the IC50 are outlined in Table 1. Lorglumide served as CCK1 standard and L-365,260 was used as CCK2 standard.
The change from N-propyl into the N-butyl group resulted in a manifold increase of activity and the best substituent on the central nitrogen atom was found iso-butyl, as seen for derivative 7. The introduction of a halogen atom into the para- position of the phenyl group resulted in an increase of binding affinity, possibly due to enhanced lipophilicity.
Lactames, such as pyrrolone 15, containing an aromatic ring, directly connected to the N-position, showed a micromolar activity > 10μM. Most interestingly, the introduction of an N-benzyl substituent to the pyrrolone template, instead of an alkyl group, resulted in non-selective CCK-ligand, pyrrolone 16. Again, halogen atoms, such as chlorine, only marginally changed the binding affinity for the chlorinated N-benzyl lactame 17. The introduction of a spacer, a single CH2 group, resulted in a phenyl-ethyl derivative 20, which represented a highly CCK2 selective ligand. Lactame 20 is 450 times selective for the CCK2 / gastrin receptor. Halogenation, the introduction of a para- chlorine atom on the phenyl–position, lactame 21, did not enhance binding affinity any further; possibly due to drug receptor interaction of the phenyl group with a lipophilic cavity within the CCK receptor.
Overall, the introduction of alkyl groups most preferred an isobutyl- group, provided a CCK1 selective antagonist and a fluorinated analogue had potent anticancer properties via the CCKC receptor [30]. The N-benzylated pyrrolone 16 displayed a non-selective receptor binding profile and the introduction of a single methylene group enhanced the selectivity towards the CCK2 receptor.
The phenyl-ethyl hydroxyl-pyrrolone, lactam 20, is named PNB-001 a CCK2 / gastrin selective antagonist and the drug design summary are outlined in Figure 2. The phenyl ethyl derivative PNB-001 completed preclinical development as anti-inflammatory analgesic and progressed into phase 1 clinical trials for the treatment of arthritic pain.
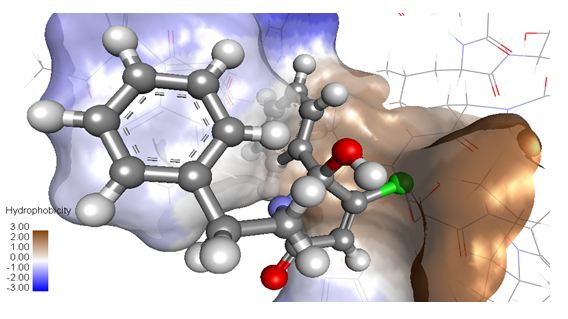
The docking of PNB-001 into the CCK2 receptor is outlined in Figure 3 and some key interactions are highlighted for one final pose of minimal energy (Figure 3).
The 5-hydroxy group of the central pyrrolone template interacted via hydrogen binding with the N group of Trp114. The phenyl group of the N-phenylethyl- side chain bound to the aromatic indole system of Trp114 and electron withdrawing groups may enhance these aromatic interactions. The lipophilic pocket allowed principally a wide range of substituents, but only phenyl and not cyclo-hexyl could be realised synthetically. The 5- phenyl group of the pyrrolone template bound via Ile 184 and Leu 133, based on van der Waals interactions and not aromatic interactions. The introduction of electron withdrawing groups, such as halogen atoms, is therefore not enhancing affinity and optimisation on this side is with limited effect.
Gaining dual CCK –gastrin antagonistic activity was found beneficial in analgesia potentiation as well as for anxiolytics, but here direct analgesic activity and the anti-inflammatory effect are entirely linked with the CCK2 –gastrin receptor [31,32].
In vitro experiments using isolated tissue preparations: The CCK2 selective phenyl ethyl derivative PNB-001 occurred a potent binding affinity and the CCK-gastrin - antagonism was studied using penta-gastrin (CCK-5) induced contractions of the rat duodenum. Initially CCK4 was used, an agent, which trigged panic attacks in patients, but in vitro CCK4 has a low solubility and low potency in the micro-molar range [33,34]. The best CCK2 selective agonist in vitro and in humans is CCK-5 and therefore, pentagastrin was used to analyse the agonist or antagonist properties of PNB-001 [35].
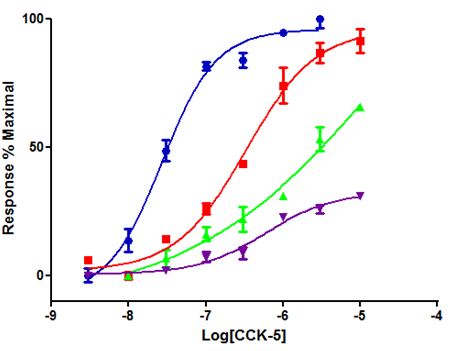
The concentration response curve of penta-gastrin, CCK-5, was recorded and shifted to the right by a nanomolar concentration of PNB-001, thus confirming the antagonistic properties of this ligand (Figure 4) [3].
100 nM of PNB-001 with 30 min of incubation time fully blocked the CCK4 and CCK5 induced contractions. For the 5 min incubation cycle, 10 nM of PNB-001 shifted the CCK-5 concentration response curve to the right and from 30 nM onwards, the antagonist showed a reduced maximum response (Figure 4) [36]. At high nano molar concentrations PNB-001 acted as non-competative antagonist. However, PNB-001 is now a confirmed potent and selective CCK2 /gastrin antagonist.
As the clinical trial outcome of selective CCK/gastrin antagonists was found questionable in the treatment of anxiety and depression, the aim of the programme was, to focus on selectively designing CCK2 antagonists for the treatment of inflammation. In vitro, spontaneous contractions correlate with inflammation and anti-inflammatory steroids such as dexamethasone reduced spontaneous contractions of the duodenum [37,38].
DSS, dextran sulfonic acid sodium, is a standard agent to induce inflammation and it was used here in vitro using isolated organ preparations of the duodenum.
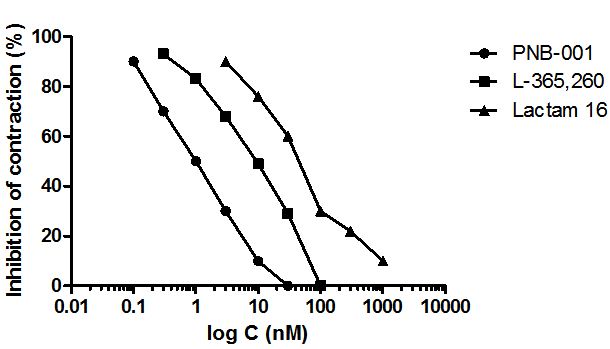
L-365,260 was applied as CCK2 standard and the mixed CCK antagonist lactam 16, together with the highly CCK2 selective antagonist, PNB-001 were all tested under the same conditions. The concentration response curves, showing how these agents inhibit contractions very low concentrations, are outlined in Figure 5.
An IC50 of 1 nM was determined for CCK2 antagonist PNB-001 (Figure 5). The Merck CCK2 standard occurred a ten times lower IC50 and the benzylated derivative 16, had the lowest anti-inflammatory effect. Considering the chemical similarity between the lactame 16 and PNB-001, the addition of an extra CH2 group resulted in a remarkable effect. The CCK1 antagonism may oppose the anti-inflammatory effect, but the possible mechanistic pathway is outside the scope of this publication.
Based on the in vitro results with respect to anti-inflammatory activity, PNB-001 was selected for further in vivo assays. Here the anti-inflammatory action of the molecule, supported by anti-gastric activity, was supposed to create a synergistic therapeutic effect.
Under consideration of failed clinical trials for panic, positive pain results and our own results with respect to inflammation, our attention turned to full systematic in vivo evaluation of PNB-001 as anti-inflammatory analgesic [39].
In vivo evaluation: CCK antagonists potentiate the analgesia of opiates and usually have no analgesic effect on its own [4]. For Z-360 an interesting weak analgesic effect in the formalin test was observed [40]. Thus, a first evaluation of the analgesic properties of PNB-001 was performed using the formalin test.
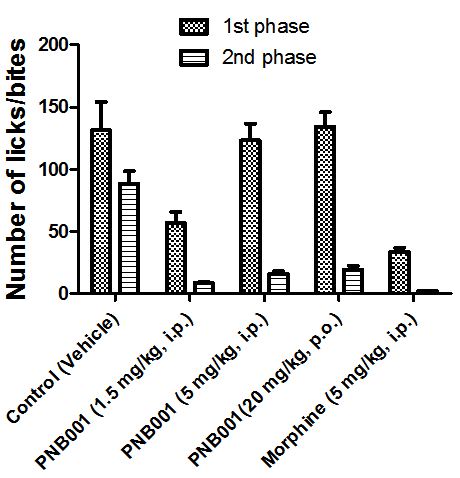
Opiates, such as morphine, reduce the response in form of licks and bites to formalin in the first phase of the assay. Anti-inflammatory agents are active in this assay in the second phase.
PNB-001 showed only at the 1.5 mg/kg dose some opiate like effects and the 5 mg dose by IP administration is equivalent to the 20 mg/kg dose by oral administration (Figure 6). The activity in the second phase of the formalin test reconfirmed the anti-inflammatory activity found in vitro and in vivo.
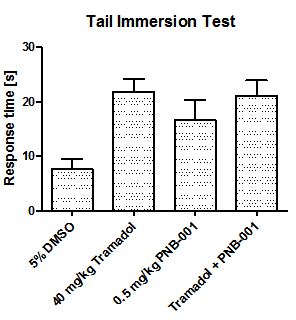
In order to evaluate the pain managing properties of the new agent, the partial opiate agonist tramadol was included in a study, in which the hot plate assay as well as the tail immersion test was used to evaluate analgesic activity in rodents.
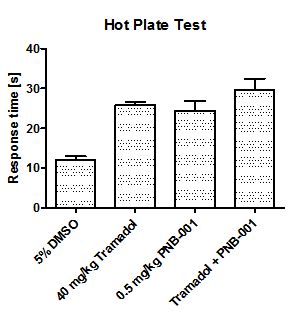
Bar 1 is the baseline with a response time about 12s. The maximum analgesic effect in the hotplate is 26 s for 40 mg/kg tramadol, a more than 100% of change from the control (Figure 7).
The analgesic efficacy of 0.5 mg/kg PNB-001 by IP administration as a single agent was found equivalent to 40 mg/kg tramadol (SC administration). Interestingly, there is no significant potentiation of tramadol analgesia with PNB-001, the selective CCK2 / gastrin antagonist, which works as analgesic on its own.
However, this analgesic activity was reconfirmed in a second standard analgesic assay in rodents using the tail immersion test and the results are outlined in Figure 8.
5% DMSO in water served as control in the tail immersion test in mice and tramadol at 40 mg/kg was applied as analgesic standard (Figure 8). Test compound and standard were found not significantly different in this assay and a small potentiation of analgesia was observed, which was not significant. In principal, the same analgesic effect of the CCK2 antagonist PNB-001 was observed for the hotplate and the tail immersion assay in mice without potentiation of analgesia [41]. The small, but significant analgesic activity is due to the gastrin antagonising properties of the agent.
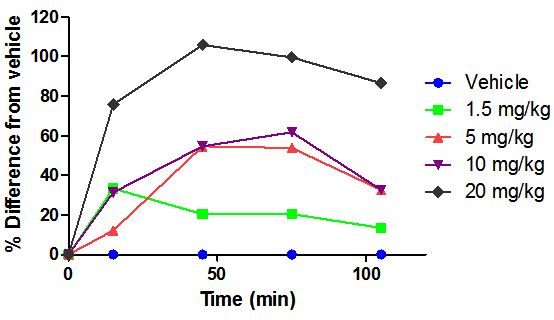
Finally, the tail immersion test was performed in rats by oral administration. Rats were used as a second species and the route of administration was changed from IP to PO administration (Figure 9). The % change from the vehicle was assessed and the results are outlined in Figure 9.
For the 1.5 mg/kg dose a 20% change from the vehicle was achieved, which increased dose dependently towards 20 mg/kg. A 50% change from the control was observed for 5 and 10 mg /kg, while the maximum response was found for 20 mg/kg in rats by PO administration after 1 h. Rats seem to be loss responsive compared to mice, but the active dose range confirmed the oral bioactivity of about 10%, which was obtained in PK analysis in vivo in rats and 0.5 mg/kg by IP administration was found equivalent to 5 mg/kg by oral administration.
CCK antagonists potentiated the analgesia of opiates and usually have no analgesic effect on their own. For Z-360 also, an interesting weak analgesic effect was observed in the formalin test and CCK analgesia was linked with delta opiate activity [6].
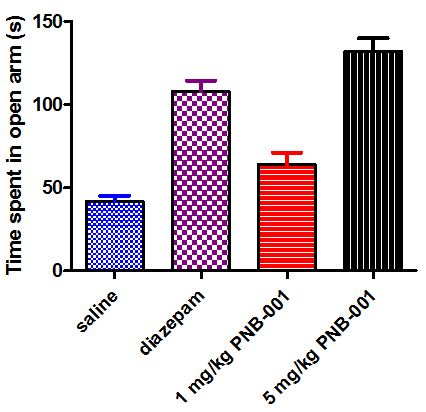
To complete the CNS evaluation of PNB-001, a standard anxiolytic assay, the X-maze test was applied using mice (Figure 10) [42,43].
Mice in general dislike open areas and the anxiolytic diazepam (4 mg/kg) increased the time significantly they spent in open arms. For PNB-081 an anxiolytic effect was observed for the 1 mg/kg dose and this increase further for the 5 mg/kg dose by PO administration.
CCK4 induced panic in humans and generally CCK2 antagonists are associated with anxiolytic properties [44]. Our finding are supported by the detection of CCK receptors in wide key areas of the brain [45].
As part of the preclinical development, the pharmacokinetics of PNB-001 was fully analysed. In summary PNB-001 showed a good half-life in dogs and rats. Protein binding was determined of 92.4% in human plasma and very high membrane permeability was determined by using the Caco-2 monolayer assay for both molecules. In terms of regulatory toxicology, for PNB-001 a slight increase of ALT was observed in dogs, but not in rats at doses > 1000 mg/kg and only after 90 days.
The target molecule PNB-001 was synthesised in only 2 steps from one readily available starting material and will potentially deliver an affordable therapeutic agent for long term pain management. PNB-001, a gastrin antagonist, is reaching phase 1 clinical trial in April 2018 as anti-inflammatory analgesic. A first in class analgesic CCK2 antagonist was developed under the consideration of membrane penetration, half-life and bioavailability. On-going is a preclinical programme to extend general inflammation to neuro-inflammation.
The experimental work was partly supported by PNB Vesper Life Sciences. The animal studies were performed in compliance with relevant laws and institutional guidelines. The treatment procedures were approved by the ethical committee, Faculty of Medicine, Khon Kaen University (BEA030699).