Carcinosarcoma of Lung: Case Report
Carcinosarcoma of the lung is a rare, highly aggressive tumour with a dual component, carcinomatous (epithelial differentiation) and sarcomatous (connective differentiation). Its prognosis depends on the possibilities of surgical excision and the size of the sarcomatous contingent, which is classically more chemosensitive. We report the case of metastatic pulmonary carcinosarcoma in a smoking patient.
Keywords:Carcinosarcoma; Sarcomatoid Carcinoma; Aggressive Tumour
Carcinosarcoma is a tumour comprising a non-small cell carcinoma (squamous or adenocarcinoma) and a sarcoma with heterologous elements (rhabdomyosarcoma, chondrosarcoma, osteosarcoma). Their clinical presentation is not different from other types of bronchial cancers. Most of the available data come from old clinical studies or anatomo-pathological series based on a histological definition prior to the 1999 WHO classification, which individualized them within non-small cell bronchial carcinomas. In the 2015 version of the WHO classification, the sarcomatoid carcinoma includes pleiomorphic carcinomas, carcinosarcomas and blastoma pulmonary. They are characterized by their great aggressiveness and poor prognosis. The treatment is the same as those for other non-small cell lung carcinomas.
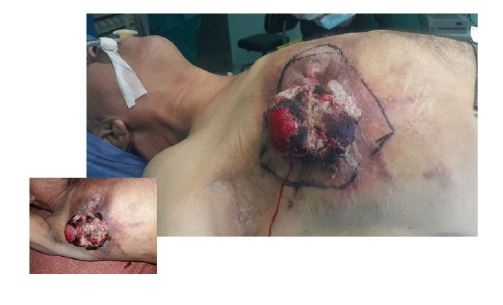
This is a 56 year old patient, chronic smoker for 40 years, at a rate of 30 pack/year, with a history of father who died of pulmonary neoplasia at the age of 58 year old (no documents concerning the histological type). Following the death of his father, he consulted for smoking cessation assistance when he had no respiratory symptoms. Despite medical treatment and behavioral measures to assist withdrawal, the patient continued to smoke and then lost interest. One year later the patient presented to the withdrawal aid consultation complaining of coughing with chest pain and altered general condition which dates from 3 months before. The clinical examination found a patient with ECOG (Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group) performance status at 1, with exquisite pain on palpation of the shoulder and right scapula (Table 1).
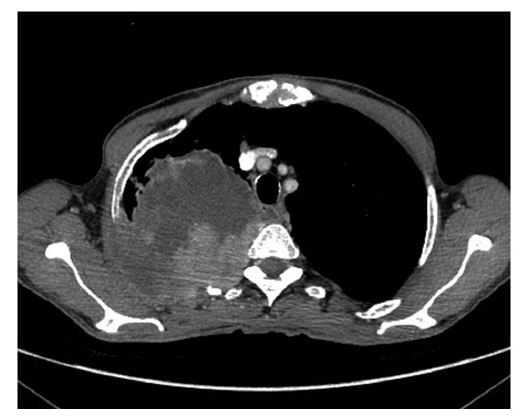
The chest X-ray had objectified opacity of the right apex reaching to the wall. A thoracic CT scan was completed, showing a large right upper lobar mass with a long axis of 11 cm, invading the superior vena cava, with a costal and vertebral parietal extension. A bronchial fibroscopy was strictly normal, despite careful exploration of the superior lobar branch. The histological diagnosis of carcinosarcoma was retained on CT-guided biopsy which had identified two components: carcinomatous (epithelial differentiation) and sarcomatous (conjunctive differentiation). It was a stage IV tumor due to the presence of secondary pulmonary and adrenal localizations. The patient was referred to oncology for palliative chemotherapy after a multidisciplinary consultation meeting. The pain was stabilized under analgesic stage 2 (tramadol), but his general statut is getting worse and worse. The patient died after 4 months after several sessions of chemotherapy (Figure 1 & 2).
Carcinosarcoma of the lung is rare and accounts for only 0.2-0.3% of bronchopulmonary cancers [1,2]. This tumour affects preferentially male smokers (sex ratio of 7 men/1 woman). The clinical picture is not very specific. The carcinosarcoma may be proximally located with endobronchial, mediastinal or vascular extension, which may cause ventilation problems, obstructive pneumopathy and bronchial suppuration, haemoptysis, etc.; or peripherally located with invasion of the thoracic wall, with a worse prognosis due to its later discovery, as is the case in our patient. Carcinosarcoma is a histological subtype of sarcomatoid carcinoma, which also includes pleomorphic carcinomas and pulmonary blastomas (Table 1) [3]. Diagnosis is based on the analysis of the surgical specimens but is still possible on small, good quality biopsies.
The principles of treatment are the same as those for other non-small cell lung carcinomas. For the early stages: Surgery seems to allow a satisfactory local control, similar to that of other non-small cell carcinomas [1, 4-9]. The role of adjuvant treatments, radiotherapy or chemotherapy, is difficult to assess because of the lack of a prospective controlled series. However, the frequency of parietal, mediastinal and vascular disease with early local relapse makes the use of adjuvant chemotherapy and radiotherapy permissible, following the same principles as for other non-small cell carcinomas [10].
For metastatic stages:
The cytotoxic agents used for metastatic carcinoma are identical to those used for non-small cell carcinoma (platinum-based combinations) [11]: carboplatin/paclitaxel and cisplatin/gemcitabine in the first line, docetaxel in the second line. Progressively, carcinosarcomas are aggressive tumours with systemic metastases. early, occurring not only at the usual metastatic sites of non-small cell lung cancers, but also at the usual metastatic sites of large cells (brain, bone, liver) but also in unusual sites such as the esophagus, small intestine, the peritoneum, subcutaneous tissue, or kidney [4, 12-15]. The course of carcinosarcomas marked by rapid tumour growth [16-18] a median short median recurrence-free survival between 6 and 8 months.