Descending Necrotizing Mediastinitis : Which Surgical Approach ? About Five Cases
Objective : compare a less aggressive descending necrotizing mediastinitis management with equivalent results to those of the actual series which use an aggressive approach.
Methods: a five years retrospective study of five patients (three men and two women) treated in our departement for descending necrotizing mediastinitis.
Results: the infection origin was a dental abscess in all cases. All the patients have had a transcervical approach associated to a thoracic one in all cases. These incisions permitted evacuation of the pus collections and debridement of necrosis.Systematically, the incisions were closed up. Tubes for draining were placed in neck and mediatinum. An irrigation system was putted in throw the draining tubes for three patients.Post operatively, we aknowledge good recovery for all patients.
Conclusion: closing up the incisions after surgical treatment of descending necrotizing mediastinitis and irrigation throw draining tubes is a real therapeutic strategy.
Acute mediastinitis is a serious infection of the mediastinal connective tissues and the structures which they surround. One of the most lethal forms of mediastinitis is descending necrotizing mediastinitis (DNM), which usually occurs as a complication of odontogenic infections. It is associated with high mortality unless it is diagnosed and treated promply, Old age and chronic medical conditions like diabetes or debilitated patient are important predisposing factors. The evolution of antibiotics, diagnostic imaging, and surgical management, the mortality rate has declined marginally to 20–40% [1]. In our study, we compare results of differents surgical approaches.
Over a period of five years, five patients were admitted for DNM in our departement. There were three men and two women aged between 22 and 55 years old, three of them were diabetic.These patients presented with clinical signs related to the initial infectious site (Table 1) and signs of extension of the infection to the neck and upper mediastinum: subcutaneous cervical collections, subcutaneous emphysema, redness with cardboard skin on the neck and upper chest.
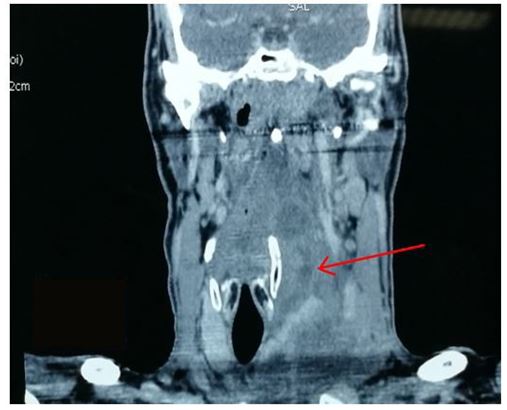
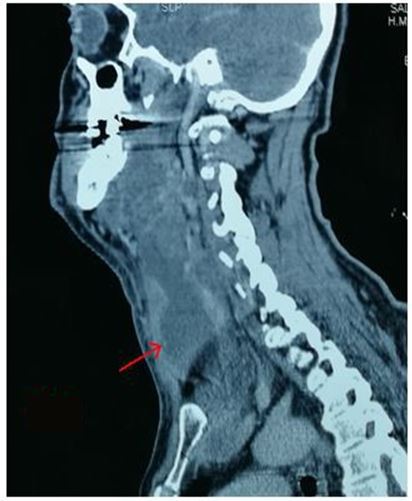
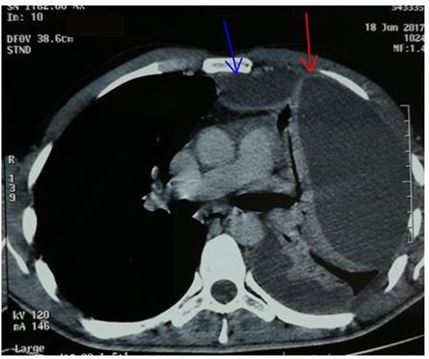
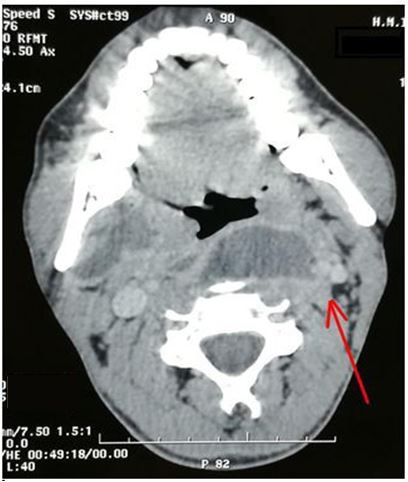
Chest X-ray revealed mediastinal widening (5 patients) and / or pleural effusion (5 patients).All our patients benefited from a preoperative chest and neck CT allowing to specify the site and the extent of the various lesions (Figures 1,2,3 & 4).
The medical management of these patients included a probabilistic antibiotherapy, and a surgical procedure to control the origin of the infection, through pre-sternocleidomastoid cervicotomy.wich allow to give access to the different collections of pus in the neck and mediastinum to the tracheal bifurcation, debridement of necrotic tissue and abundant washing with povidone iodine and oxygenated water diluted in saline serum at 0.9%. At the end of the procedure, the wound was closed after multiple suction drainage at the various cervical and mediastinal stools remaining at the detachments.
sub-mandibular incision was sometimes associated to cervicotomy.The cervical approach was associated with a thoracic approach in order to complete the mediastinal and pleural drainage inaccessible by cervicotomy.
The video-assisted thoracoscopy was not available immediately in the emergency operation room, all patients received surgical treatment within one hour after their admission to the emergency room.
Postoperatively, a continuous irrigation-aspiration system with a diluted solution of povidone iodine (30 ml of povidone per 500 ml of 0.9% saline) was installed at the various drains (including those of the mediastinum) to perform local mediastinal treatement.
All patients had clinical signs pointing to the diagnosis of descending mediastinitis and cervicothoracic scan that made the presemptive diagnosis :
An oedematous infiltration of the soft tissues of the neck and the mediastinum, gaseous bubbles between the different planes and subcutaneously and the purulent collections. It also allowed precise mapping of lesions (Table 1).
The starting point of the infection was of dental origin in all cases. In three cases, the infection was polymicrobial,in two cases the germs isolated were (Streptococcus hemolytic patient # 3 and E.coli case # 2). For the five patients, the initial antibiotherapy (cefepime+ vancomycin+aminoglycoside.) was readjusted postoperatively according to the antibiogram data after bacteriological study of the different samples.
Table 2 summarizes the modalities of surgical treatment and postoperative follow-up. Depending on the location of the lesions, pre-sternocleidomastoid cervicotomy was associated with an under mandibular incision in two patients (2 and 3).
For four patients, a thoracic approach was performed: a parasternal mediastinotomy once and a postero-lateral thoracotomy four times. For cases 1, 2, 4 and 5, the primary dental infection was treated during the same operating time. Postoperatively, an irrigation-suction system was installed on the drains in four patients with insulinotherapy for diabetes patients
Finally, five patients recovered from their mediastinitis. In the perioperative period no major complications were noted. One patient a required a tracheostomy (# 3).
The chest CT control performed systematically between the second and seventh postoperative day was satisfactory without residual collection in cases 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5. Postoperative follow-up at 12 months of the intervention provided in the five patients did not reveal any sequelae or recurrence.
Descending necrotising mediastinitis (DNM) is a rare and very severe life-threatening complication from common odontogenic and oropharyngeal infections [2,3], reaching the cervical, mediastinal, pleural, or even the pericardium and peritoneum.[2-4] This particular sequence is conditioned by the anatomical communications existing between these different regions.
Anatomy of the cervical and thoracic area and especially of communication channels can explain the evolution of this affection and management of DNM. The mediastinal contamination is done by propagation of cellulite flows along the aponevroses which delimit the cervicomediastinal spaces [3,5,6].
From an infectious focus (tonsillitis, sub-angulo-maxillary phlegmon, etc.) the infection reaches the level of lateral cervical spaces: the retrovisceral space (71% of cases), the perivascular space (21% of cases) and peritracheal space (8% of cases) [7,8].
The retrovisceral space of Henke ends in the right upper and posterior mediastinum, predilection site of purulent collections. When the infection has crossed the cervico thoracic outlet , the collections reach the mediastinal spaces, thus breaking the high mediastine resulting in a pyothorax or a pyopneumothorax, sometimes with parenchymal lesions like pulmonary abscess
The pericardium is most often the seat of a reactive aseptic effusion but it can become purulent [3]. Nerose fluids can diffuse into the retroperitoneal space, causing peritonitis if the barrier of the posterior peritoneum breaks [9].
The major risk of this cellulitis in its cervical or mediastinal location is vascular ulceration with rupture and fatal hemorrhage or possibly arteriovenous fistula, such as the pulmonary fistula described by Economopoulos et al. [10] and operated successfully.
DNM is caused by a mixture of aerobic and anaerobic bacteria found in the buccal flora are the predominant microorganisms isolated from DNM patients [2,3,11]
The most common aerobic bacteria include alpha haemolytic Streptococcus, Staphlococcus aureus and Klebsiella pneumoniae, and even proteus and staphylococcus [12].The common anaerobic bacteria include Peptostreptococcus, Bacteroides fragilis, Prevotella and Porphyromonas.there is usually a microbial polymorphism and most germs are difficult to detect because crops grow poorly [3]. These germs cause necrotizing and extensive cellulitis with haemorrhagic foci and rapid evolution.
A clinical manifestation are usually noisy, associating infectious signs of buccopharyngus with signs of mediastinal irritation before the septic shock table sets in and becomes irreversible. In a patient with a recent history of dental infection or ENT, trismus, retrosternal chest pain, dysphonia and dyspnea appear. To these elements, is added a toxic-infectious table with alteration of the general state, anernary, dehydration leading to functional and then organic renal insufficiency. Disorders of consciousness are pejorative elements that are aggravated by respiratory failure with hypoxia and hypercapnia. The clinical examination at the beginning found a cervical inflammatory placard with cervicothoracic crepitation related to subcutaneous emphysema, an important element for the diagnosis [13].
In misleading forms and at the beginning stage, the diagnosis is essentially based on radiological data. Chest X-ray generally shows widened mediastinum, subcutaneous emphysema, and sometimes a mediastinal hydroaeric level. Cervicothoracic CT is gold key for early stage diagnosis [5, 9,14,15]
it allows to find strongly evocative lesions, like the modification of the density of the mediastinal fat which becomes heterogeneous. It makes it possible to specify the extent and the ratios of the cellulitis at the cervical and thoracic level, especially with the vascular structures after the injection of the product of contrast. In addition to diagnosis, CT can guide cellulitis drainage and monitor its evolution . The favorable evolution in our cases was obtained thanks to the early practice of the cervico-thoracic CT which made it possible to make the diagnosis before the stage of the complications.
The complications usually encountered during this affection are [5,16]:
- pleural empyema, pulmonary parenchymal lesions ;
- pyopneumothorax, purulent pericarditis,
- vascular lesions (ulcerations, rupture).
Other complications are possible: peritonitis by migration through the esophageal hiatus [17] or subphrenic abscess. Estrera, et al. Have described cranial nerve palsies (IX, X, XII), intracranial suppurations [11]. All these complications result in rapid death in a severe and irreversible sepsis chart. Mortality of this affection varies between 36% [5,18] and 75% [7] with an average of 50% [8].
Descending necrotizing mediastinitis is a medical and surgical emergency that must be treated before the onset of its dreadful and irreversible complications.
Drainage is essential:
- endobuccal drainage by retropharyngeal puncture;
- cervical drainage with a large cervicotomy and placement of large drains a little distance from the vessels
- possibly thoracic drainage by anterolateral thoracotomy in case of pyothorax
Estrera, et al. [4] and Scaglione et al [6,14] emphasized the interest of cervicothoracic CT for diagnosis, For many authors, an exclusive cervical approach is sufficient if the process does not descend beyond a plane passing through the tracheal bifurcation [4,19,20]. Beyond this plane, a complementary thoracic approach is essential. It may be necessary also if there are posterior mediastinal lesions not accessible by cervicotomy, it also allows to drain and wash the pleural cavity. For many other authors, a combined cervical and thoracic approach must be performed immediately [15,21,22]. At the end of the intervention, two attitudes can be discussed. The first is to close all operating sites (cervical and thoracic) on several suction drains. Postoperatively, permanent irrigation-lavage-aspiration with beta dine serum by the drains is put in place during the first days until the disappearance of the signs of infection in the recovered liquid.This attitude requires a monitoring of the balance of the inflow and outflow of the irrigation liquid. In the second strategy, the cervical surgical wound is left open [20-23].
The post-operative wound cares is daily done in the operating room until the total control of the infection, the wound is closed secondarily. We believe that this technique has several disadvantages: risk of haemorrhagic accidents following the weakening of the vessels by repeated handling, the removal of the edges of the wound leads to poor tissue vascularization and delayed healing, difficult closure secondary with retraction of the skin, favoring nutritional losses, exposure to a significant anesthetic risk, heavy psychological impact for the patient
In our series, we adopted the first attitude, resulting in a short-term survival result of 100% close to that of current series between 80 and 87.5% [15,19, 20,22]. These results demonstrate that immediate closure of surgical sites is the most reliable but depends on close clinical and CT surveillance. In addition, the irrigation of the operating sites seems to have a favorable influence on the duration of hospitalization. Indeed, for the patients irrigated, the stay lasted 20, 21 and 15 days whereas it was 30 and 35 days for patients without irrigation.
Large spectrum antibiotherapy should be well adapted to the germs usually encountered. The first-line antibiotherapy is a triple combination: penicillin G or cephalosporin, aminoglycoside and imidazole. It can be modified according to the data of the antibiogram while knowing that there is a microbial polymorphism and that the germs are of difficult microbilogical culture [3]. The duration of antibiotic treatment should be at least four to six weeks [24]. Resuscitation is also essential with adequate caloric intake and nitrogen. The use of subclavial and jugular venous pathways is formally contraindicated [3,7]. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy has been proposed in anaerobic necrosis but rarely used because of technical problems (pleural and cervical drains) [7].
In the literature , we find some alternative treatement like immunoglobulins and polymyxin B hemoperfusion treatement used after surgery. The immunological treatement should be assessed in resistant cases, and intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIG) can be tried in treatment for shoked patient [25] The treatment of respiratory failure sometimes requires the use of ventilation assisted by tracheal intubation and not by tracheotomy, which would often be performed in full cellulite [3]. The monitoring of these patients focuses on the general state, the thermal curve and the local state by controlling the permeability of the drains and their location through CT.
DMN is a rare entity and a high life threatening complication of infection from the oropharyngeal region. Early and fast diagnosis, surgical management and postoperative care with close wound technique with close surveillance through multiple CT scan reduce mortality. Prevention and multidisciplinary approach still the best way to reduce this life-threatening complication.