Drug Interactions with Catecholamines and Metabolites. Evidence of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation On Pathways
For patients with neurological disorders, particularly Parkinson Disease, medications as well as specific clinical features and the phase of disease should guide their treatment. Pharmacological management is complex and should be individualized according to the needs of the patient. Dopaminergic drugs are the focus of many therapies targeting the motor system, where high inter-individual differences in response are common. However, the evident beneficial effects of L-Dopa may cause side effects and its toxicity found in in vitro assays has been attributed to the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS): L-Dopa is converted to dopamine (DA) and its metabolism and autoxidation gives rise to quinones, semiquinones, and hydrogen peroxide. Other mechanism suggest that adrenaline (A) and noradrenaline (NA) react with (•)OOH, which suggests that these are better peroxyl radical scavengers that some referenced scavengers, besides, we can´t forget to Homovanillic acid, as a metabolite of dopamine, reflecting central dopamine metabolism. This revision is to show multiple clinical risk factors which have been identified as well numerous metabolism pathways that have been hypothesized considering moieties structural changes.
Keywords:Catecholamines; Dopamine; Epinephrine; Norepinephrine; Oxidative Stress
Catecholamines are characterized by a catechol group (a benzene ring with two hydroxyl groups) to which is attached an amine (nitrogen-containing) group. Among the catecholamines are dopamine, epinephrine (adrenaline), and norepinephrine (noradrenaline). Catecholamines are synthesized in the brain, in the adrenal medulla, and by some sympathetic nerve fibres. In cells, the stimulatory effects of epinephrine (figure 1) are mediated through the activation of a second messenger known as cAMP (cyclic adenosine monophosphate). The activation of this molecule results in the stimulation of cell-signaling pathways that act to increase heart rate, to dilate blood vessels in skeletal muscle, and to break down glycogen to glucose in the liver [1]
Catecholamines can be created from any one of the following three amino acids: L-Phenylalanine (PHE), L-Tyrosine (L-4-hydroxyphenylalanine; TYR), or L-DOPA (L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine; DOPA). These amino acids are provided from natural sources, with L-tyrosine being the most common. Dopamine itself is also used in the biosynthesis of the following related catecholamine neurotransmitters [2] (figure 2).
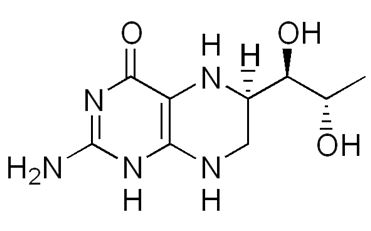
L-Phenylalanine is converted into L-tyrosine by the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) with molecular oxygen (O2) and tetrahydrobiopterin (THB) (figure 3) as cofactors.
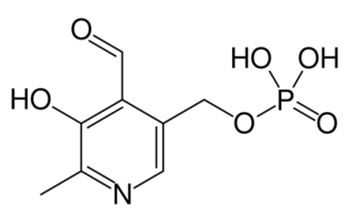
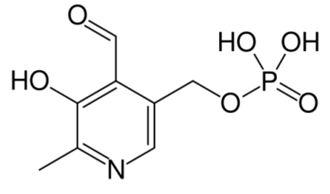
L-Tyrosine is converted into L-DOPA by the enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) with tetrahydrobiopterin (THB), O2, and ferrous iron (Fe2+) as cofactors. L-DOPA is converted into dopamine by the enzyme aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AAAD; also known as DOPA decarboxylase (DDC)) with pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) (figure 4) as the cofactor.
Dopamine is converted into norepinephrine by the enzyme dopamine β-hydroxylase (DBH) with O2 and L-ascorbic acid (figure 5) as cofactors. Finally, norepinephrine is converted into epinephrine by the enzyme phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase (PNMT) with S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAMe) (figure 6) as the cofactor.
Although tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) is the rate limiting step in the biosynthesis of catecholamines, this enzyme may play a direct role in the pathogenesis of Parkinson Disease (PD), especially through oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory mechanisms. Regulatory mechanisms and function of TH are promising in improving gene therapy approaches as well as other treatment modalities [3,4].
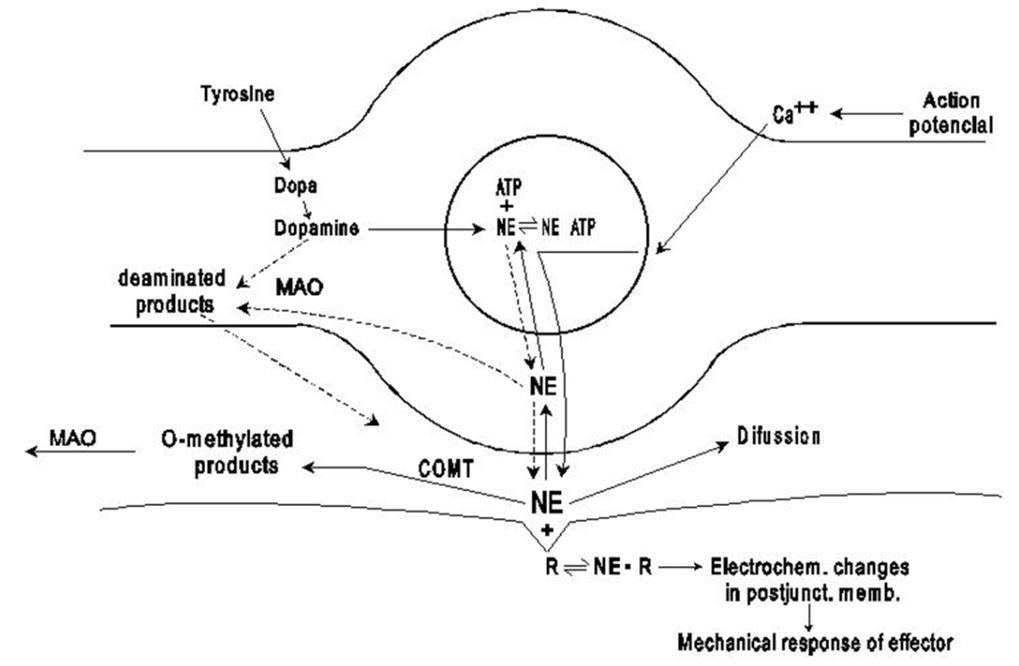
Upon synthesis, dopamine is transported from the cell cytosol into synaptic vesicles by the vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2). Dopamine is stored in vesicles and remains in there until an action potential occurs and forces them to merge with the cell membrane via a process known as exocytosis, thereby dumping dopamine into synapses. Once in the synapse, dopamine binds to and activates postsynaptic dopamine receptors, resulting in the signal of the presynaptic cell being propagated to the postsynaptic neuron [5,6]
Dopamine also binds to presynaptic dopamine receptors, which can either excite the presynaptic cell or inhibit it depending on their electrical potential. Presynaptic receptors with an inhibitory potential are called auto receptors and inhibit neurotransmitter synthesis and release. They serve to keep dopamine levels normalized in certain pathways when release is acutely disrupted and becomes too high or too low.
After dopamine has performed its synaptic duties, it is taken up via reuptake back into the presynaptic cell by either the high-affinity dopamine transporter (DAT) or the low-affinity plasma membrane monoamine transporter (PMAT). Once back in the cytosol, it is subsequently repackaged into vesicles by VMAT2.
Dopamine is directly broken down into inactive metabolites by two enzymes, monoamine oxidase (MAO) and catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT). It is equally metabolized by the two respective isoforms of MAO, MAO-A and MAO-B (figure 7).
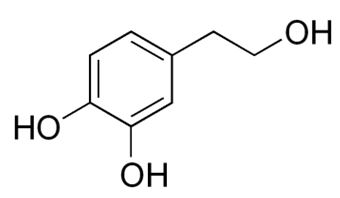
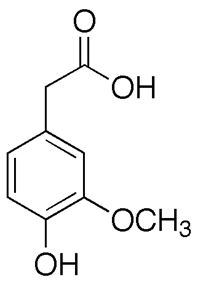
Dopamine is metabolized by MAO into 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde (DOPAL). DOPAL is further metabolized into 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC) by the enzyme aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH). DOPAL can also be reduced to 3,4-dihydroxyphenylethanol (DOPET; also known as hydroxytyrosol (figure 8) by aldose reductase(AR) to a lesser extent.
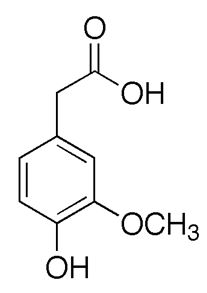
Finally, COMT reduces DOPAC and DOPET to homovanillic acid (HVA) (figure 9) and 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylethanol (MOPET), respectively, which are then excreted in the urine.
Early seizures combined with pharmacological treatments, may influence the development of dopaminergic neurotransmission in the frontal cortex. For example, perinatal asphyxia plus carbamazepine affects extracellular levels of dopamine and DOPAC in the frontal cortex and stimulated the release of dopamine, which provides evidence for the altered availability of dopamine in cortical brain areas during brain development [7].
COMT can also directly metabolize dopamine into 3-methoxytyramine (3-MT), which is then subsequently metabolized to HVA by MAO and is excreted in the urine as well. Monoamine oxidase (A and B), and the production of hydrogen peroxideas a byproduct of the reaction between the monoamine oxidases and their monoamine substrates has also implicated monoamine oxidase-sensitive events in intrinsic cell death pathways, particularly those centered on oxidative stress and peroxyradical-mediated mechanisms. Consequently, the inhibition of monoamine oxidase has been considered as adjunctive therapy in neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease [8,9]. However, catechol also known as pyrocatechol or 1,2-dihydroxybenzene is formed endogenously in the organism from neurotransmitters including adrenaline, noradrenaline, and dopamine [10].
In most areas of the brain, including the striatum and basal ganglia, dopamine is inactivated by reuptake via the DAT, then enzymatic breakdown by MAO into DOPAC. In the prefrontal cortex, however, there are very few DAT proteins, and dopamine is inactivated instead by reuptake via the norepinephrine transporter (NET), presumably on neighboring norepinephrine neurons, then enzymatic breakdown by COMT into 3-MT [11]. The DAT pathway is roughly an order of magnitude faster than the NET pathway: in mice, dopamine concentrations decay with a half-life of 200 milliseconds in the caudate nucleus (which uses the DAT pathway) versus 2,000 milliseconds in the prefrontal cortex Dopamine that is not broken down by enzymes is repackaged into vesicles for reuse by VMAT2 [11].
In the brain, dopamine plays an important role in the regulation of reward and movement. As part of the reward pathway, dopamine is manufactured in nerve cell bodies located within the ventral tegmental area (VTA) and is released in the nucleus accumbens and the prefrontal cortex. In vivo the dopamine concentration in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) was 4.8 ± 1.5 nM but in the red nucleus was 0.5 ± 0.2 nM [12]. Its motor functions are linked to a separate pathway, with cell bodies in the substantia nigra that manufacture and release dopamine into the striatum.
Dopamine has many functions in the brain, including important roles in behavior and cognition, voluntary movement, motivation, punishment and reward, inhibition of prolactin production, sleep, dreaming, mood, attention, working memory, and learning [13,14]. Dopaminergic neurons (neurons whose primary neurotransmitter is dopamine) are present chiefly in the ventral tegmental area of the midbrain, the substantia nigra pars compacta, and the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus.
Dopaminergic neurons form a neurotransmitter system which originates in substantia nigra pars compacta, ventral tegmental area (VTA), and hypothalamus. This innervation explains many of the effects of activating this dopamine system. For instance, the mesolimbic pathway connects the VTA and nucleus accumbens; both are central to the brain reward system [15]
The level of extracellular dopamine is modulated by two mechanisms: tonic and phasic dopamine transmission. Tonic dopamine transmission occurs when small amounts of dopamine are released independently of neuronal activity, and is regulated by the activity of other neurons and neurotransmitter reuptake [16,17]. Phasic dopamine release results from the activity of the dopaminecontaining cells themselves. This activity is characterized by irregular pace making activity of single spikes, and rapid bursts of typically 2-6 spikes in quick succession [18]. Concentrated bursts of activity result in a greater increase of extracellular dopamine levels than would be expected from the same number of spikes distributed over a longer period of time [19].
Cocaine and amphetamines inhibit the re-uptake of dopamine; however, they influence separate mechanisms of action. Cocaine is a dopamine transporter and norepinephrine transporter blocker that competitively inhibits dopamine uptake to increase the lifetime of dopamine and augments an overabundance of dopamine within the parameters of the dopamine neurotransmitters [20]. Like cocaine, amphetamines increase the concentration of dopamine in the synaptic gap, but by a different mechanism. Cocaine promotes activation of D1-expressing nAcc neurons: enhancement of IP3R-mediated responses via σ1R activation at the endoplasmic reticulum, resulting in augmented Ca2+ release and amplified depolarization due to subsequent stimulation of transient receptor potential canonical channels [21]. Amphetamines and methamphetamine are similar in structure to dopamine, and so can enter the terminal bouton of the presynaptic neuron via its dopamine transporters as well as by diffusing through the neural membrane directly. By entering the presynaptic neuron, amphetamines force dopamine molecules out of their storage vesicles and expel them into the synaptic gap by making the dopamine transporters (DAT) work in reverse [22]. Human dopamine (DA) transporter (hDAT) regulates dopaminergic signaling in the central nervous system by maintaining the synaptic concentration of DA at physiological levels, upon reuptake of DA into presynaptic terminals. DA translocation involves the co-transport of two sodium ions and the channeling of a chloride ion [23]. The DAT is a principle target of various psychostimulant, nootropic and antidepressant drugs, as well as certain drugs used recreationally, including the notoriously addictive stimulant cocaine [24]. Indeed, narcotics and stimulants increase the concentrations of dopamine in the presynaptic clefts, exerting an excitatory effect [25].
Dopamine reduces the influence of the indirect pathway while increasing the actions of the direct pathway within the basal ganglia. Insufficient dopamine biosynthesis in the dopaminergic neurons can cause Parkinson’s disease, a condition in which one loses the ability to execute smooth, controlled movements [26]. Dopamine depletion may induce renin-angiotensin system (RAS) upregulation as a potential compensatory mechanism. However, RAS hyperactivation also exacerbates NADPH-oxidase activity, oxidative stress and the microglial inflammatory response and contribute to progression of dopaminergic neuron loss. The authors propose that manipulation of the brain RAS may constitute an effective neuroprotective strategy against the aging-related risk of dopaminergic degeneration, in fact one of the reported mechanisms is the chronic inhibition of RAS by the use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, which resulted in an increase in AD levels [27].
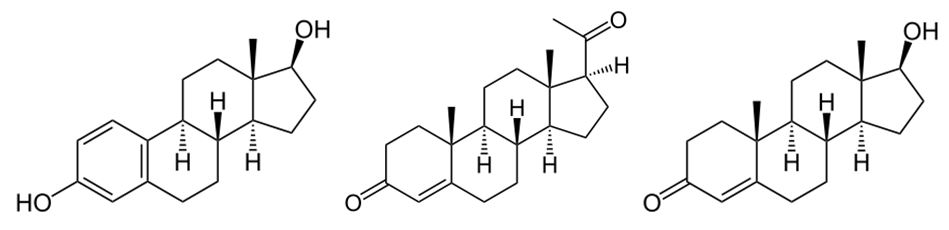
In humans, drugs that reduce dopamine activity (neuroleptics, antipsychotics) have been shown to impair concentration, reduce motivation, cause anhedonia (inability to experience pleasure), and long-term use has been associated with tardive dyskinesia, an irreversible movement disorder [28]. Antipsychotics have significant effects on gonadal hormones including significantly lower levels of estradiol (figure 10a) and progesterone (figure 10b) in women, whereas men display significantly lower levels of testosterone (figure 10c) and DHEA when undergoing antipsychotic drug treatment compared to controls, and drugs acting at all three monoamine transporters including dopamine transporter should provide more efficacious antidepressants activity.
Antipsychotics are known to cause hyperprolactinaemia leading to amenorrhea, cessation of normal cyclic ovarian function, loss of libido, occasional hirsutism, false positive pregnancy tests, and long-term risk of osteoporosis in women. The effects of hyperprolactinemia in men are gynaecomastia, galactorrhea, impotence, loss of libido, and hypospermatogenesis [29]. Furthermore, antipsychotic drugs are associated with weight gain, diabetes, drooling, dysphoria (abnormal depression and discontent), fatigue, sexual dysfunction, heart rhythm problems, stroke and heart attack.
Cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYPs) metabolize many drugs that act on the central nervous system (CNS), such as antidepressants and antipsychotics; drugs of abuse; endogenous neurochemicals (dopamine). This takes place primarily in the liver, but metabolism can also occur in extrahepatic organs, including the brain. Knowledge of brain CYP-mediated metabolism may help us understand why patients respond differently to drugs used in psychiatry and predict risk for psychiatric disorders, including neurodegenerative diseases and substance abuse [30].
The development of addiction is connected with CNS reinforcement system and dopaminergic neurotransmission, and drugs of abuse increase release of dopamine, norepinephrine and other neurotransmitters [31]. This theory can be discussed in terms of drugs such as cocaine (figure 11), nicotine (figure 12), and amphetamine (figure 13), which directly or indirectly lead to an increase of dopamine in the mesolimbic reward pathway of the brain, and in relation to neurobiological theories of chemical addiction, arguing that this dopamine pathway is pathologically altered in addicted persons.
These drugs have some common direct or downstream effects, including modulation of dopaminergic systems through its action on the dopaminergic signaling pathways, cocaine affects the HPA axis, and brain nuclei responsible for movements, and rewarding effects.
Dopamine is commonly associated with the reward system of the brain, providing feelings of enjoyment and reinforcement to motivate a person to perform certain activities. Dopamine is released (particularly in areas such as the nucleus accumbens and prefrontal cortex) as a result of rewarding experiences such as food, sex, drugs, and neutral stimuli that become associated with them [32]. While mesolimbic dopamine (DA) is a critical component of the brain circuitry regulating behavioral activation and effortrelated processes. Although nucleus accumbens (NAc) DA depletions or antagonism leave aspects of appetite and primary food motivation intact [33]. Therapeutic strategies involving drugs acting not only at the targets of dopamine transporter, but also at other molecular targets to improve their efficacy and their tolerability in clinical disorders (table 1).
Dopaminergic neurons of the midbrain are the main source of dopamine in the brain. Symptoms of catecholamine excess or pseudopheochromocytoma can be clinically indistinguishable from pheochromocytoma. Patients with pseudopheochromocytoma appear to have an amplified cardiovascular responsiveness to catecholamines with enhanced sympathetic nervous stimulation and increased secretion of dopamine, epinephrine, norepinephrine, and their metabolites [57]. While in consecutive children who are 1 month to 15 years old and met the clinical criteria for fluid-refractory septic shock were randomly assigned to receive either dopamine (5-10 μg/kg/min) or epinephrine (0.1-0.3 μg/kg/min). Dopamine was associated with death and epinephrine was associated with a survival [58]. The administration of catecholamines, however, should always be reevaluated and titrated to the minimum deemed necessary, when they are commonly used in intensive care medicine.
On the other hand, catecholamines and oxidative stress resulting in neurodegeneration and locomotor disorder are the main events in Parkinson’s disease (PD) [59-61].
There is an age-associated increase in oxidative damage to the brain, and aging is considered a risk factor for PD. A pathological imbalance in PD between the acetylation and deacetylation of the histone proteins around which deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is coiled, in favour of excessive histone deacetylation [62]. Dopaminergic neurons show linear fallout of 5-10% per decade with aging; however, oxidative damage includes mitochondrial dysfunction, dopamine auto-oxidation, α-synuclein aggregation, glial cell activation, alterations in calcium signaling, and excess free iron. Moreover, alterations in transcriptional activity of various pathways, including nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2, glycogen synthase kinase 3β, mitogen activated protein kinase, nuclear factor kappa B, and reduced activity of superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione with aging might be correlated with the increased incidence of PD [63,64], a neurodegenerative disorder that affects 2% of the population older than 60 years.
Explosive overpressure brain injury (OBI) results in increased hypothalamic expression of oxidative stress and activation of the sympatho-adrenal medullary axis, as increased sympathoexcitation. The mechanism may involve the elevated AT1 receptor expression and NADPH oxidase levels in the hypothalamus, related with dopamine [65]. Other pathological states have also been associated with dopamine dysfunction, such as schizophrenia, autism, and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, as well as drug abuse, and management of this condition is often difficult and frustrating for both the physician and the patient.
Neurotransmitters adrenaline and noradrenaline regarding oxidative stress, are better peroxyl radical scavengers and can be capable of reducing oxidative stress, by scavenging free radicals and by sequestering metal ions, and at the same time, they might lose their functions in the process due to the associated structural modifications [66]. Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction are well known contributors to Parkinson disease (PD). Oxidants and superoxide radicals are produced as byproducts of oxidative phosphorylation, making mitochondria the main site of reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation within the cell and the site of the first line of defense against oxidative stress [67]. Some studies suggest that mitochondrial c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), plays in the etiology of 6-hydroxydopamine-induced (6-OHDA) (figure 14) oxidative stress, and the authors propose that inhibitors that block association of JNKs with the mitochondria may be useful neuroprotective agents for the treatment of Parkinson disease, as is the case of cell-permeable peptide of the outer mitochondrial membrane protein, Sab (SH3BP5), Tat-Sab KIM1 demonstrated neuroprotective effects in the study of Chambers et. al. [68]
In dopaminergic neurons of the nigrostriatal dopamine (DA) projection from the substantia nigra to the dorsal striatum become dysfunctional and slowly degenerate in Parkinson’s disease, where the evidence implicates oxidative stress as an underlying factor in both the initiation and progression of the disease, including hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Whose effect of acute increases in local H2O2 concentration on both electrically evoked DA release and basal. Increases in endogenous H2O2 in the dorsal striatum attenuated electrically evoked DA release, and also decreased basal DA levels [69]. Oxidative stress and oxidized dopamine contribute to the degeneration of the nigrostriatal pathway in Parkinson’s disease (PD). Selenium transport protein selenoprotein P (Sepp1) and Sepp1 in midbrain was expressed in neurons of the substantia nigra (SN), and expression was concentrated within the centers of Lewy bodies, the pathological hallmark of PD. Therefore, the authors indicate a role for Sepp1 in the nigrostriatal pathway, and suggest that local release of Sepp1 in striatum may be important for signaling and/or synthesis of other selenoproteins with neuroprotection activity [70].
PD disease appears to have a multifactorial mechanism, however, oxidative stress and neuro-inflammation, including activation of NADPH-dependent oxidases, play a major role in the progression of dopaminergic cell death [71,72]. NADPH oxidase was originally identified in immune cells as playing an important microbicidal role. In neurodegenerative and cerebrovascular diseases, inflammation is increasingly being recognized as contributing negatively to neurological outcome, with NADPH-oxidase as an important source of superoxide. Probably the activated enzyme complex transports electrons to oxygen, thus producing the superoxide anion (O₂˙⁻), a precursor of reactive oxygen species. The advantage of a targeted NADPH oxidase inhibitor that would inhibit the production of superoxide is clear [73].
A possible role of DNA repair systems in ageing and neurodegenerative diseases after DNA damage was observed in the brain of individuals affected by neurodegenerative diseases, and whether the study on DNA repair gene polymorphisms (XRCC1 Arg399Gln, XRCC3 Thr241Met XPD Lys751Gln, XPG Asp1104His, APE1 Asp148Glu, and HOGG1 Ser326Cys), suggested that APE1, XRCC1, and XRCC3 genetic variants may be a risk factor by increasing oxidative stress that might cause the loss of dopaminergic cells in the sustantia nigra and locus caeruleus, leading to abnormal signal transmission, and ultimately, the development of PD [74]. While Nox1/Rac1 could serve as a potential therapeutic target for Parkinson’s disease. Because dopaminergic neurons are equipped with the Nox1/Rac1 superoxide-generating system, and Stress-induced Nox1/Rac1 activation causes oxidative DNA damage and neurodegeneration [75].
Other study, suggest that the loss of serum response factor (SRF), decreases levels of the anti-apoptotic proteins brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and Bcl-2, a plausible underlying cause of increased sensitivity to oxidative stress, and the dysfunction of the SRF-activating mitogen-associated kinase pathway may be part of Parkinson’s disease etiology [76].
Dopamine in the mesolimbic pathway increases general arousal and goal directed behaviors and decreases latent inhibition; all three effects increase the creative drive of idea generation. This has led to a three-factor model of creativity involving the frontal lobes, the temporal lobes, and mesolimbic dopamine [77]. Some authors suggest that the frontal cortex and striatum regions are more sensitive to oxidative damage which could be related to the parallel monoamine perturbations [78].
Dopamine has been shown to be involved in the control of movements, the signaling of error in prediction of reward, motivation, and cognition. Cerebral dopamine depletion is the hallmark of Parkinson’s disease. A central strategy has been to target glutamate receptors with intravenous infusions of the N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist ketamine. Other strategies have been based on modulation of cholinergic and γ-aminobutyric acid GABAergic transmission, neuronal plasticity, stress/hypothalamic pituitary adrenal(HPA)-axis, the reward system and neuro-inflammation [79]. Inflammation is deleterious for organs with reduced capacity of regeneration, such as the brain. In patients who are very sick, supportive treatment is equally important and several drugs are used to reduce brain swelling and inflammation, or simply affect cerebral functions and causes health complications. An alternative in the future treatment of this health complications is that neuro-inflammation and associated infiltration of inflammatory cells into central nervous system may be inhibited by 3-hydroxy-3-methyl glutaryl co-enzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitors, and attenuate neuroinflammatory markers [80]. Peripheral inflammation leads to immune responses in brain characterized by microglial activation, elaboration of pro-inflammatory cytokines, reactive oxygen species, and secondary neuronal injury. The inducible cyclooxygenase (COX), COX-2, mediates a significant component of this response in brain via downstream proinflammatory PG signaling [81]. These authors report that PGE2 EP4 signaling mediates an anti-inflammatory effect in brain by blocking LPS-induced proinflammatory gene expression in mice, and suggest that EP4 selective agonist decreased LPS-induced proinflammatory gene expression in hippocampus and in isolated adult microglia. In plasma, EP4 agonist significantly reduced levels of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines, indicating that peripheral EP4 activation protects the brain from systemic inflammation. Probably the mechanism that is directly implicated in controlling oxidative stress and inflammatory response could be an attractive strategy to prevent the onset and/or delay the progression of neurodegenerative diseases. This can be supported by Kato and cols. [82], whom propose the possibility that modulating microglia may be a key target in the treatment of various psychiatric disorders.
Some authors have involvement oxidative stress in developmental brain disorders, due events or clinical disorders that induce inflammation (table 2).
Abnormalities in dopaminergic neurotransmission have also been demonstrated in painful clinical conditions, including burning mouth syndrome [97] and restless legs syndrome [98]. In general, the analgesic capacity of dopamine occurs as a result of dopamine D2 receptor activation; however, exceptions to this exist in the PAG, in which dopamine D1 receptor activation attenuates pain presumably via activation of neurons involved in descending inhibition [99]. In addition, D1 receptor activation in the insular cortex appears to attenuate subsequent pain-related behavior.
It is the second most common degenerative disease of the central nervous system, due to the progressive loss of dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta, causing the loss of dopamine neurotransmission [100]. The prevalence of the disease is 1 to 2 per 1000 and affects 1% of the population over 60 years of age, with male predominance [101,102].
The etiology is not defined, however 5 to 10% are of genetic origin, most cases are considered idiopathic and are associated with aging. Risk factors associated with inflammation have been observed, such as environmental factors, exposure to pesticides, heavy metals, traumatic injuries, and bacterial and viral infections [103]. The main pathophysiological processes in PD are autonomic neuronal destruction, accumulation of alpha synuclein, misfolding proteins, mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress, impaired autophagy, altered intracellular calcium homeostasis, inflammation and impaired neurogenesis [104-106]. Lewy body is the cytological hallmark of PD and contains misfolded α-synuclein, the same protein that also accumulates in related disorders, including multiple system atrophy and dementia with Lewy bodies, collectively termed “synucleinopathies”[107].
The clinical picture is characterized by the presence of motor and non-motor symptoms, the non-motor symptoms present are dementia, hyposmia, depression, and emotional changes. In the case of motor symptoms are bradykinesia/ akinesia, resting tremor, rigidity, postural abnormalities, and non-motor symptoms are dementia, hyposmia, depression, emotional changes [108]. The fundamental elements to establish the diagnosis are a detailed anamnesis and detailed neurological examination. The clinical diagnosis is made by the presence of motor symptoms, which include bradykinesia and at least one of tremor, rigidity or postural instability, being defined as confirmed, probable or possible diagnosis, depending on the evolution of several neurocognitive aspects obtained from different scales. The Movement Disorder Society (MDS) diagnostic criteria are the best known and have a high sensitivity and specificity [109].
Currently, the diagnosis has evolved through clinical, pathological and genetic criteria, which are complemented by neuroimaging or biochemical data [110-112].
The treatment of PD depends on the diagnosis and prognosis because of its impact on quality of life. The treatment of this pathology requires multidisciplinary management.
The initiation of pharmacological treatment for the management of motor symptoms requires adequate decision making shared with the patient to consider the benefits and risks. However, it is important to consider that there is currently no effective therapy to stop the progression of the disease. Therapy is currently based on the control of motor and non-motor symptoms and replacing dopamine.
Treatment for PD has classically involved maximizing endogenous dopamine by medicinal options that either replace dopamine or augment the dopaminergic pathway. The medications are unfortunately limited, given they are not curative and involve potential short-term and long-term side effects (table 3).
The long-term use of levodopa in Parkinson’s disease has been linked to dopamine dysregulation syndrome [113]. This drug crosses the blood-brain barrier and its administration replenishes the loss of DA in dopaminergic neurons in PD patients, and is converted to DA and its metabolism and autoxidation gives rise to quinones, semiquinones, and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Due metabolic pathways, driven by the enzymes aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC) and catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT), significantly deplete the amount of L-Dopa reaching the brain, may have a protective effect on dopaminergic cells [114].
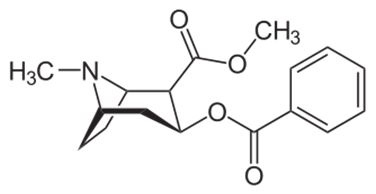
Levodopa is a dopamine precursor used in various forms to treat Parkinson’s disease and dopa-responsive dystonia. It is typically co-administered with an inhibitor of peripheral decarboxylation (DDC, dopa decarboxylase), such as carbidopa (figure 15) or benserazide (figure 16).
Inhibitors of alternative metabolic route for dopamine by catechol-O-methyl transferase are also used. However, L-DOPA induced increase in endogenous 6-OHDA levels will have the ability to cause oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunctions that eventually leads to Lewy body formation in dopaminergic neurons resulting in its degeneration, and the use of potent anti-oxidants along with L-DOPA would help in attenuating the neurodegeneration caused by endogenous 6-OHDA and would ultimately delay the progression of PD [115]. The binding of L-dopa to GPE (Gly-Pro-Glu is the N-terminal tripeptide of insulin-like growth factor-I, which is naturally cleaved in the plasma and brain tissues), tripeptide might represent a promising strategy to supply L-dopa to parkinsonian patients [116].
Long-term over-consumption of food items containing β-PEA could be a neurological risk factor having significant pathological consequences. Due the toxicity of beta-phenyl ethyl acetate (β-PEA) has been linked to the production of hydroxyl radical (·OH) and the generation of oxidative stress in dopaminergic areas of the brain, and this may be mediated by inhibition of mitochondrial complex-I [117].
Antipsychotic medications act largely as dopamine antagonists, inhibiting dopamine at the receptor level, and thereby blocking the effects of the neurochemical in a dose-dependent manner. The older, so-called typical antipsychotics most commonly act on D2 receptors, while the atypical drugs also act on D1, D3 and D4 receptors, though they have a lower affinity for dopamine receptors in general [118]. Abnormally high dopaminergic transmission has been linked to psychosis and schizophrenia. However, clinical studies relating schizophrenia to brain dopamine metabolism have ranged from controversial to negative, with homovanillic acid (HVA) (figure 17) levels in the CSF the same for schizophrenics and controls [119]. Due HVA is a major catabolite of dopamine and its concentration in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) provides insight into the turnover of dopamine [120].
HVA can be reflecting central dopamine metabolism, primarily situated in the striatum. Low HVA concentrations in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) may indicate metabolic deficiencies in the pathways of the biosynthesis or catabolism of dopamine. Due to a defect in the biosynthesis or reuptake of dopamine, is expected to cause extrapyramidal features. A decrease of HVA may be due to dysfunction of dopamine neurons or in the CSF is mainly a secondary or epiphenomenon in a variety of clinical conditions [121]. A trial of 1388 cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) samples from children with neurological disorders (mean age 3y 10mo, SD 4y 5mo; 712 males, 676 females. Showed correlations among CSF HVA, reporting neurological diseases with abnormal CSF HVA values such as pontocerebellar hypoplasia, perinatal asphyxia, central nervous system infections, mitochondrial disorders, and other genetic diseases, and no clear limits for CSF HVA values pointing towards primary diseases can be stated [122].
The aim of this article is analyze the effect of drugs on the catecholamine pathway, since is fundamental to promote the search for new therapeutic options in neurodegenerative pathologies, as is the case of PD. The catecholamines dopamine, epinephrine and norepinephrine are synthesized from L phenylalanine, L tyrosine or L DOPA. DA has important functions in the brain, behavior, cognition, motivation, reward system, inhibition of prolactin production, sleep, mood, memory and learning.
During DA metabolism, TH is a fundamental key in the synthesis of catecholamines and in the development of neurological disorders; any change in the expression or activity of this enzyme will have a direct effect on the production of DA, so it is considered important in the pathogenesis of PD. The processes mainly linked to PD are proinflammatory mechanisms and oxidative stress. Currently DAT is the main target in the therapy of psychostimulant drugs, iotropics, antidepressants and recreational drugs.
In several studies the impact of drugs on the catecholamine pathway has been reported, this effect is important to consider during the treatment of patients with neurological disorders due to the presence of long and short term side effects [28].
In addition, antipsychotics are associated with weight gain, diabetes, sialorrhea, dysphoria, fatigue, sexual dysfunction, heart rhythm disturbances, strokes, heart attacks and effects on gonadal hormones, in the case of women it causes hyperprolactinemia, cessation of ovarian function, loss of libido, hirsutism, osteoporosis and in men gynecomastia, galactorrhea, loss of libido and hypospermatogenesis [29].
The purpose of this article is to promote the search for new therapeutic strategies in PD, since there is currently no treatment that prevents the progression of the disease or avoids the presence of short and long term side effects [28]. The most representative and effective drug for the control of motor symptoms of PD is currently Levodopa. In the long term, the development of dopamine dysregulation syndrome, increased oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunctions have been reported [100]. Adjuvant therapy is recommended during the treatment of PD, however such drugs may cause or worsen the presence of dyskinesia, as well as non-motor dopaminergic effects.
The importance of this article lies in knowing in detail the metabolism of catecholamines to improve the treatment of neurological disorders. Currently, the search for new therapeutic strategies continues, as is the case of HT, an enzyme that is still under study protocol and from which promising results are expected, and new research is focused on preventing the progression of the disease and reversing the maintenance of dopamine levels, with the main objective being to prevent the inflammatory process and oxidative stress.
Indeed, biochemical and physiological abnormalities in presence of drugs or natural products provoke changes in catecholamine’s pathways responses, and oxidative stress resulting in neurodegeneration and locomotor disorder are the main events in Parkinson’s disease. However, the discovery of new drugs or new potential uses safety for currently available drugs is crucial for treating this neurological disorder.
Funding: This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, private, or not-for-profit sectors.
We thank Dr. Cyril Ndidi Nwoye Nnamezie, an expert translator whose native language is English, for his help in preparing this manuscript. The authors express their profound gratitude to the National Institute of Pediatrics (INP) for the support in the publication of this article, following format PRISMA.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
DCGa,b,c,d, HJOb,c,d, MPSb,c,d, FTJb,c,d, MOHb,c,d, NLRb,c,d, SDAb,c,d
(a) Contributed to conception. (b) Critically revised the manuscript for important intellectual content. (c) Drafted manuscript. (d) Gave final approval. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.