Endothoracic Goiter Operated Only by Posterolateral Thoracotomy: About 5 Cases
Introduction: Substernal goiter or secondary endothoracic goiter usually can be managed successfully by a neck approach. However, partial or total sternotomy, or even thoracotomy, is warranted only in a minority of patients. Our goal is to specify the characteristics of this form of goiter, and precise indications for realize a posterolateral thoracotomy.
Material and Methods: It was a retrospective study involving 5 patients, all operated for an endothoracic goiter only by thoracotomy.
Results: Among five patients, it was 3 women and 2 men, with an average age of 47.4 years. Four cases have already been operated for cervical goiter by cervicotomy alone, and only one patient had a notion of cervical goiter which later totally disappeared. Also, for 3 patients, the discovery was accidental. The substernal goiter was in the right side for all patients. For all patients, the cervicothoracic CT found a heterogeneous mass, with calcification lesions in 2 patients, and necrosis zone in 2 patients. The five patients were operated by posterolateral thoracotomy. Operative follow-up was simple in 4 patients, and only one patient had a wall infection.
Conclusion: Total thyroidectomy by cervicotomy is universally considered the standard surgical approach to substernal goiter. In selected cases, a posterolateral thoracotomy is used for better vascular control, and realized especially in patient already operated by cervicotomy approach.
Keywords: Endothoracic Goiter; Cervical Approach; Thoracotomy
Goiter is localized or generalized hypertrophy of the thyroid gland. It is usually cervical but may have an intrathoracic development extending beyond the upper orifice of the thorax and descending more or less to the mediastinum (following certain factors such as age, positive pressure of the thorax) which is called substernal goiter, mediastinal goiter, or endothoracic goiter, firstly described by Haller in 1749 [1]. The definition of this form of goiter remains today non unanimous [2]. The clinical presentation is often dependent on the size and localization of the goiter. The management of endothoracic goiter is primarily surgical usually by a neck approach, or rarely by sternotomy [3,4]. The posterolateral thoracotomy approach is exceptional in goitre surgery; either this approach is unique or associated with cervicotomy. We conducted this study to analyze the clinical, paraclinical and operative particularities of endothoracic goiters treated only by posterolateral thoracotomy without association to other approaches.
It was a retrospective study collecting clinical, paraclinical and operative data from 5 patients, all operated for an endothoracic goiter, into our department of thoracic surgery in CHU Hassan II Fez. We have included all substernal goiter operated exclusively by posterolateral thoracotomy alone, and we have excluded other goiters operated by any other approach: cervicotomy, manubriotomy, sternotomy, anterolateral thoracotomy or any other approach. We have also excluded any patient operated in our department for cervical goiter combined to thoracotomy.
The data for these five patients is summarized in the (Table 1). It is 3 women and 2 men, with an average age of 47.4 years. Four cases have already been operated for cervical goiter by cervicotomy alone, and only one patient had a notion of cervical goiter which later totally disappeared. Also, for 3 patients, the discovery was accidental, and the other 2 patients, had dyspnea and chest pain for everyone. The endothoracic goiter was in the right side for all patients. Chest X-ray showed in all patients’ opacity of the superior mediastinum, and all had received an injected cervicothoracic CT. It was a heterogeneous mass in all patients, with calcification lesions in 2 patients, and necrosis zone in 2 patients. Before being operated, all patients had a thyroid assessment returning without subnormality. The five patients were operated by posterolateral thoracotomy passing through the 6th intercostal space. Operative follow-up was simple in 4 patients, and only one patient had a wall infection, supported by a daily dressing change, and antibiotic therapy. The anatomopathological study did not find any malignancy in the 5 cases. It is a multiheteronodular thyroid hyperplasia in 4 patients and a vesicular adenoma in a single patient.
Goiter is an increase in the volume of the entire thyroid whose location is most often cervical. It is related to an increase in follicular capital, number or size of vesicles. It can be part of thyroid pathology (Basedow, Hashimoto, toxic multinodular goitre). Simple goiter, largely favored by iodine deficiency, is a goiter that is not one of the pathologies mentioned above. Goiter surgery is common and recognized as easy; however, it has complications that can be serious by injury of recurrent laryngeal nerve which the routine demonstration is the most important lesson of thyroid surgery.
As a definition, if goiterous tissue is present below the superior thoracic orifice, it should be defined as substernal or endothoracic goiter [6]. The frequency of this form is variously appreciated by the authors, and it varies from 2.5% to 20% of all thyroidectomies [7]. If this tissue is an extension of a cervical goiter, it can be classified as secondary intrathoracic goiter, and if unconnected with the thyroid proper and judged to be an ectopic gland, as primary intrathoracic goiter [8,9]. The main difference between the two is that primary intrathoracic goiter derives its blood supply from local mediastinal vessels, whereas the secondary is supplied via a vascular pedicle arising from the inferior thyroid artery [8,9]. Also, endothoracic goiter can be classified as prevascular and retrovascular goiter. Prevascular goiter is an expansion in the upper thoracic orifice in front of the thyro-pericardial blade and the innominate vein, developing in the thymic box. However, behind the innominate vein: is a retrovascular goiter, contained on the left by the carotid and subclavian artery, tending to slide to the right, which explains the right predominance of this form of goiters, as was found in all our patients. In our series, all cases are a secondary intrathoracic goiter, because it is most often a cervical goiter that has already been operated, as described in 4 patients, or cervical goiter that has migrated completely into the mediastinum, which it was reported in one patient. The diagnosis of this form of goiter is carried out on the basis of clinical history, physical examination, and imaging findings, although it is confirmed with intraoperative findings. Various diagnostic classification systems have been introduced, but the most comprehensive one appears to be that of Cohen and Cho [10]. All our patients are included in the grade 4 of this classification since we chose only endothoracic goiter operated only by posterolateral thoracotomy. Clinically, the endothoracic goiter usually exerts pressure on neighboring anatomic structures, namely the trachea and esophagus, resulting dyspnea and dysphagia, and occasionally, excessive pressure is exerted on large venous structures, resulting in venous congestion. Usually on the chest x-ray it is opacity of the upper mediastinum with regular contours, polycyclic, with or without tracheal deviation. It is the cervico-thoracic CT that will affirm the endothoracic goiter, and appreciate its volume, its fluid or solid content, its position relative to the trachea, mediastinal vessels and esophagus [11,12]. All forms of goiter must be operated after euthyroidism in the biological assessment to avoid the risk of a thyrotoxicosis.
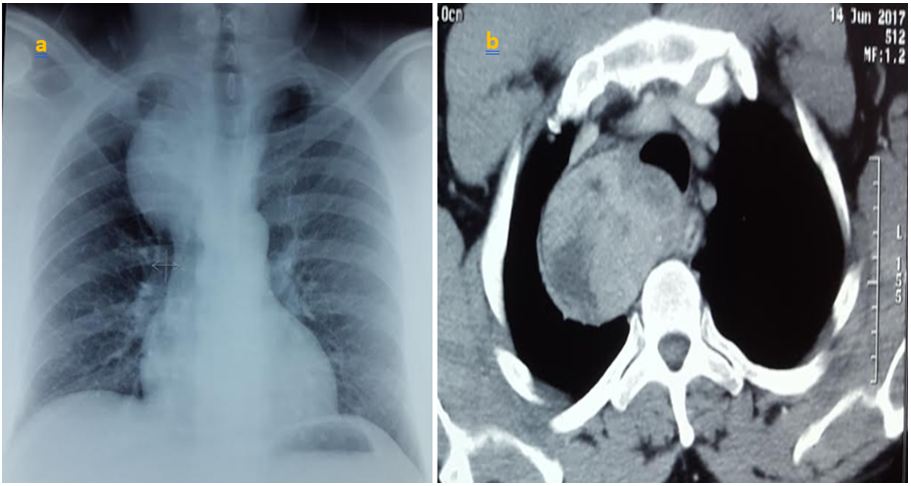
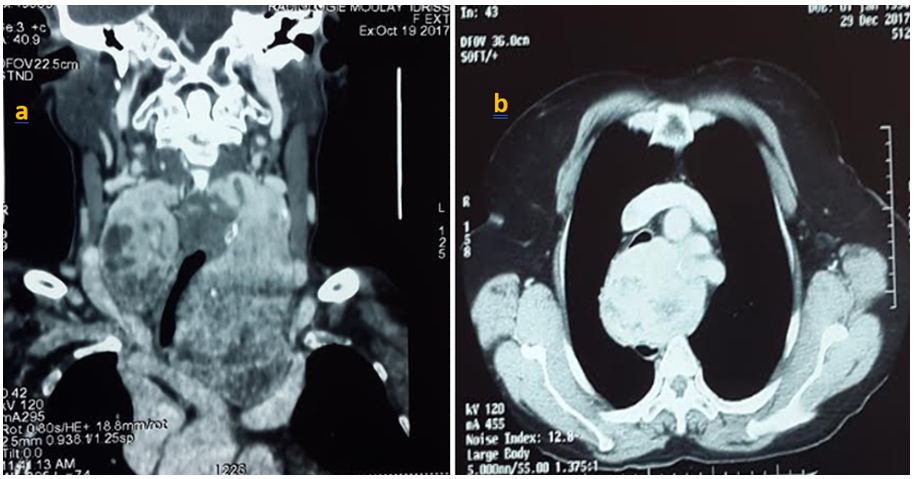
Most endothoracic goiters are extirpable by cervicotomy, and the use of sternotomy or thoracotomy is exceptional. Even large and retrotracheal goiters, in some cases, may be extracted cervically (Figure 1) [13]. The lower poles of the cervical thyroid should therefore be dissected, and the cervico-mediastinal orifice should be scanned for an in apparent thyroid extension at the base of the neck [14]. All our patients benefited from a posterolateral thoracotomy, in view of the posterior development of goiter, and for a better vascular control of this form of goiter whose vascularization is mediastinal (Figure 2).
Posterolateral thoracotomy remains an approach that is rare in endothoracic goiter. This access is especially seen in patients who had cervical goiter operated by cervicotomy. It is mostly done on the right side because of the presence of the aortic cross and its vessels which limit the development of endothoracic goiter.