Preparation and Properties of Water-Soluble Fluorescent Multifunction Nanohybrid Probes
Most water-soluble fluorescent multifunction hybrid materials applied as chemical sensors and bioimaging suffer from damage to the sample, thermal stability, compatibility and high cost. For this observation, a unique path has been well-educated toward visible to NIR fluorescent probe with remarkably enhanced contrast. In the report, the novel macromolecular fluorescent hybrids developed with Octavinyl-polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane (OV-POSS) with superior thermal stability were designed by linking hybrid OV-POSS-Amine (OV-POSS-A) with cyanuric chloride (CC) and acryloyl chloride fluorescence hydrazine (F-H) (hybrid OV-POSS-A-CC-FH). The resultant material confers well biological compatibility, good water disparity, and apparent high brightness fluorescence in biological imaging applications when compared with other systems. The Molecular structure of resulting hybrids was confirmed by FTIR, TGA, H-NMR spectra, FE-SEM, UV-Vis-NIR and Fluorescence Spectroscopy [1]. The hybrids working as chemo sensor exhibits high selectivity for Cu2+ with fluorescence-enhancement in water solution at λem=551 nm. The bound ratio of hybrid OV-POSS-A-CC-FH-Cu2+ complex was determined to be 1:1 according to the Job plot. The association constant (Ka) of Cu2+ bound sensors was 1.7×107 with the detection limit (DL) of 0.06×10-9 M. The system has also been applied in bioimage successfully with a red fluorescent image. Moreover, it is also applicable for naked-eye detection of Cu2+ selective sensors with a color change from colorless to bright green.
Keywords:OV-POSS-A-CC-FH-Cu2+; Fluorescent; Simple Chemosensor of Cu2+ Ions; Water-Soluble; Cell Imaging
Designing of chemosensors is one of the most essential researches, and it is challenging yet necessary to develop chemosensors. Particularly fluorescent enhancement chemosensors with high selective recognition of metal ions have been attracted great interest because of its practical applications in the field of chemistry, medicine, biology and environment [1-4]. H. Haase, et al. investigations of the physiological and effects of metal ions are frequently based on in vitro cell [5]. Ksenia, et al. targeted examination on the cellular or even molecular level [6]. Ionic liquids are remarkable chemical compounds; the main aim is to study the advantages of ionic liquid pharmaceutics and studies of ions in liquids modern chemistry, biology, and medicine. For improving the application in an environmental and living cell, recently, research has mainly focused on water-soluble fluorescent sensors. Xu, et al. prepared a coumar in-based fluorescent turn-on chemo dosimeter which was successfully applied for Hg2+ and Fe3+detection in solution and living cell and even in organisms [7]. Xu, et al. also designed chromophore for simultaneously colorimetric detection of trace Ag+ and Fe3+[8]. Copper (Cu2+) is the third most abundant transition metal ion in the human body after Fe3+and Zn2+ which they are important in the environment pollution and is essential for many biochemical and physiological functions [9-12]. Among all ions, copper trace amounts help to provide the energy needed for the biochemical processes, which help to form the hemein of blood [13,14] and Cu2+ possesses two faces of one coin either boosting or damaging a human being healthy [15]. However, when human and animal bodies intake too little or too much copper from food, water, air, etc., various symptoms like vomiting, lethargy, neurotoxicity, increased blood pressure and respiratory rates may appear [16]. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency has set the limit of copper in drinking water to be 1.3 ppm so it is important to detect, there are several classic techniques such as atomic absorption spectrometry, fluorescence spectrometry and electrochemical techniques could detect Cu2+, however, most of the mentioned techniques need advanced instrumentations [17,18]. Therefore, chemo-sensors allowing naked-eye detection have progressed over other methods, because it is easy to operate, and is portable, the methods for highly selective and sensitive detection of copper are highly desirable [19]. So, it is of great importance to develop simple, rapid and precise sensor methods to detect and monitor the concentration of Cu2+ [20]. Most of the fluorescence sensors for Cu2+ ion reported more technical drawbacks, such as a poor limit of detection (LOD) [21,22], solvent toxicity, complicated synthesis of sensor molecules [23], a hardly controlled fluorescence change, water solubility, and thermal stability [24]. However, the aggregation and precipitation of the resulting dispersion should be considered in fluorescence qualitative or quantitative detections. To progress the valuable methods for the preparation of many substances is still a challenge. Recently, some researchers reported that the hybridization of fluorescent dyes with silica and carbon materials is advantageous to improve their dispersibility in pure water and the prepared hybrid materials. For the above goals, we selected a molecular hybrid method to solve all these problems. It is known that among all these materials, cyanuric chloride (CC) derivatives have been studied for a decade, especially its amino derivatives which have the advantages of preparation simplicity, high efficiency, excellent selectivity and easy of control. CC is also commercially available and inexpensive reagent, which makes it very attractive [25]. It is an essential organic intermediate of which three chlorine can be replaced by –NH2 -OH, -SH (or), and -NHR step by step with a high yield based on simple thermodynamic control [26]. Fluoresceine (FL) is widely employed as a platform for various fluorescence material and labels because of its high fluorescence quantum efficiency in aqueous media [27]. Its amide is also considered as one of these promising materials, stable over wide pH intervals (pH 3–11), and simple and economical as well [28]. Only a few fluorescent probes for hydrazine have been reported, in our previous publication, it is known; the functionalized OV-POSS with near absorption (Squaraine dye (SQ)) showed important application in solar cell [29,30]. SQ one of the most popular sensing compounds to be used as a colorimetric sensor. This can be due to its special rigid D-π-A-π-D conjugation structures [31]. The “huge” inorganic OV-POSS is an ideal platform to prepare the hybrids, which has been used to improve the mechanical, thermal, photostability, optical limiting and dielectric properties of organic dye [32,33]. In this work, the water-soluble functionalized OV-POSS as a nano-structured platform will be used to prepare aqueous functional probe which then aqueous molecular nanoprobe OV-POSS-A-CC-FH. (Scheme 1) was almost achieved quantitatively by the continuous one-pot method after the functional OV-POSS being made amino-functionalization (OV-POSS-Amine) by heck reaction. It is found that the work provides a reference for the screenings of water-soluble fluoresce in materials with high sensitivity detection of Cu2+ and can promote their further applications in bio images.
Acryloyl fluorescein, Sodium carbonate, and dichloromethane were purchased from Shenyang Meixi chemical company,Ltd. Palladium acetate (AR) other chemicals were of analytical grade and obtained from Shanghai, chemical reagent company. All chemical reagents were used directly without any purification.
The absorbance as a function of wavelength was measured using a Lambda 35 UV-Vis spectrophotometer with a 1cm square quartz cell. The fluorescence spectra were obtained on a PerkinElmer LS 55 spectrometer. The electrospray ionization mass spectra were determined by an LCQ Fleet spectrometer (Thermo Fisher).Scans were collected at a resolution of 1 cm-1 scanning from 4000 to 500 cm-1. FTIR spectra have performed on a Perkin Elmer Model 882 infrared spectrometer in the range of 4000 to 500 cm-1. by mixing each sample with KBr. H-NMR spectra were recorded using a Bruker AMX-500 spectrometer operating at 400 MHz, with tetramethylsilane (TMS) as the reference and CDCl3 as solvent [1].
Was synthesized by following the method in our work hybrid-POSS-Amine 0.2 g was added slowly to cyan-uric chloride, 1.845 g in acetone 35 ml with constant stirring for 4h at 0 °C [34]. Sodium carbonate sol 10% was added to neutralize HCl evolved during the reaction. Finally, the content was poured into crushed ice; the solid separated was filter washed with water dried and recrystallized from ethanol many times. IR (KBr), υ (cm-1): 1465, (C-N),870(C-Cl),1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.27 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 88H), 6.58 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 84H), 5.15 – 1.75 (m, 98H), 1.91 (s, 3H), 1.27 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 0.13 – 0.01 (m, 17H).
Acryloyl fluoresceine (Ac-Flu) was prepared by the reaction of fluoresceine and acryloyl chloride (Ac) in the presence of triethylamine. The mixture of 20 ml of CH2Cl2, 3.0 g of fluoresceine, and 5.0 ml of triethylamine was put into 100 ml three-necked round bottom flask equipped with a thermometer, a condenser, a dropping funnel, and a magnetic stirring bar. The flask was then maintained at 0 °C, while 1.0 g Ac dissolved in 20 ml dry dichloromethane CH2Cl2 then added with a dropping funnel for 30 min. The reaction mixture was stirred at 25 °C for 24 h. Evaporation removed CH2Cl2, and the crude product was finally purified by silica gel chromatography usingCHCl3/ethanol (30/1) as an eluent for Ac-Flu. The chromatography furnished about 2.1g of an orange-colored solid that could be dissolved in CH2Cl2, acetone, methanol, DMF, and other organic solvents and filtered. Acryloyl fluoresceine (Ac-Flu) 80 ml of methanol and 2.4 ml of hydrazine drop wise at 79 °C for 24h and pour it in a big amount of THF and evaporated by rotary evaporation and recrystallization three times in hexane. IR (KBr), υ (cm-1):1335–1250 (s) (C–N),910–665 (s,b)(N–H),1760–1665 (s) (C=O),1600–1585 (m) ,(C–C)stretch (in-ring) aromatics.1H-NMR , FTIR (KBr), v/cm-1: 1680 (C=O), 1170 (C-N), 3413, 3285 (N-H), 1600,1503, 1452 (Ar-H); 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 9.83 (s, 1 H,OH), 7.78 (d, J=6.3 Hz, 1 H, Ar-H), 7.50 (s, 2 H, Ar-H), 6.99 (d,J=6.4 Hz, 1 H, Ar-H), 6.59 (d, J=2.3 Hz, 2 H, Ar-H), 6.46 (m,J=7.5 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 6.41 (d, J=7.6 Hz, 2 H, Ar-H), 6.39 (m, J=7.5 Hz, 1 H, CH), 4.39 (s, 2 H, NH2).5 (m), (C–C) stretch (in-ring) aromatics.
Acryloyl chloride fluoresceine hydrazide (Ac-FH) 0.01 g (0.01 mmol) was dissolved in 5ml THF stirred until dissolved and heated to 40-45 °C and 0.07 g of hybrid OV-POSS-Amine-CC dissolved in 15ml THF and added dropwise for 5 h at room temp. Sodium carbonate sol 10% was added to neutralize HCL evolved during the reaction. Finally, the content was poured into crushed ice the solid separated was filter washed with dried and recrystallized from ethanol to give our last system, processes according to the published method[5]. IR (KBr),υ (cm-1): 3000- 3500 (NH),1465(C-N), 870(C-Cl). H-NMR (400 MHz, D2O) δ 12.28 – 11.86 (m), 11.86 – 11.65 (m), 11.65 – 11.30 (m), 8.42 – 7.89 (m), 7.67 – 6.64 (m), 5.20 – 4.99 (m), 4.46 – 3.97 (m), 5.96 – 0.58 (m), 5.20 – 0.58 (m), 3.78 – 0.08 (m), 0.08 –3.84 (m) [1].
L929 cells were cultured in Dulbecco’s adjusted eagle medium (DMEM) with 10% (v/v) fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 100 IU mL-1 penicillin-streptomycin under a humidified atmosphere (5 % CO2, 95 % air) at 37 °C. After the cells were seeded in 12-well plates one day, they were incubated with 10.0 μM OV-POSS-Amine-CC-Ac-FH for 0.5 h, washed with 10% PBS three times to remove the remaining OV-POSS-Amine-CC-Ac-FH. After being incubated with 10.0 μM Cu2+ for 0.5 h and washed three times with PBS, the imaging of resultant cells was recorded under inverted fluorescence microscopy.
The FE-SEM images shown in Figure 1 are typical surface morphologies of OV-POSS-A (a), OV-POSS-A-CC (b), F-H (c) and hybrid OV-POSS-A-CC-FH (d). In the morphology of hybrid OV-POSS-A, few porous surface shapes were observed, the morphology of the hybrid OV-POSS-A-CC shows stacked lamellar structure, while, the morphology of FH shows flower-like structures, and the morphology of hybrid OV-POSS-A-CC-FH shows particles anchoring on the material forming homogenously. So that, OV-POSS treatment improved the interfacial strength and the interfacial compatibility of the system. This might be referred to the lubricating effects of OV-POSS particles, which made the molecular movement of the structure easier. It was detected that the dispersed phase particle size was reduced in the presence of OV-POSS. In the thin film OV-POSS-A-CC-FH, good compatibility was achieved in this morphology and also the propagated amines groups made it very soluble in water.
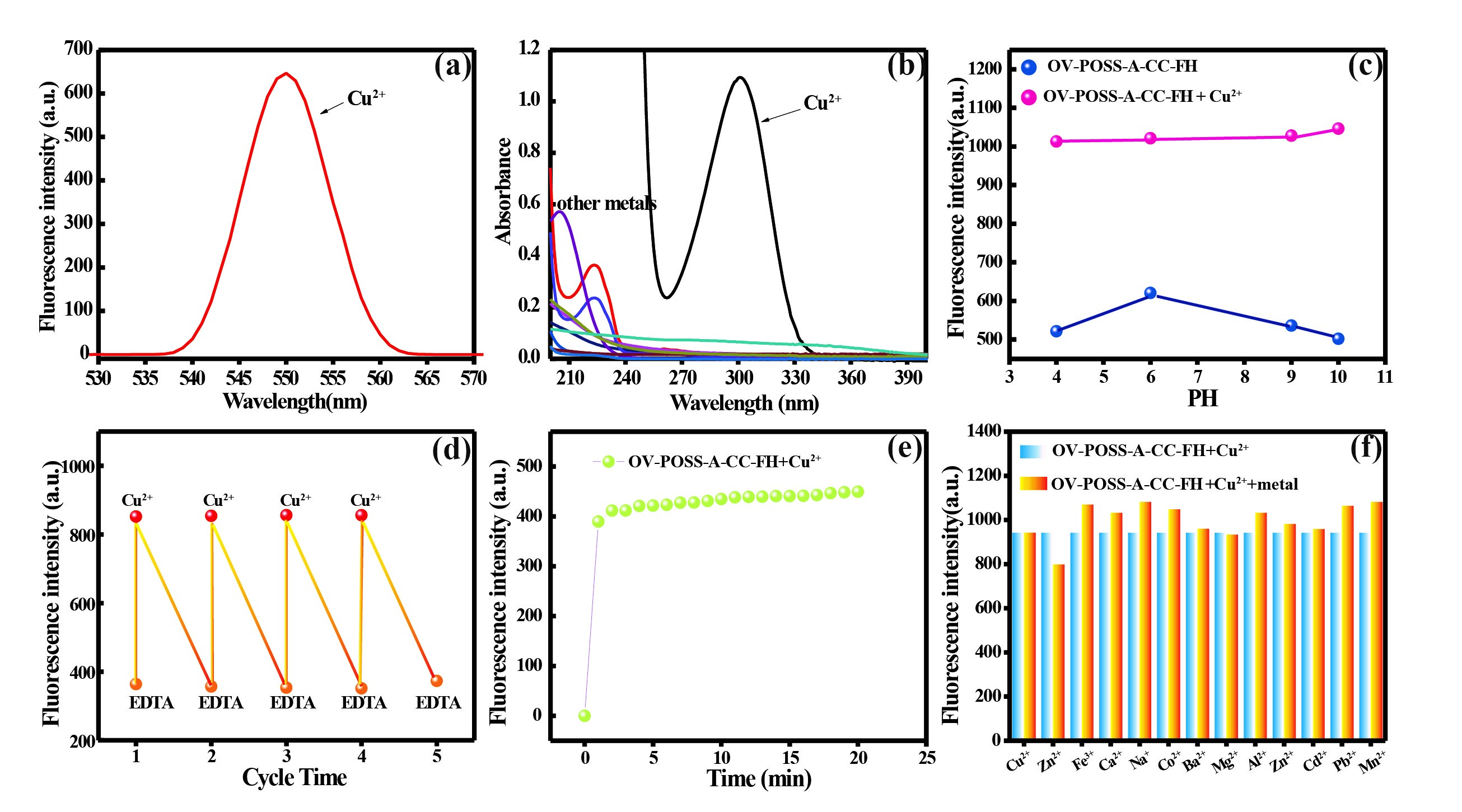
It is very important for a good chemical sensor to have high selectivity. Thus, selectivity investigations were carried out. When Cu2+ was added into hybrid OV-POSS-A-CC-FH solution (10-5 M) strong fluorescence with peak wavelength at 551 nm was shown, hinting that significant response of hybrid OV-POSS-A-CC-FH for Cu2+. No significant change of the fluorescence spectrum was observed in the presence of other metal ions, i.e., Al3+,Co2+, Ba2+, Fe3+, Mn2+, Mg2+, Na+, cd2+, Zn2+, Ca2+, pb2+ and hybrid OV-POSS-A-CC-FH as shown in Figure 2a. The increase of absorbance intensity is may be attributed to the formation of the complex between hybrid OV-POSS-A-CC-FH and Cu2+ as shown in Figure 4a. Figure 2b exhibits UV-vis absorption spectra of the binding behavior of OV-POSS-A-CC-FH towards different metal ions, such as Cu2+, Fe3+, Al3+,Co2+, Ba2+, Mn2+, Mg2+, Na+, cd2+, Zn2+, Ca2+ and pb2+. It can be seen from Figure 2b that other ions except Cu2+ have not any obvious absorption band change. When the addition of 1eq. Cu2+ into the solution immediately resulted in a significant absorbance enhancement at about 300 nm as well as a change in the color of the solution from colorless to green, implying that the hybrid OV-POSS-A-CC-FH can serve as a visual or ‘naked eye’’ detection of Cu2+.
The effect of pH 4.0~10.0 on the fluorescence intensity of hybrid OV-POSS-A-CC-FH at 551 nm was investigated in the absence and presence of Cu2+. According to the investigation between pH 4.0~10.0 emission plot shown in Figure 2c, the fluorescence intensity in different PH value on OV-POSS-A-CC-FH-Cu2+ complex don’t change, there is the only slight effect on the probe itself as shown in Figure 2c, indicating that our system is better chemosensor for Cu2+ in a large span of pH, that is, OV-POSS-A-CC-FH as a chemosensor for Cu2+ possesses high environmental suitability.
To check the reusability of hybrid OV-POSS-A-CC-FH to sense Cu2+ the fluorescent intensity of our system was recorded with the addition of 1.0 Equiv. ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) repeatedly in water as shown in Figure 2d. After adding 1.0 Equiv, the reversibility nature of hybrid OV-POSS-A-CC-FH toward Cu2+ was examined by the addition of EDTA. The fluorescence intensity of the system could be regulated reversibly by the alternation of Cu2+ and EDTA, which could be attributed to the complexation-dissociation reaction between Cu2+ and EDTA. Such a reversible fluorescence behavior of hybrid OV-POSS-A-CC-FH could be repeated up to 4 cycles while retaining the same level of efficiency. Therefore, our system can be reversibly used and recovered with EDTA as a recovering reagent. The response rate and stability of the present OV-POSS-A-CC-FH to Cu2+ at different times after the addition of 1.0 Equiv. Cu2+ was investigated as shown in Figure 2e. The fluorescent intensity increased and kept unchangeable from 0 to 20 min after adding Cu2+, suggesting that the present OV-POSS-A-CC-FH to sense Cu2+ was quick and stable. For an excellent chemosensor, high selectivity is a matter of necessity. The selectivity for sensing Cu2+ was further illustrated by checking the fluorescent intensity at 551 nm. To confirm the selectivity of sensor hybrid OV-POSS-A-CC-FH, the competition experiments were also measured by addition of one equivalent of other metal ions, such as Cu2+, Fe3+, Al3+,Co2+, Ba2+, Mn2+, Mg2+, Na+, cd2+, Zn2+, Ca2+, pb2+ respectively to the water solution of OV-POSS-A-CC-FH in the presence of one Equivalent Cu2+. As shown in Figure 2f, it is easy to find that there were no obvious changes. All the coexistent metal ions had no obvious interference with the detection of Cu2+. These results indicated that the sensor of our system displayed an excellent selectivity toward Cu2+.
To obtain more insight into the fluorescent properties of the OV-POSS-A-CC-FH towards Cu2+ was investigated as shown in Figure 3a. when Cu2+ was added with increasing concentrations of Cu2+, the fluorescence intensity of sensor hybrid OV-POSS-A-CC-FH at 551 nm was gradually increased. And there was good linearity between the fluorescence intensity at 551 nm indicating that sensor OV-POSS-A-CC-FH could detect Cu2+ ion quantitatively in Figure 3b, a linear relationship between F/F0 and Cu2+ concentration was between 0~3 nm with R2 = 0.98. The obtained regression equation, y= 0.76+1.57x, indicates good linearity and was further used as a calibration curve in the quantitative determination of Cu2+ from environmental samples. As shown in Figure 3c, with increasing concentrations of Cu2+, the absorbance intensity of the sensor at 551 nm was gradually increased. And it showed in Figure 3d that there was good linearity between the absorbance intensity indicating that the sensor of OV-POSS-A-CC-FH could detect Cu2+ ion quantitatively. A linear relationship between absorption and Cu2+ concentration was between 0.1~1.2 ×10–2 mol•L-1 with R2 = 0.990 with an obvious color change from colorless to bright green after adding Cu2+ as shown in Figure 3e, 3f.
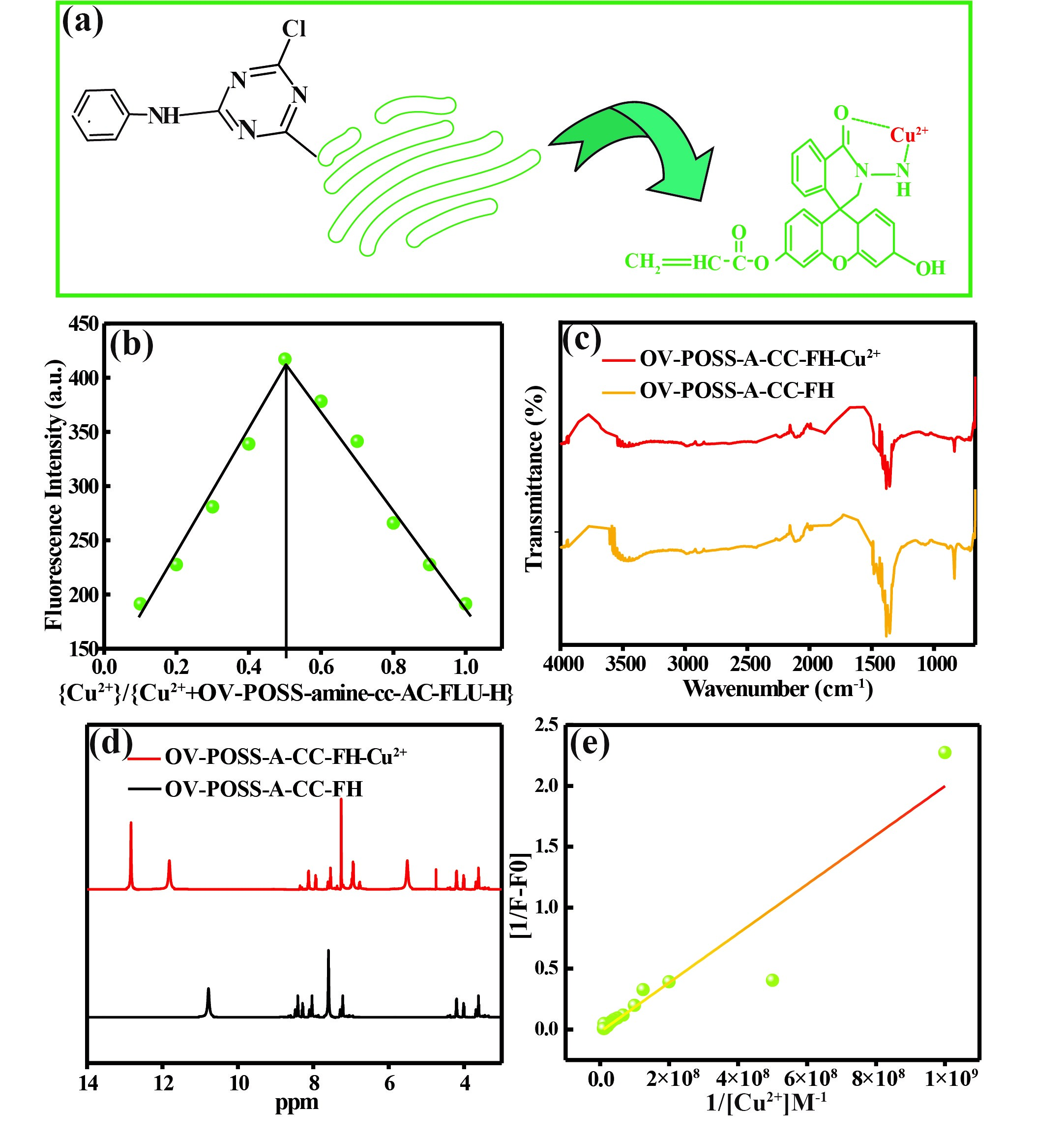
In order to determine the stoichiometry of hybrid OV-POSS-A-CC-FH-Cu2+ complex, the method of continuous variation (Job plot) was investigated as shown in Figure 4b. Sensor OV-POSS-A-CC-FH to Cu2+ formed a 1:1 complex which is in good agreement with the previous equation Figure 4a. We calculated the numbers of Cu2+ by the equation, 0.6=X/1+X were X=1, which indicated that a 1:1 complex was formed. The result indicates that a 1:1 stoichiometry is most likely due to the binding mode of hybrid OV-POSS-A-CC-FH and Cu2+. To obtain a clear understanding of the structure of the OV-POSS-A-CC-FH-Cu2+ complex, FTIR measurements were primarily employed and are depicted in Figure 4c. The peak around 3458 cm-1 belongs to the stretching vibration of (N-H), the peak 1374-1380 cm-1 for (C = O) and (C = N) was remarkably reduced in the IR spectra of OV-POSS-A-CC-FH-Cu2+, which suggested that the carbonyl group in the ring and the two N atoms in the hydrazide moiety were involved in the coordination of OV-POSS-A-CC-FH with Cu2+. Figure 4d shows H-NMR of OV-POSS-A-CC-FH and OV-POSS-A-CC-FH-Cu2+ in the D2O solution [1]. As can be seen from Figure 4d, after the addition of Cu2+, the hydroxyl peak near disappears because the OV-POSS-A-CC-FH undergoes intermolecular proton transfer. The proton of the FH shifted from 7.7 to 8.3 when reacted with Cu2+ and the OV-POSS-A-CC-FH ring is broken. The two benzene rings are fixed in the same plane under the action of the oxygen bridge so that the molecule has a rigid coplanar structure and Cu2+ is part of the OV-POSS-A-CC-FH. The oxygen in the carbonyl group is involved in coordination, the OV-POSS-A-CC-FH moiety undergoes intermolecular charge transfer, and the carbonyl oxygen becomes an oxygen negative ion. The amino peak near 5.5 was disappeared after the addition of Cu2+ and it could be speculated that Cu2+ coordinated with N in the OV-POSS-A-CC-FH amide group. Linear relationship between the reciprocal of relative fluorescence intensity [1/F-F0] and the reciprocal of Cu2+ concentrations was shown in Figure 4e with a linear slope of 2.01×10-9 and an intercept of 0.0192. The slope and intercept values were obtained based on the Benassi-Hildebrand formula below. And the Detection limits (DL) and association constant (Ka) can be also determined from the fluorescence titration curves. The detection limit (DL) of sensor hybrid OV-POSS-A-CC-FH for Cu2+ was calculated by the Sterne-Volmer plot: DL=3σ/S=0.06×10-9, where σ is the standard deviation of the blank solution, S is the slope of the calibration curve. The association constant (Ka) of hybrid OV-POSS-A-CC-FH-Cu2+ complex was calculated by the Benassi-Hildebrand: 1/(F-F0) = 1/{Ka× (Fmax-F0×[Cu2+]n}+1/(Fmax-F0), where F is the fluorescence intensity at 551 nm at any given Cu2+ concentrations, F0 is the fluorescence intensity at 551 nm in the absence of Cu2+ and Fmax is the maximum fluorescence intensity at 551 nm in the presence of Cu2+. The association constant Ka was evaluated graphically by plotting 1/ (F-F0) against 1/ [Cu2+] and the Ka value was 17×107.
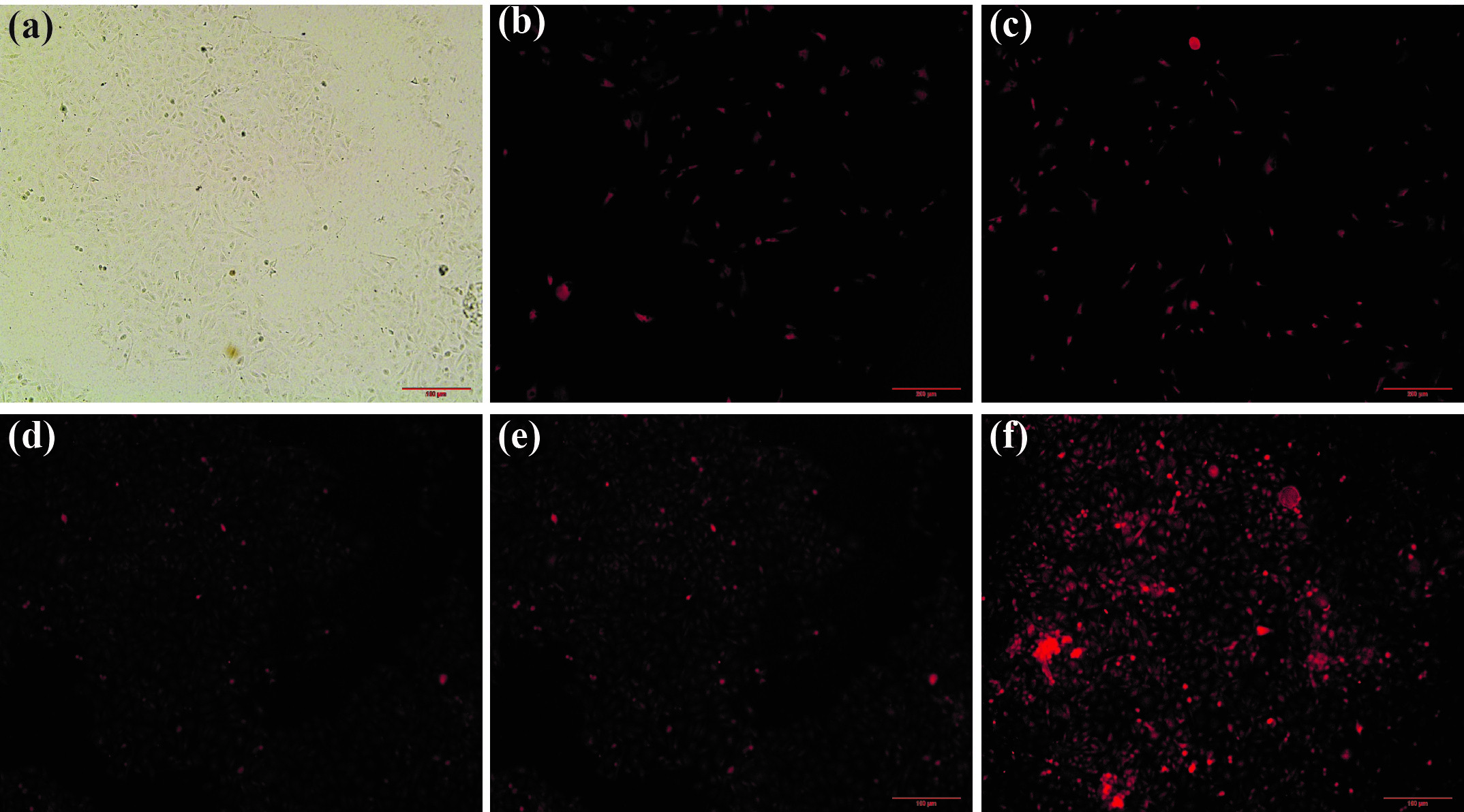
Owing to good dispersion in aqueous solution, OV-POSS-A-CC-FH is a promising material for biological applications. Con-focal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) was used to observe the cellular uptake of hybrid OV-POSS-A-CC-FH with Cu2+. As shown in Figure 5a, the fluorescent image of cells was incubated with OV-POSS-A-CC-FH for 24 h at 37 °C. Once Cu2+ was introduced into the solution, in Figure 5b, 5c,5d, 5e, 5f, the fluorescence intensity was improved and became visible for cells. Moreover, the fluorescence intensity became gradually stronger with increasing Cu2+ concentration. The results revealed that hybrid OV-POSS-A-CC-FH could diffuse into the cell as a fluorescent chemical-sensor for quantitatively monitoring of the Cu2+ in living biological samples.
We highlight the recent progress towards the development of a system for bioimaging. an aqueous multifunctional nanohybrid probe with ultraviolet to near-infrared absorption was designed and prepared with good compatibility, and brightness floridness image. The nanohybrid probe was used in the detection of Cu2+ in aqueous solution over a wide range of tests and displayed excellent colorimetric and fluorescent response to Cu2+ that can be conveniently detected even by the naked eye. That is, it showed a clear color change from colorless to green for Cu2+. Moreover, it was also applied in cell imaging with good cell permeability.
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 21671037and 21771036). This work was supported by the open fund of Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory for Soft Functional Materials Research (Xiamen University).

.JPG)
.JPG)
.JPG)
.JPG)
.JPG)
.JPG)
.JPG)