Serum Creatine Kinase: A Predictive Biomarker for Diagnosis of Acute Compartment Syndrome in the Paediatric Population
Background and Aim: Acute Compartment Syndrome (CS) of the limb is difficult to diagnose in the paediatric age group due to their tolerance of absolute CP with no clinical sequelae. This study was aimed to analyse Serum Creatine Kinase (SCK) level in patients with clinical CS in the paediatric population and to correlate its serum levels with CP and with indications of fasciotomy in the paediatric population in the emergency room.
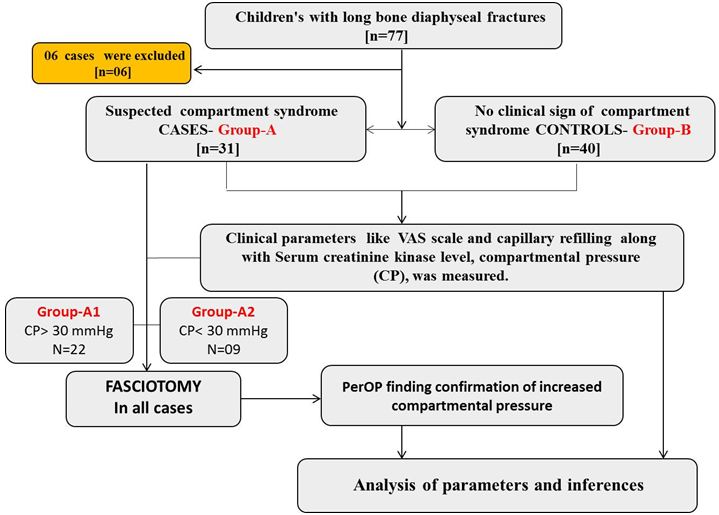
Materials and Method: In this prospective case-control study, total cases (Group-A; n=31) and controls (Group-B; n=40) with diaphyseal simple fractures with and without clinically suspected ACS respectively, were included. In all patients, the clinical parameters (visual analogue scale and capillary refilling), compartment pressure and SCK levels were measured. Furthermore, cases (Group-A) were divided into Group-A1 (pressure >30 mmHg) and Group-A2 (pressure < 30 mmHg, considered false negative). Fasciotomy done in all cases.
Results: Demographics data between cases and controls showed non-significant differences. Fasciotomy in all cases showed per-operative sign of CS. Even in false negative cases (29.5%), SCK was elevated significantly. The CR, CP and SCK were significantly increased in cases over control. A positive correlation was found between SCK with CP as well as CR in Group-A1 and but with only capillary refilling in Group-A2.
Conclusion: SCK level may use as a potential predictive biomarker to diagnose the CS as an adjuvant to clinical diagnosis to decide the intervention.
Keywords: Serum Creatinine Kinase; Acute Compartment Syndrome; Compartment Pressure
Compartment syndrome (CS) is one of the true orthopaedic emergencies, especially in paediatric patients. The reason of difficulty in identifying the high-risk suspected of CS paediatric patient are multifactorial and can affect the treatment prognosis. A physician’s inability to communicate with young children can interfere with diagnosing CS in a timely fashion. As in most of the medical centres, the surgeons are often involved in caring different patients, however, they should be aware of the aspects of CS that are unique to children and should be able to identify patients who are at risk and would benefit from close monitoring. In consequences of late diagnosis, early diagnosis is important from a medicolegal standpoint [1,2]. The difference in fasciotomy thresholds has yet to be demonstrated in the literature; however, Mars and Hadley found that children showed a tolerance of absolute pressures of 30 mm Hg with no clinical sequelae, as long as they were not within 30 mm Hg of the mean arterial pressure. Therefore, is not necessary to monitor Compartmental Pressure (CP) in every child who may be at risk for ACS. Given the prevalence of CS following extremity fracture, the difficulty in timely diagnosis, and the ramifications of a delay in diagnosis, a precise, reliable, and non-invasive means for early diagnosis is needed [3]. Time to decompressive fasciotomy is a crucial factor in any case of adult CS and is especially important in paediatric CS. Basic science research has shown that ischemia begins as soon as 4 hours after elevated intracompartmental pressure (ICP) and that 8 hours of elevated pressures can induce irreversible tissue necrosis. As per Flynn, et al. (2011) measuring four compartments at the bedside of an awake, the young injured child may be difficult or even impossible [4].
Creatine kinase (CK) also known as creatine phosphokinase (CPK) or phospho-creatine kinase, is an enzyme expressed by various tissues and cell types. Although elevated serum CK titer is known to be associated with muscle injury, it is unknown if there is a threshold level highly associated with CS. This study was aimed to analyse the SCK level in patients with clinical CS in the paediatric population and to correlate its serum levels with CP and with indications of fasciotomy in the paediatric population in the emergency room.
After institutional ethical approval and patient’s informed consent, in this prospective case-control study total cases (n=31) and controls (n=40) were enrolled. The whole of the study was carried out at an institutional trauma centre in between January 2011 to August 2016.
Including criteria were following: case (Group-A): Patients with a long bone diaphyseal fracture of age 6-16 yrs with clinically suspected acute CS of both sexes; controls (Group-B): Patients with a long bone diaphysial fracture of age 6-16 yrs without clinically suspected acute compartment syndrome of both sexes. However, patients with congenital heart disease, Rhabdomyolysis, Muscular dystrophy, Autoimmune disease, Pathological fracture, Acute kidney injury and known neurological cases, Immuno-compromised and non-willing patients were exclusion criteria of the study. In this study duration, total 06 patients were excluded from the study.
In all patients, the clinical parameters (VAS and CR), CS (measured using 18 gauge needle, a sterile pipe, and sphygmomanometer) and SCK levels (ELISA kit-Abcam-ab185988) were measured as per standard protocol. The CR time was measured by pressing on the nail of affected limb for five seconds with a finger or thumb, and noting the time needed for the color to return once the pressure is released. The patients’ basic demographics, diagnosis, treatment, and complications were also noted.
Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism for Windows program (7.0 version). The continuous variables were evaluated by a mean (± standard deviation) or range value when required. For Categorical data, Chi-square or Fisher test was used. However, for comparison of the means between the two groups, analysis by Student’s t-test with 95% confidence interval, Mann–Whitney U-test, and the Pearson correlation coefficient was used. A p < 0.05 or 0.001 was regarded as significant.
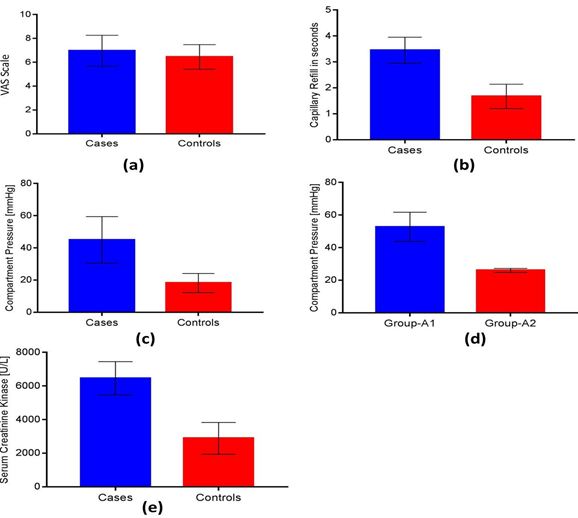
All the demographic data between case (n=31) and control (n=40) showing non-significant differences (Table 1). Fasciotomy in all cases (n=31) showed per-operative sign of CS. When decompression is done: Muscle bulge out with pressure, Muscle colour improve along with capillary refilling (CR) improvement (Table 1) (Figure 1).
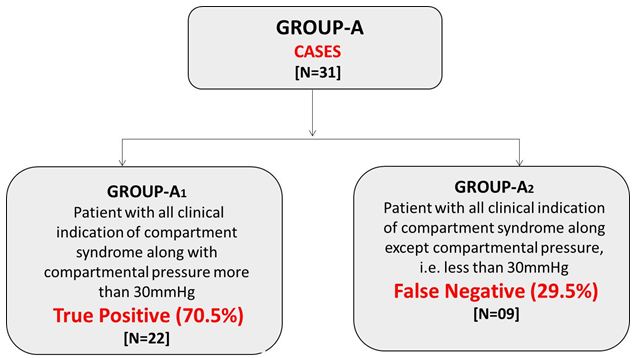
Even in false negative cases (29.5%) having all clinical indication of CS along except CP, SCK showed elevated level, i.e., 7310.66±775.44. VAS scale in cases (Group-A) and controls (Group-B) was 6.96±1.30 and 6.45±1.03 respectively, showing the statistically insignificant difference. The CR in cases (Group-A) and controls (Group-B) was 3.45±0.50 and 1.67±0.47 respectively, showing the statistically significant difference (<0.0001). The CP between cases (Group-A) and controls (Group-B) was 44.96±14.45 and 18.17 ±5.92 respectively, showing the statistically significant difference (<0.0001). Furthermore, cases (Group-A) patient with all clinical indication of CS along with CP were divided into Group-A1 (more than 30 mmHg) and Group-A2 (less than 30 mmHg) (Figure 1 and 2).
The CP within cases between Group-A1 and Group- A2 was 52.72±8.98 and 26 ±1.22 respectively, showing the statistically significant difference (<0.0001) (Figure 3) (Table 2).
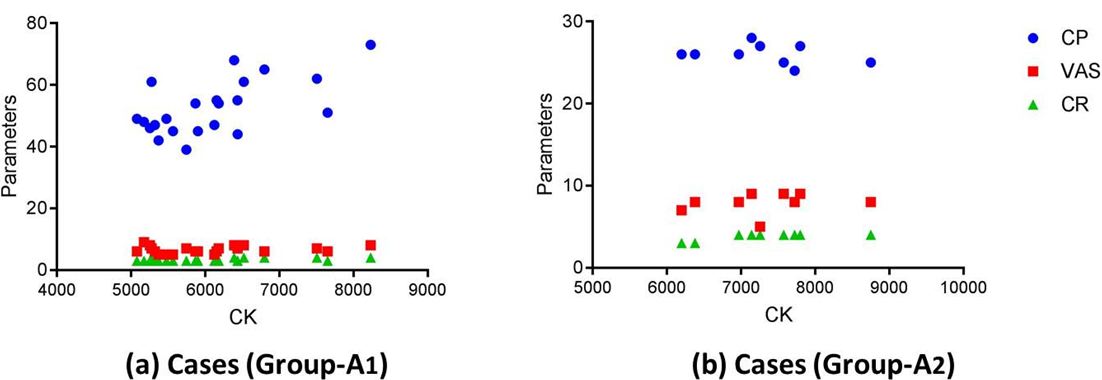
The SCK between cases (Group-A) and controls (Group-B) was 6043.04±681.30 and 3589.88±323.16 respectively, showing the statistically significant difference (<0.0001). A positive correlation was found between SCK levels with CP and CR in Case-A1 and only with CR in Case-A2 (Figure 4) (Table 3).
The CS of the limb is difficult to diagnose especially in the paediatric age group and represents a surgical emergency. Significant muscle damage can occur with CP >30 to 40 mmHg or within 10 to 30 mmHg of diastolic BP and is considered as a strong indicator for fasciotomy [5,6]. Accurate measurement of CP is user dependent and there is no consensus on values to define CS. So, due to difficulty in diagnosis within time and ramifications of a delay in diagnosis, a precise and reliable means for early diagnosis is needed.
The reasons for delayed diagnosis of CS in this younger population are multi-factorial. Paediatric CS is different from Adult. Children experience higher normal resting pressures than do the adults (13.3 to 16.6 mm Hg and 5.2 to 9.7 mm Hg, respectively) [5,6]. They are often non-verbal, easily irritable (apprehensive, crying), and too young to cooperate. Pain is non-specific and an assessment of compartment firmness (or pressure) by manual palpation, which is only 54% sensitive and having lack of objectivity.
Many young patients in hospitals are admitted to pediatric floors where routine orthopaedic care is not the norm and staffs are unfamiliar with the signs and symptoms of evolving CS in the paediatric age group.
In the present study, we hypothesised that as the severe muscle breakdown causes a significant SCK elevation, so significant elevated level of SCK may be found in Acute CS which might be directly proportional to the CP. In the present study, we observed a significant difference in cases in CR, CP and serum CK as compare to controls. However, in about 30% of cases, the CP showed less than 30 mmHg (False Negative). Our observation shows approximately 10 fold rise in serum CK levels in cases. In cases, CR correlates with serum CK level and the serum CK and CR found to be significantly correlated with fasciotomy findings. Therefore, our finding concluded that the serum CK level may use as a potential predictive biomarker to diagnose the CS as an adjuvant to clinical diagnosis to decide the intervention.
In reference to our study observations, the finding of elevated SCK with CS is plausible. The SCK is stored in muscle cells and the cellular ischemia ensues when compartment pressure exceeds capillary pressure. Although ischemia would be expected to generate cellular debris, including the liberation of SCK from cells. As the extremities have the large muscle mass, it is likely possible to mark the sudden rise in SCK as one of the early diagnostic/prognostic biomarker for CS.
As per our study observations, some other studies such as Lampert, et al. (1995), who report two cases of compartment syndrome of the lower leg [7]. During sedation and mechanical ventilation SCK activity of more than 8,000 U/l was found in both patients. After extubation, clinical symptoms of the compartment syndrome were found. In another retrospective study, Ihedioha et al. (2005) in patients with compartment syndrome [8]. Their observations suggested that although raised SCK levels are not diagnostic, they are a useful adjunct in making a diagnosis. Therefore, SCK estimation should be done in patients with suspected compartment syndrome. Moreover, an early fasciotomy (<12 hours) has a significantly lowering the elevated CK levels, confirming the view that the earlier the decompression, the lesser the muscle damage. Liu, et al. (2009) in a study observed 20 times more elevated SCK level at two hours after injury than in normal patients [9]. Twenty-four hours later, SCK reached its maximum of about 42 times more than the normal. After one week, the value SCK recovered to a normal level. However, the pathological changes of muscle were irreversible. They concluded that an alteration in SCK level can reflect the progression of disease objectively. If it increased sharply, the chance of compartment syndrome was high. Therefore continuous monitoring the dynamicity of SCK after injury can provide an assistant for early diagnosis of compartment syndrome and evaluating the there pathogenetic condition. In the latest study by Valdez, et al. (2013), out of 97 patients with isolated tibia/fibula fracture, 39 had CS [3]. They observed in a univariate and also in the multivariate model, SCK level greater than 4,000 U/L is highly associated with CS.
Based on the above review of the literature, this report is the first to find a correlation between SCK with CP and CR. Our study observations relied on above-described studies concluding that the SCK level may use as a potential predictive biomarker to diagnose the CS. Despite our potentially promising findings, limitations of the study due to single-centric study and small sample size must be acknowledged that limits the generalizability of the findings.
The CS of the limb is difficult to diagnose especially in paediatric age group due to multifactorial reasons and represents a surgical emergency. Also, the accurate measurement of CP is user dependent and there is no consensus on values to define CS. So, due to difficulty in diagnosis within time and ramifications of a delay in diagnosis, a precise and reliable means for early diagnosis is needed. Although elevated SCK titer is known to be associated with muscle injury, it is unknown if there is a threshold level highly associated with CS. In this study, we concluded that SCK level may use as a potential predictive biomarker to diagnose the CS as an adjuvant to clinical diagnosis to decide the intervention.
The authors have no conflict of interests in this article.
This study was supported by Department of Orthopedics Surgery with collaboration with the Department of Biochemistry, King George’s Medical University, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India.