Side Effects of Phenytoin in the Oral Cavity: A Review
The purpose of this article is to share with professionals in dentistry and related personnel in health area, the oral findings in epileptic patients under treatment of phenytoin. Epilepsy contributes to the ingestion of phenytoin, which is the oldest non-sedative antiepileptic; It was put on sale in 1938, after a systematic evaluation of compounds such as phenobarbital. We know the merits of the drug, the benefits of the patient and the promotion in the health institution in Venezuela to improve the life of the epileptic. In most specialized literature the long-term use of phenytoin causes gingival hyperplasia which is the only side effect but at the moment its pathogenesis is not accurately known and its etiology is unknown causing pain when chewing, speech disorder, gingival hemorrhage, periodontal abnormalities, dental malocclusion, and cosmetic damage.
Keywords: Anticonvulsants; Phenytoin; Side effects; Gingival hyperplasia
Epileptic patients tend to present a host of different types of crises that can change as the disease evolves, so the oral cavity has several alterations either by the use of certain antiepileptic drugs or by the frequency of seizures in more advanced stages; Therefore, dentists should be familiar with the antiepileptic drugs used in their treatment and the side effects they produce in the oral cavity. Antiepileptics are a group of substances of different chemical structure and various mechanisms of action, capable of reducing or inhibiting a current crisis or preventing the advent of others. It is called anticonvulsants for its ability to prevent seizures, however because not all forms of epilepsy are clinically manifested with convulsions, this term is less adequate and the antiepileptic outcome is clearer. Discovered in 1908 and applied up to 1938 Phenytoin is currently one of the most useful antiepileptic drugs in the clinic, providing beneficial effects in patients. Respect for the undesirable toxic effects of the drug and that interest this study, correspond to the oral manifestation of gingival hyperplasia, the only oral alteration associated with the consumption of phenytoin and cited in the specialized literature.
John h. Jackson defined epilepsy as "a sudden, rapid, and excessive discharge of brain cells." Epilepsy has its origin in brief and sudden changes in the functioning of the brain. For this reason, it is a neurological condition, caused by an excessive and temporal neural discharge. There are involuntary movements, psychic and sensory disorders or of the consciousness and disturbances of the autonomous nervous system (quoted by Browne, T., Holmes, G. in 2008) [1].
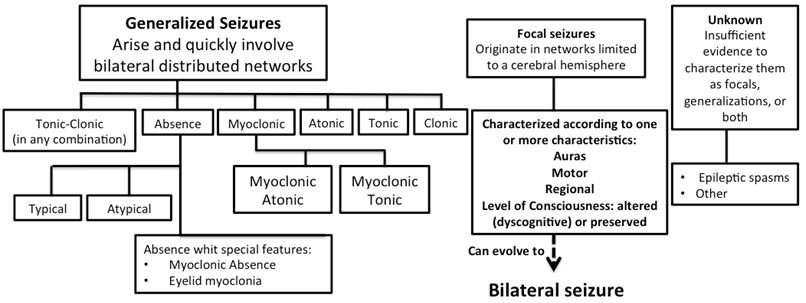
Anticonvulsant drugs are intended for the treatment of epilepsy, a disease with a high risk of invalidity. The medicinal products used belong to different pharmacological groups (Figure 1) (Table 1).
clinical form are rigorously contraindicated in another. It is important to note that treatment is rigorously twin [2].
Anticonvulsants include: Phenytoin also called Diphenylhydantoin (4) is a common-use antiepileptic. It is an FDA-approved compound in 1953 for use in seizures. Heinrich Biltz synthesized phenytoin for the first time in 1908. Biltz sold his discovery to Parke-Davis, who did not find an immediate use for her. In 1938, scientists H. Houston Merrit and Tracy Putnam discovered their usefulness in controlling convulsive states without the sedative effects that accompany phenobarbital.
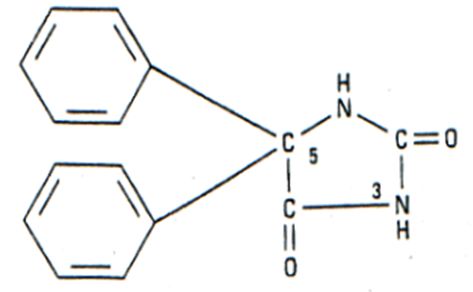
According to the pharmacological basis of the therapeutics, Goodman and Gilman, in contrast to the casual discovery of the anticonvulsant qualities of bromides and phenobarbital, Phenytoin was the result of a research planned in search of new Substances capable of suppressing seizures caused by electroshock in Laboratorio animals [4] (Figure 2).
Phenytoin has the following structural formula (Figure 2):
In adults the dosage is 4-7mg/kg divided into two daily shots. A single daily dose is sufficient in cases of easy control, especially in monotherapy. In refractory cases two or three daily shots are advised. In children the doses are somewhat higher, while in the elderly it is advisable to start with doses of 2-mg/kg (Table 2). Doses of load may be used intravenously or orally. The use of phenytoin serum concentrations is clinically useful. The accepted therapeutic range is 10-20/mL [5].
It is dispensed in capsules of 30 and 100 mg for oral use, and in the form of sterile solution of 50 mg/ml, with a special solvent, for parenteral use. Phenytoin preparations include 50 mg tablets and suspension for oral use, which poses 125 for 5 milliliters.
The absorption of phenytoin after ingestion is slow, sometimes variable and occasionally imcomplete [4]. Particle size and pharmaceutical additives affect both the velocity and the degree of absorption. The absorption of phenytoin sodium from the gastrointestinal tract is almost complete in most patients, although the time required to achieve its maximum effect oscillates from 3 to 12 hours and depends on multiple factors, these fluctuations are reduced during Chronic Drug Administration, common to the 7-10 afterdeposit [6]. The absorption is unpredictable after intramuscular administration as some of the drug is precipitated in the muscle; this route of administration is not recommended for phenytoin. On the contrary, fosphenytoin, a phosphate-soluble precursor of phenytoin, is absorbed well after intramuscular administration [7]. Phenytoin has a high fixation on plasma proteins. It is apparently true that the total plasma concentration decreases when the percentage that is fixed is reduced, as in uremia or hypoalbuminemia; However, the correlation of free concentrations with the clinical states remains uncertain. The values of the drug in the cerebrospinal fluid are proportional to the free plasma concentration. Phenytoin accumulates in the brain, liver, muscle and adipose tissue, where it is fixed to the endoplasmic reticulum of the cells [8].
Phenytoin is metabolized in main mode by means of the parahydroxylation at 5-(P-hydroxyphenyl)-5-phenyl hydantoin (HPPH), which is later conjugated to glucuronic acid. Metabolites are clinically inactive and are excreted in the urine. Only a very small portion of phenytoin is excreted without change; The elimination of phenytoin depends on the dosage. The half-life of phenytoin varies from 12 to 36 hours, averaging 24 hours for most individuals who are within the low to medium therapeutic interval. Much longer average lives are observed in higher concentrations. With low blood concentrations, it takes 5 to 7 days to achieve blood values in equilibrium after each dose change; In higher concentrations it may take 4 to 6 weeks before the blood figures are stabilized [7].
Phenytoin (Defenilhidantoína) is a primary drug for all kinds of epilepsy, except for the small Mal. It has been studied more widely in the laboratory and clinic than any other Antiepiléptico 4. Anticonvulsant drugs raise the threshold of seizures and/or reduce discharge intensity. Phenytoin produces anticonvulsant activity without depressing the central nervous system (CNS). Reduces repeated discharges induced by sustained depolarization [3]. It obtains it by altering the conductance of sodium, potassium and calcium, the membrane potentials and the concentrations of certain amino acids and the neurotransmitters acetylcholine and gamma-aminobutítico acid (GABA) [8]. This medication does not elevate the convulsive threshold produced by the convulsive agents; If it does not restore the pathological increase, it limits the development of the maximum convulsive activity and reduces the diffusion of the Epileptógeno focus [9].
At elevated concentrations, phenytoin also inhibits the release of serotonin and noradrenaline, promotes dopamine reuptake, and inhibits the activity of the monoamine oxidase enzyme [8]. The therapeutic plasma levels of phenytoin for most patients is between 10 and 20 micrograms/mL. Phenytoin exerts its anticonvulsant effects with fewer sedative effects than phenobarbital.
Epileptic patients often stay with anticonvulsant drugs to suppress crises. The literature published in various articles of Internet was systematically reviewed the effects of antiepileptic drugs on oral health; Although it is true, there are effective first-choice antiepileptic drugs in the control of widely used seizures, but that in the long term cause oral repercussions. The most common side effect caused by antiepileptic drugs is gingival hyperplasia is common in patients who use phenytoin chronically. The lesion constitutes an uncontrolled growth of connective tissue that does not modify the number of cells and fibers and is reversed after the drug has been interrupted.
Gingival hyperplasia caused by these drugs produces local damage, inflammation and alteration of growth factors and cytokines that cause increased synthesis of procollagen as well as other components of the cell matrix [10].
Gingival enlargement was first described by Kimball in 1939, associated with chronic administration of a drug for the treatment of epilepsy, phenytoin [11]. Since then, gingival enlargement has been reported in association with the ingestion of various drugs [12].
gingival enlargement is considered a multifactorial alteration in whose development can influence the age of the patient, the genetic predisposition, the administered doses, the duration of treatment, the plasmatic levels reached, the plaque Bacterial and previous existence of gingival or periodontal involvement [13].
The gingival enlargements represent an exaggerated increase in volume, in response to a variety of local and systematic conditions, generally manifesting at the level of the interdental papillae and not extending beyond the Mucogingival union [14].
Gingival hyperplasia is related to concentrations of phenytoin in gingival tissues (stimuli of fibroblasts, phenomenon observable only in the presence of teeth, initiating in the Papilla interdental) and cell barley, blocking the effect of the hormone Parathyroid, originating bone and radicular changes (Hall and Angelopoulos 1986 quoted by Goodman, G., Goodman, L. and Lich, M., Vernon, J., Greemberg, M.) [4,10].
Gingival hyperplasia by Phenytoin has an incidence between 10% and 60% of the cases [15,16]. Its emergence may occur after the first month of treatment, but it is usually not produced before the 3 months following initiation of therapy, with a tendency to affect gingival tissues around the vestibular surfaces of the teeth [17]. Previous. It is presented as small nodular formations of papillary gum (one or two papillae) and can increase rapidly in size, preventing proper oral hygiene. Microscopically, the gingiva shows a layer of stratified squamous epithelium, although most of the gum is composed of dense collagen bundles. The number of inflammatory cells is minimal (Lhermitte and Mamo quoted by the medical Journal of the General Hospital of Mexico, S.S.) [18].
Some local factors favor the accumulation of biofilm, such as defective restorations, fractured teeth, or caries lesions, these should be eliminated, and fixed or removable prostheses should be designed to minimize retention of Plaque and avoid an inflammatory process that complicate hyperplasia [19]. Due to the functional and aesthetic difficulties that cause the gingival enlargement induced by the drugs is necessary an adequate treatment for its correct elimination and to avoid recurrences, consisting usually in basic periodontal therapy:
Gingivectomy: It is a surgical procedure by which excision and suppression of the gingival tissue (gum) is performed injured or reduced a periodontal pouch, that is, the space that is formed between the gum and the tooth consequence of the long-term use of the Phenytoin or accumulation of the low bacterial plaque of the gum, which may cause resorption of the bone of support and worsening of periodontal disease.
Gingivoplasty: It is a process similar to that of gingivectomy, but it is used for a different purpose, since its purpose is to obtain adequate contour of the gingiva in absence of periodontal bags, only in order to return its architecture and normal physiology [20]. It is usually done after a gingivectomy.
In addition, a strict control of the biofilm by the patient combined with rigorous professional maintenance therapy is imperative, in case the plate control is difficult to achieve by mechanical means, such as the toothbrush or the Interproximal, the use of chlorhexidine mouthwashes should be considered. To reduce the neutralizing effect of toothpaste in chlorhexidine, there must be a minimum interval of 30 minutes between brushing and mouthwashes. Chlorhexidine is cationic and forms low-solubility salts with anions, the result is a decreased antimicrobial effect. Sodium Laurilsulfato, which is widely used as a detergent in toothpastes, is anionic [21]. Rigorous preventive regimes must be installed. The patient should be aware of the consequences of poor oral hygiene [22].
Caring for gum diseases and other oral problems is very important. These conditions may cause discomfort, but they can also contribute to systemic health problems. Infections in the mouth, for example, can enter the bloodstream, causing septicemia.
If abnormalities are detected along the gum line, the dentist may recommend follow-up visits to monitor the growth or contraction of the gums, along with the evidence to determine the cause. When gingival hyperplasia is detected in time, it may be possible to deal with less invasive techniques than in cases where the condition has been allowed to persist.
In some cases, gingival hyperplasia may be treated by changing medications or altering the patient's diet. Other cases may require surgery to remove excessive growth of the gums, which may include reconstructive surgery to repair the remaining gums. A gingivectomy, is a very simple ancient surgical technique, which completely eliminates periodontal pouches and hyperplasias with predictable esthetic results. Among its disadvantages we have limited indications, wide and painful wound, second intention scarring, risk to bone exposure, loss of keratinized gum so it must be done by specialist in this area (periodontist). You can include sending tissue samples to laboratory pathology to learn more about the cause.
However, it is important to eliminate dental biofilm effectively with meticulous oral hygiene, avoid gingival irritants such as calculus or overextension of restorations, and use mouthwashes with chlorhexidine or triclosan.
Patients with epilepsy in almost all aspects of oral health and dental status The condition is significantly more serious than in the general population (non-epileptic), in addition, patients who have poor control of epilepsy and frequent crises Generalized tonic-clonic conditions present worse oral health compared to patients who are better controlled or have only seizures that have nothing to do with the masticatory apparatus.
Treatment with phenytoin sodium produces clinical and histological alterations in the gingiva of epileptic patients and there is a direct relationship between the oral hygiene index and the degree of gingival hyperplasia. A correct oral hygiene technique is recommended and the use of adjuvants decreases periodontal problems. If hyperplasia persists, use surgical techniques such as gingivectomy to remove the excess gum and gingivoplasty to model and restore the gum architecture as the hyperplasia can generate the late rash (when it occurs in Pediatric patients), malpositions, halitosis, decalcification and a bad aesthetic.