Theory-of-Everything
This universe is the so-called “clockwork organism”. If a meta-galaxy is compared to “clock”, each “part” of which that’s composed will be each object (galaxy, star, elements, and atom). For them to be each member of an organism, they must have individuality within them. The universe is made up of being with unique characteristics (size, mass, velocity) that harmonize with each other within a single framework. The natural world is formed by such harmony principle. If it’s so, to elucidate such mechanism of harmony has to be the main purpose of physical science. The key which solves the mystery is to consider natural law by the angle as “the interaction of the substance and the energy”. If we look back to history of physics, we will find that a study has developed through the angle of the approach action. But the natural reality couldn’t be made that clearly. The methodology reached the limit already, and it didn’t seem to lead any more development by such approach. A completely new way of thinking is needed for us to get correct and deep understanding to nature at present. Therefore, I have conducted my research from a unique perspective. It was that each member of this world exerts force or energy on each other by remote action. As a result, I have succeeded in explaining all the forces and energies in the natural world with a single theory.
Keywords: The Ionization Energy; Schrodinger’s Cat; Japan Kilogram Standard; Relationship; Object Elasticity; Parties
This paper is the revise which gave correction to the article I announced in the past “Unified description of all force” (PACS Nos. 01.55. +b; 89.90. +n). That’s the more systematic universal contents as theory and is the one which guarantees the correct consistency to the experimental data. And also, I considered so that the law I found based on an original stance of “formula negativism” might be expressed by mathematics of the very simple junior high school level in it. In this paper, the statements follow one major structure. It runs through the entire paper (please see Table 1)..
Please read pleasantly
Then, I’ll enter statement.
Therefore, the try to catch four of force in unifying way has been formed out of physicists. They have built a basic answer about it through history. It was the proximity theory which is a common view of present-day physics. During shifting to the quantum theory from classical physics soon, that was developing into the way of thinking which handles a source of force by a model as an exchange of a particle. It has been thought a source of the electromagnetic force is exchange of a photon, and that a source of gravity is exchange of graviton [2]. But those aren’t observed yet, and proximity theory isn’t proved to be right. The try which unifies four kinds of force isn’t also successful yet. Hence, unless they are realized in the language of the proximity theory, they are not correct. On the other hand, discovery of such particle isn’t needed to inspect right of the remote theory. As long as we have a solid theoretical system and existing experimental data, we can adequately prove that it is correct. We have value which should convert into remote theory from proximity theory greatly in view of such point. Then, I’d like to touch about the difference between the proximity theory and the remote theory here. Proximity theory handles force by a model as “exchange force”. Therefore, a concept as reciprocation of gauge particle [3] for such exchange has to be assumed absolutely. And reciprocation needs time. Therefore, the spread of force in proximity theory involves limited speed. To begin with, since the birth of the equations of motion [4], physics has focused its research on the motion of objects. It can be said that the essence is “movement model”.
It’s suitable for such model’s describing the state from which speed and the point of view of the object change successively. So, it’s natural to handle communication of force between the objects with an action through medium with limited time. Therefore, it has been thought the medium which mediates between that has to exist for force to spread by action through medium from old days. It has been expected that force moves space with time successively while being transmitted through a medium.
However, Michelson-Morley experiment proved in 1887 that ether doesn’t exist [5].
If becoming it like this, physicists should model again once more, the mechanism that the energy (gravity and light) is transmitted without making them mediate between a medium. It is scientifically honest attitude to theorize a new picture of the force propagating at infinite speed. Without time, without the medium of either an ether or gauge particles in the space that separates objects.
So, I stood as remote theory and derived the hypothesis that the energy is “the relationship with which it’s tied between the objects” intuitively. I called that “relational theory” or “relational physics”. Though it’s a natural thing, this theory handles force and the energy based on a “relationship model”. Consider, for example, the “relationship” between a man and a woman. A “opposite sex relationship” is established immediately when a man and a woman, as “parties”, meet face-to-face on the spot. Even in a vacuum, even in space. Only a remote theory could lead to such a conclusion. In this respect, relational theory doesn’t require a medium to convey the force. But instead, it requires a new concept of “parties” that constitute the force. For example, in the gravitational force that constitutes between the earth and the moon, the earth and the moon are “the parties concerned”. In the electromagnetic force that constitutes between a metal and a magnet, the metal and the magnet are “the parties concerned”. In the romantic relationship that brings together a man and a woman, the man and the woman are “the parties concerned” that constitute it. It is the position of relational theory that without the existence of these “parties” there would be no force or energy. And in order to be called a “relationship” there must be an (invisible) bond connecting two or more “parties”. If you can see it, it’s no longer energy or force (except for visible light [6]).
Now, as mentioned earlier, there is no need for a medium in relational physics. Therefore, there is also no need for time for the force to act between objects. It means that the speed of transmission of the force is infinite. In addition, the way the position and speed of the objects change is not seen as the objects moving, but as the “relationship between the objects” changing. For example, consider the case of an apple fruit falling from a tree branch toward the ground. It is not seen as the apple’s falling motion, but rather as a change in the “three-way relationship” composed of the apple, the branch, and the earth over time. That is the basic idea of relational physics.
Indeed, the proximity theory (classical physics and quantum theory) is one of the best theories that can explain many experimental facts. However, the remote theory makes it possible to further understand the unity of forces such as gravity and electromagnetism, as well as the duality of particles and waves in light. This will lead to a deterministic prediction of the behavior of electrons in atomic structures. This will in turn promote the development of semiconductor physics and the revitalization of the industry. I believe that it is my relational theory that will lead the scientific world in the future.
Now, with this background in mind, let us further organize this theory.
I have developed a new “relational model” based on the remote theory, which defines force and energy as “relationships”. The ratio- nale for this is based on the fact that all energy (except for visible light) is invisible to the human eye. And it should be viewed as a “relationship between objects” rather than matter. In addition, when we look at the properties of light, we can find both wave and particle characteristics [7]. But we also have reason to believe that the superordinate concept that encompasses them is exactly “a relationship”.
Such a concept is the most basic and universal way of explanation that can cover all the features that appear in the results of ex- periments examining light, heat, and force. Because of its pervasiveness, it can integrate both wave and particle properties without contradiction.
The first time such duality was recognized in physics was when the double-slit experiment [8] and the photoelectric effect experi- ment [9] were found to have different characteristics. In the double-slit experiment, when light is irradiated toward a wall with two light loopholes, a stripe pattern is created on the screen behind the wall. It reminds us that light has the properties of a wave. This is because if the light grains only traveled in a straight line, the screen would only have a dark pattern with no gradient in the form of a grid of squares.
On the other hand, consider an experiment on the photoelectric effect. When high-frequency light, such as X-rays or ultraviolet light, is bombarded on metals, electrons are ejected from them.
It reminds us that light is a grain like a gun-ball. The reason for this is that the tiny particles, such as electrons, were bounced around because of the concentrated interaction at one small point. The above two different pictures of light are understood by modern physics (commonly known as “physics”) in terms of the duality of particles and waves. Because it was double experiment with dou- ble results. The reason is that since both were present, it was deemed that it had to be treated as a duality.
Such an interpretation is not necessarily wrong, but it does not fully capture the nature. Therefore, it will be necessary to extract further essences that encompass duality.
In my view, light is energy, and energy is a “relationship”. Hence, light is a “relationship”. If that is the case, then there must be “parties” to constitute light. The “parties” are the multiple relational components that hold the energy from the edges. It will be structured differently for each experiment. If the experimental method is different, the “parties” will be different, and if the “parties” are different, the “relationship” will be different.
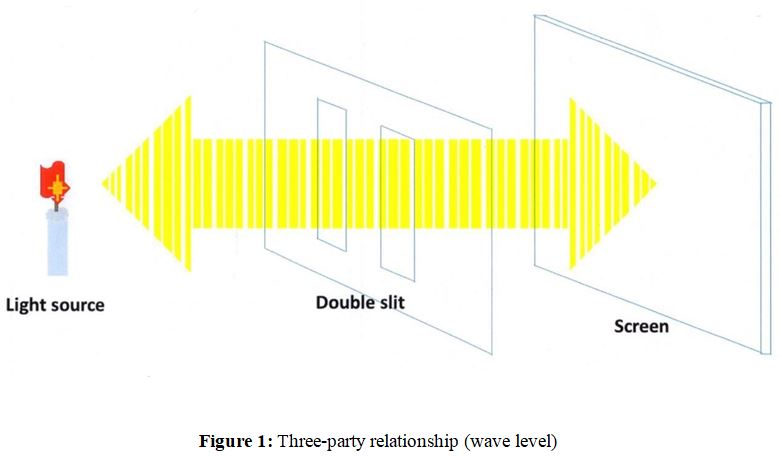
Now, let’s take a closer look at the double-slit experiment with this in mind. The “parties” there can be broadly divided into three: the light source, the slit, and the screen. In other words, a “three-party relationship” has been created there (Figure 1).
It is a thinner relationship than a “two-party relationship”. The double-slit experiment was the expression of such a “relationship” in the form of waves. The double-slit experiment made the “relationship” into a wave level. The thin relationship between the three parties has emerged as a somewhat expansive wave nature.
Let’s take a closer look at the experiment of the photoelectric effect. The two main “parties” there are the light source and the metal. In other words, a “two-party relationship” has been established (Figure 2). It is a stronger relationship than a “three-party relation- ship”.
The photoelectric effect is the manifestation of such “relationship” in a microscopic form reminiscent of particles. Experiments with the photoelectric effect have brought “relationships” to the level of particles. Because the relationship is so strong, as if it were a “red thread of fate”, the area of action is limited to the narrow range of a single electron. The strong relationship between the two parties was expressed as a particle nature.
Thus, by conducting two different experiments, the “parties” will be different, the “relationship” will be different, and the results of the experiments will be different. What modern physics is pointing out through the concept of the duality of particles and waves is about the equivalent of that difference. For example, when a man and a woman meet face to face, the “opposite sex relationship” is formed. And when a man meets a man, the “same sex relationship” is formed. Although we are the same person, our narrowly defined “relationship” differs depending on which gender we face. Thus our position be “same sex” or “opposite sex”. This is the very “duality of same sex and opposite sex”. Both positions are correct. Also, when we face our elders, we are “juniors”, and when we face our juniors, we are “seniors”. Although we are the same person, our relationship in a narrow sense differs depending on who we are facing. Thus our position becomes “senior” or “junior”. This is exactly the “duality of senior and junior”. Both positions are correct. We are both a “senior” and “junior”. As our position differs depending on the opponent, we cannot limit ourselves to one or the other. In other words, duality.
The same is true for the duality of particle and waves. Since the “parties” in each experiment are different, it is natural consequence that the “relationships” in the narrow sense are also different. As long as there are two different members in the experiment, it is natural that there will be two different “relationships”, or duality, in the narrow sense.
Therefore, if we extract the essence between the particle’s nature and the wave nature, it can be regarded as a “relationship” in a broad sense. This is because it is a broad superordinate concept that can be applied in both experiments.
Because of this, I was convinced that all forces and energies in nature could be universally explained using the model of “relation- ship”.
Now, let’s move on to a detailed discussion of it. My image of space-time is something like an animation book. It is a film booklet made up of many consecutive manuscripts. When we flip through them, the pictures on the manuscript look as if they are moving. I modeled the image of the universe by analogy from there. In this context, space refers to the individual sheets of the animation book, and time refers to their continuous change (Figure 3).
What this space-time model reveals is that “relationships” are an essential requirement for both space and time. Space is concept that consists of all the elements that make up a film and the “relationships” that connect them to each other. Time is a concept that consists of the “relationship” that connect a film to the next film. However, the requirements for establishment of spatial and temporal relationships are different. There is a difference in that the former takes no time at all to complete, while the latter takes time to complete. The difference is as follows. The former connects objects to each other in zero seconds, while the latter connects the present object to the future object over a period of time longer than zero seconds. If the current object and the future object are connected in zero seconds, then the flow of time would stop. But in reality, this is not possible. On the other hand, the relationships that connect the objects that make up a space are always established in zero seconds. It is easy to understand if you think of it as an animation book. If all manuscripts were connected to each other in zero seconds, it would not be an animation book at all. But the components of each film are connected in zero seconds.
In addition, my image of the universe is based on the model of a “clockwork organism”. In other words, each film has an organic structure. The term “organic” refers to a state in which the various elements are related to each other and influence each other. And they are harmonized in a finite order. In the case of a watch, it is composed of various parts, and each part creates autonomy by harmonizing with each other. These characteristics apply not only to the universe as a whole, but also to the global environment and the human body. In that model, the universe is defined as a “clock”, individual objects are defined as “parts”, and energy and force are defined as their “source of action”. Of course, the terms “clock” and “parts” are metaphors, but I used them to support my remote theory of the universe. In other words, I defined all the forces and energies that exist in the natural world as “relationship between objects”, like the “intertwining” of the gears inside a clock.
Therefore, the concept of “individuality” of an object is derived from this. The members of this universe are designed to be unique, or else they would not be able to interact with each other. Just as a watch has a long hand and a short hand, a large screw and a small screw, a large gear and a small gear, the individual parts that makes up this world also have a wide variety of unique faces. And again, the “relationships” that connect these unique objects are seen as force and energy.
If we compare it to Coulomb’s law [10], the electric charge corresponds to “individuality” (they are strictly different concept), and the Coulomb force corresponds to the “relationship”. This is the similarity between relational physics and Coulomb’s law. The dif- ference is as follows. Coulomb’s law (electromagnetism) assumes that repulsion acts between objects with the same sign of charge. In contrast relational physics assumes that repulsion does not exist between objects with equal individuality. The theory says that there is neither repulsion nor attraction between equivalent individuality. For example, let’s consider the example of a magnet.
Magnets have an S-pole and an N-pole. They attract each other when different poles are brought close to each other. And they repel each other when poles of the same sign are brought close to each other [11]. If we look only at such a phenomenon, it seems that the repulsion force works between poles of the same sign. However, relational physics does not take such an interpretation. It sees the “relationship” between poles with the same sign of a magnet as being “irrelevant”. The reason why it is “irrelevant” is that there is no difference in individuality between poles with the same sign of a magnet. Since this universe is a “clockwork organism”, every member within it must be unique. In other words, the composition of this world must be rich in variety. It is because of this richness of variety that forces and energies can arise in this universe. If this is the case, then the “relationship” between poles with the same sign of a magnet is not rich in variety at all, and is, so to speak, the “ultimate unrelated world”. Therefore, no force of attraction arises at all. So, how should we think about the action that looks like repulsion? At first glance, it seems as if repulsion has occurred, but the force that is manifested there is not repulsion. It is “the force brought about by the action of human hands bringing magnets closer together”, not the force inherent in magnets. The repulsion force in electromagnetism is likened to rela- tional physics, which is explained as follows. It is the phenomenon of a magnet being pushed farther away due to a human hand injecting force into the “irrelevant space” created between poles with the same sign. It’s just that it looks like repulsion. There must be a difference in individuality in order for the force to arise. If objects with the same individuality are brought close together, there will be no “relationship” (force or energy) at all. Therefore, we can conclude that there is no repulsion in nature.
Now, let’s take a closer look at relational theory.
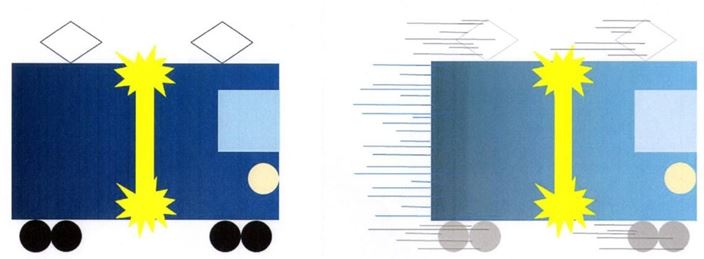
Every force and energy are a “relationship”. In order to be able to say so, there must be multiple parties that sandwich it, each party must be unique, and the speed at which they are related must be infinite. In order to convert such requirements into mathemat- ical formulas, I tried a thought experiment using light. Since light is a form of energy, it follows that light is also a “relationship”. Therefore, we can assume that its speed of travel is theoretically infinite.Please take a look at Figure 4.
If light is emitted from a light source installed in the ceiling of a train, it will reach the floor in zero seconds. And the vertical line will remain straight no matter how fast the car moves horizontally. I coined the term “light pillar formation” for this.
So, if the train in Figure 4 were to travel at 299792458 [ m・s1 ] [12], what would the light pillar look like? For that matter, two ways of seeing can be assumed (Figure 5).
When considering which of them is more appropriate (as I will explain in detail later), it is best to take the image of Ⓑ for the moment. I coined the term “optical band formation” for this.
I’d like to express that in a mathematical equation. The light pillar is the vertical length of the light band, so it can be expressed as “l ”. This is because it is a straight line made of light that connects the ceiling to the floor at infinite speed. On the other hand, how should we describe the horizontal length? We can think of an optical band as horizontal line of N light pillars.
Since it is the result of traveling at the speed of light for a certain period of time, it can be expressed as “ct /N ”. If so, then the optical band can be described as the product of the vertical length (l ) and the horizontal length (ct /N ).
In this regard, a single light pillar is composed of two parties that sandwich it from both ends. So, the value of the number of parties (n) is always equal to twice the number of light pillars. Therefore, the relationship between the two can be expressed by the following equation.
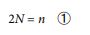
With the above discussion, the left-hand side in the equation to describe the optical band could be determined.
Now, how do we determine the right-hand side? At first glance, it may seem that it can be represented as a square with one side of equal length (i.e. “ l 2 ”). But this is not the case. This is because optical band formation is a type of formation that is always in progress and the edges are never closed. I coined the term “attempted optical band” for it. Since one of the two ends of the optical band is missing, we cannot call the members of it “both parties”. It can be said that it is in a “semi-ripe” state as an optical band. Hence, it can be expressed as “l²/2”.Therefore, the equation describing the “attempted optical band (half optical band)” is given in the following form.
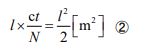
Then, substituting equation ① into equation ② and continuing the transformation, the relational equation between “c” and “n” is determined by the following process.
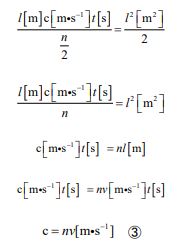
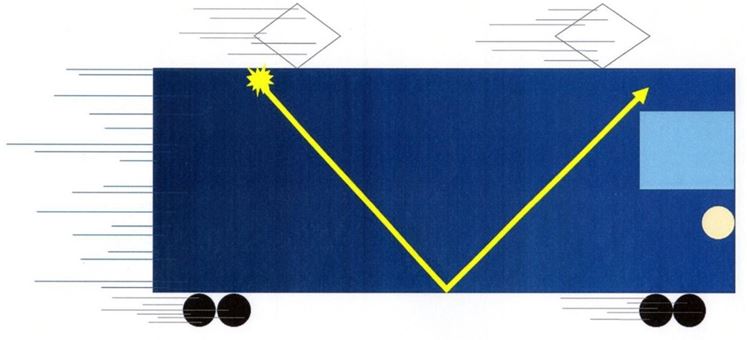
This explains why light passing through water is slower than that in a vacuum [13]. This is because the number of “n” has increased with the addition of water as a party. The same is true for Fizeau’s experiment [14]. The speed of light (c) is essentially infinite. But it has been slowed down to about 3×108[m・s-1]. This is because the value of “n” increased due to the addition of extra interaction by intervening parties such as half-mirror, gear, and reflector. The concept of “c” is a result of the artificial finite nature of speed. At first glance, it may seem to represent photons in rapid motion, but this is not the case. Rather, it appears as a single “relationship” that originally connects the light source and its destination, as they are connected at infinite speed. A particle of energy (photon) don’t move from one end to the other. We should think of it as an energy (relationship) that originally connects both ends (between the two parties) in zero seconds. If we assume that photons travel through space with time at a finite speed, then the train experi- ment can be imagined in a completely different way (Figure 6).
Comparing Figure 4 and Figure 6, you can clearly see the difference between the proximity theory and the remote theory.
Now, if we take the remote theory, we will understand the following. The gravitational force between a star and a planet and the electromagnetic force between a proton and an electron are both “relationships” that connect the two parties [15]. There is a differ- ence in velocity, size, and mass between them. In other words, there is a difference in attributes, or individuality, that can be seen. Conversely, a space filled with “relationship” will always have objects of different individuality at both ends of the space. And these objects will influence each other to create a force.
In this way, we can see “force” as an “attraction between individuality”. The degree of this is inversely proportional to the smaller the distance between the two individuality. This is because the closer the distance is, the more intense the “relationship” becomes. Therefore, if we set the distance between individuality as “l ”, both individuality multiplied together as “i²”, the force as “F ”, and the proportionality coefficient as “ka”, we have the following equation.
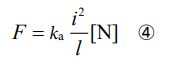
Here, we need to be clear about what “individuality” means. One thing that can be said is the following. As the number of mem- bers in a population increases, individuality decreases, and as the number of members in the population decreases, individuality increases. Also, both the planetary model and the atomic model are models in which both move in different ways. So, it is certain that the factor of speed has an effect on the amount of individuality. Therefore, intuitively, we can derive the following equation.
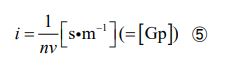
As for units, following my introduction of a new quantity called “i”, I independently invented a unit called “Gp” (named “Gala- pagos”).
Also, by substituting equation ③ into equation ⑤, we obtain the following form.
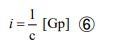
Therefore, if we transform equation ④ using equation ⑥, we can complete the equation of electromagnetic force in the following form. The proportionality coefficient “ka” has the assembly unit [N・m3・s-2], but the value is “1”.
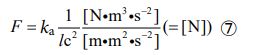
This equation is a model of the electromagnetic force equation, but at the same time it corresponds to the strong force model. The reason is that the strong force is a “relationship” between objects that is established over a very small distance. In other words, the difference between electromagnetic force and strong force is determined only by the distance between objects. Therefore, the electromagnetic force and the strong force are the same force.
Now, let’s move on to the discussion of gravity. In this regard, according to Newton’s theory of gravity, it is a force that acts between objects with mass. And its magnitude is proportional to their mass [16]. The proportionality coefficient “G” introduced in the equation is called the universal gravitational constant. Its accuracy is said to have been confirmed by Cavendish’s experiments [17] using a torsion balance. However, this raises a question. The two lead balls used in the experiment were extremely different in weight and size (the large ball weighed 159 [kg] and the small ball weighed 0.73 [kg]). According to Newton’s theory, gravity should be proportional to mass. So, if we want to exert a strong gravitational force between two lead spheres, it would be more efficient to use two equally large spheres. However, Cavendish did not so. This is because if both masses are aligned equally, the requirement for the generation of force in relational theory is not satisfied. In order for the force to arise, each of the parties that make it up must be unique. In other words, there needs to be a gap between each party in the size, mass and velocity of the object. That is why Cavendish used two lead balls of extremely different masses in his experiment. Otherwise, the space between them will become an “unrelated world”. So, no attraction will occur, just like when two poles with the same sign of a magnet are brought close to each other. Newton’s theory of gravity is a fatal logical contradiction in describing the relationship between force and mass. It is doubtful that such a thing is a faithful representation of the laws of nature.
If so, we will need to devise an entirely new equation to replace Newton’s theory of gravity, and re-model gravity accordingly.
So, I tried to derive my own theory of gravity through thought experiments (Figure 7).
First, consider the mass of the entire universe as “m”. Then, God applies a hammering force (F) to stretch it thinly into a plane consisting of a great number of parties (n). I coined the term “mass sheet formation” for this. If we set the radius of the whole universe as “l”, then the area of the universe can be expressed as “πl2”. If we derive the model based on this point, the equation is given in the following form.
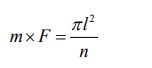
If we introduce a proportionality coefficient with the assembly unit [ N・kg・m-2 ] (the quantity symbol is “kb” and the value is “10x” ) and transform it, we obtain the following equation.
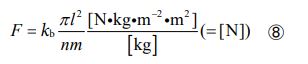
This is the new theory that correctly describes the relationship between gravity and mass (according to this equation, gravity is inversely proportional to mass). And in relational physics, gravity, electromagnetism and strong force are all the same in that they are all “relationship”. Therefore, if we express this in terms of equations, the following form is completed.
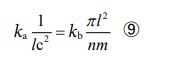
This is the formula for the Theory of Everything, which can deal with all forces in a unified manner.
I originally modeled the left-hand side as the equation for the electromagnetic force and the right-hand side as the equation for gravity. But now that I have unified them, we can calculate using either. For example, it is possible to use the left-hand side (equa- tion ⑦) to calculate gravity and the right-hand side (equation ⑧) to calculate electromagnetic force. Furthermore, by transform- ing the equation ⑨, the mass, volume, and density of an object can be calculated. Let’s derive them in order.
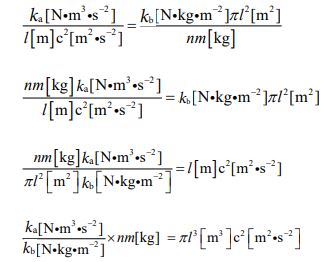
Here, the relationship between “ka” and “kb” is expressed as a new proportionality coefficient “J” (called “Junichi Parameter” after me). Along with this, I will also introduce a new unit “Skr” (named “Sakura” after a flower that represents Japan). To summarize these relationships, the quantities are given in the following form.
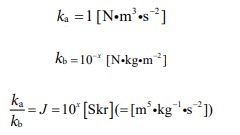
Now, let’s continue with the derivation. Since “ka/kb = J”, the equation is formed by the following process.
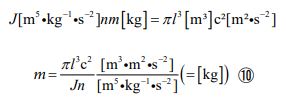
This is the formula for mass. If we transform it, we can get an expression for volume. The process is as follows.
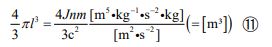
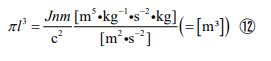
Equation ⑪ expresses the shape of the volume of a spherical object, and equation ⑫ expresses the shape of the volume of a cy- lindrical object.
Now, let’s derive the equation for density. Since volume is the amount of mass divided by density, the following equation can be used to express the relationship between them.
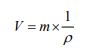
Substituting equation ⑪ into this model gives the following form.
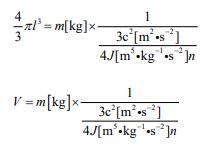
Hence, the equation to express the density of a spherical object is given in the following form.
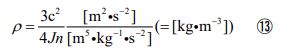
Substituting the equation ⑫ into the model described above, the equation for determining the density of a cylindrical object is given in the following form.
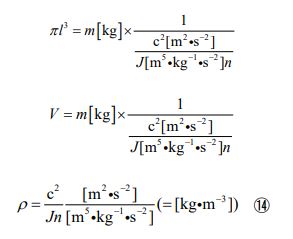
Furthermore, by substituting equation ③ into equation ⑬, we can derive an equation relating the speed of an object to its density.
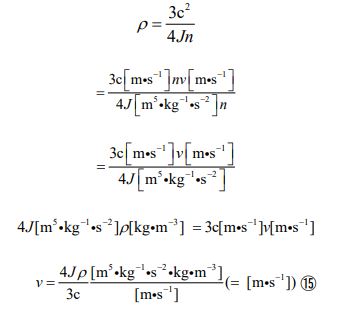
The above model will allow us to calculate various quantities about the object.
From here on, I would like to verify the correctness of my theory by applying specific data for each object to each model.
Now, let’s examine the specifics. For example, the electromagnetic force between nucleon and electron in an atomic structure, or gravity on the earth’s surface, have been calculated by many experts in the past. But they are only theoretical values and cannot be used as a standard for verification. Therefore, we should always try to compare our calculation results with some actual measured values. This is the best way to prove the correctness of the model I have built.
With this stance, I will first determine the volume and size of the hydrogen atom. Next, I will clarify the volume and size of an electron. And then I will calculate the ionization energy of the hydrogen atom based on the results of these calculations. This is because the ionization energy has been measured experimentally.
In order to calculate this, we need to know in advance about an important indispensable law. It is an original law in relational the- ory that I discovered while calculating many concrete individual objects in the macro world. It later turned out to be applicable to the micro world as well. It was about the proportionality coefficient “J”. I had initially thought of introducing it into the equation as a constant. But when I calculated it for each individual object, I was faced with the interesting result.
It was that only the number of digits in the calculated value I derived did not match the actual measurement. To solve this prob- lem, I treated “J ” not as a constant, but as a parameter. And I bundled it together as a product of the number of particles “n” (i.e., treated it as “Jn”), so that the number of digits in the calculated value would match the actual measured value. In doing so, I discovered the law expressed by the following equation.
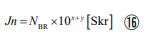
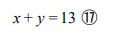
“Jn” is the product of the proportionality coefficient “J” and the number of parties “n”. “NBR” is just a number without unit, “x” is the exponential part of the quantity in “J” expressed to the power of 10. And “y” is the exponential part of the quantity in “n” expressed to the power of 10. “Skr” is a unit that indicates the quantity of “Jn”. The important point here is that the sum of “x” and “y” is always 13 and never exceeds it. Thanks to this law, I was able to determine the size of the electron, which was previously unknown.
First of all, let’s calculate the volume of a hydrogen atom. The model we will use is equation ⑪. The reason is that can be thought of as a spherical object. It is as follows.
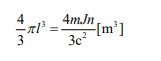
Here, the value for “m” is given in advance. 1.674 ×1027 [kg] [18]. The value of “c” is a physical constant, so it is also given in advance. 299792458 [m・s-1].
The question is how to determine the value of “n”. At first glance, it seems as if the number of parties is “2”. Because the structure of the hydrogen atom consists of one nucleon (i.e. , proton) and one electron. However, this is only the case in the macroscopic world, where objects are connected by an attractive force at some macroscopic distance. The connection between microscopic objects in the microscopic world requires a different interpretation. This means that we should change the way we count the number of parties. Depending on whether we are talking about the interaction of objects in the macro-world or the interaction of objects in the micro-world, we should judge it.
From this point of view, it is sufficient to interpret that there is one hydrogen atom as a microscopic particle here. In other word, the number of parties is “1”.
And I have already mentioned that when the value of the number of parties “n” is determined, it automatically determines the exponential part “y” for “n” and the exponential part “x” for “J”. The sum of “x” and “y” is 13, so in this case we know that “ n = 1×100 ”, and in response, the other is absolutely “ J = 1013 ”.
Now, let’s substitute each number into equation ⑪ and calculate.
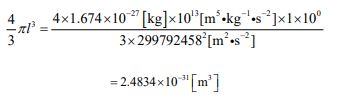
This is the value of the volume of a hydrogen atom.
Now that we know the value of the volume, we can also derive the value of the radius. The relationship between the two can be expressed by the following equation.
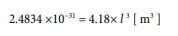
Solving this, the radius of the hydrogen atom is given by the following value.
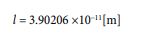
Next, let’s calculate the volume of an electron. Let’s substitute a number into equation ⑪.
The value of “m” is given in advance. 9.109 ×10-31[kg][19]. For the number of parties “n”, it is sufficient to interpret “n = 1×100”, think- ing that there is one electron as a microscopic particle. The value of “J” is automatically determined accordingly. It is “1013 ”.
So let’s get to the math.
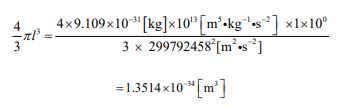
This is the value of the volume of one electron.
Now, let’s derive the radius as well. We can do this by using the formula for volume and radius. The following process will give us the value.
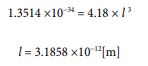
Now, let’s move on to the calculation of the ionization energy of a hydrogen atom [20].
The reason why I chose it as a material to test my theory is that it is a calculation that can be covered by the electromagnetic force model I have developed.
In the case of a hydrogen atom, it is sufficient to think as follows. The phenomenon of ionization means that an electron is ejected out of the atom, overcoming the captive force (= electromagnetic force) received from a single nucleon (= proton). Therefore, we can look at how the distance between the parties constituting the force changes before and after the ejection. By doing so, we can determine the amount of force (ionization energy) that leads to the change.
Since the size (diameter) of an electron is known, it is possible to describe how much the distance to constitute the force due to the loss of an electron from the atom has changed. Let’s try to model the phenomenon of ionization by rearranging equation ⑦.
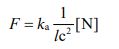
We can transform it into an equation to deal with energy.
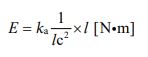
When the equation is further adjusted to a model for dealing with ionization, the following form is given.
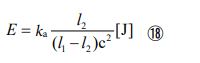
In the above equation, “l1” is the distance before ionization (i.e. , the radius of the hydrogen atom). And “l2” is the distance for one electron. And then “l1  ̄ l2” is the distance after ionization. The “E” is a quantity symbol that represents the value of ionization energy. The unit used is the joule, which deal with energy.
For a single electron, the radius is already known, so we can determine its size by multiplying it by two and converting it to a di- ameter. This can be expressed as follows.
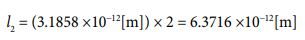
We have already got values for the radius of the hydrogen atom.
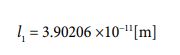
Now, let’s substitute each value into the formula ⑱ and perform the calculation. The ionization energy of a hydrogen atom can be calculated by the following process.
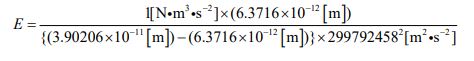
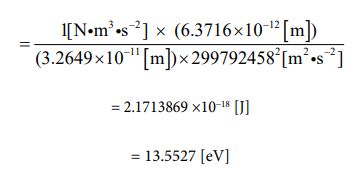
As mentioned above, the calculated results are consistent with the measured values. This is one of proofs that my model is correct
,p>Now, let’s continue with the verification of my theoryFrom here on, I want to compare the mass and volumes of individual objects with the measured values (or theoretical value if they are not available) through clarification. The materials selected were a Japanese kilogram prototype, a bowling ball, the earth, the moon, the sun, Venus, and Jupiter.
First, let’s calculate a Japanese kilogram prototype (No.6) [21]. This is a replica (platinum-iridium alloy) of the International Kilo- gram Scale, a gift from France to Japan in 1889. This cylindrical weight has the following data.
It has a radius of 0.039 [m], a height of 0.039 [m], and a mass of 1 [kg]. Since it is cylindrical, the model used for the calculation is the equation ⑫. Let’s calculate the volume. The following process is used to derive the value.
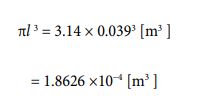
Next, let’s calculate the number of parties using equation ⑩. The value of “n” expected to be derived from this, based on the size and mass, is probably going to be in the single digits. So, we can estimate the value of “J ” to be “1013 ” at first, in anticipation of that. For “m”, it is given in advance, so we can use the value as 1 [kg]. Let’s substitute such a value. The process is as follows.
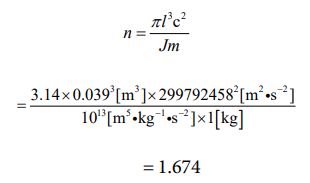
This value is not strictly correct. This is because, theoretically, the number of parties is an integer. However, it is fine as long as it is used as a process (sort of like a “party rate”) when calculating other quantities such as density or mass. Also, if we think of it as a combination with “J”, it will always be an integer, so again, no problem. It only has to be treated as a decimal here for the reason that it is convenient for calculation. If you don’t like it, you can look up the number of particles of platinum and iridium in the Periodic Table of Elements [22]. And you can record the number of parties as an integer from there. However, the setup would be more complicated.
Now, let’s calculate the value of the density using equation ⑭. The value is given in the following process.
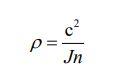

Here, the density and volume values are available. Since their product is mass, the following relational expressions can be used.
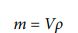
Now, let’s calculate the value of mass.
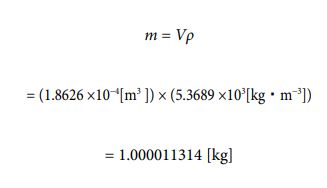
As described above, the result was the same as the measured value. You can see from this how accurate the model I have created is.
Next, let’s calculate the value of the volume and density of the bowling ball (16 pounds) [23]. And let’s see if the value of the actual mass and the calculated value match. The way is the same as for the kilogram prototype. The data required for calculation are as follows.
It has a radius of 0.1075 [m] and a mass of 7.25 [kg].
Since it is spherical, the value of the volume can be recorded as 4/3πl 3 = 5.2 ×10-3[m3 ] . The model for determining the number of parties is a variant of equation ⑩. My estimate is that the value is likely to be one digit. So, the value of “J” is naturally deter- mined by equation ⑰ as “1013 ”.
Let’s assign each number to equation ⑩ and calculate it by the following process.
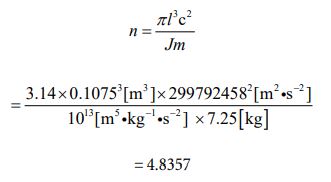
Next, the value of the density given using equation ⑬ can be obtained in the following process.
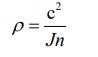
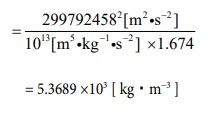
Let’s calculate the mass value by multiplying the volume and density value. It is the following process.
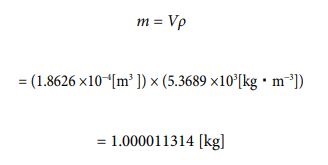
After all, the result became the same as the measured value. It speaks to the correctness of my theory.
Let’s continue the calculation for various objects as it is.
I want to treat the earth [24] a subject. The radius value is given in advance. It’s 6378137 [m]. Based on that, let’s find the circum- ference length, and determine the rotation speed from there. Since the rotation cycle is one day, it is converted to 86400 seconds. The whole calculation is as follows.
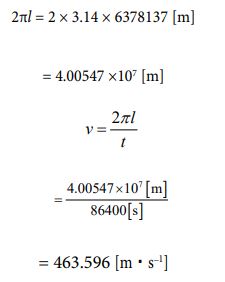
Since the speed is known, the number of parties can be clarified using equation ③. The following process gives its value.
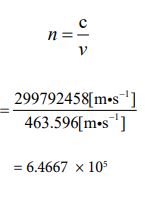
Because the number of parties has been determined, the value of “J ” is also automatically determined by equation ⑯ and ⑰. It’s “108”.
Let’s assign each numerical value to equation ⑩ and find the mass value of the earth. It is the following process.
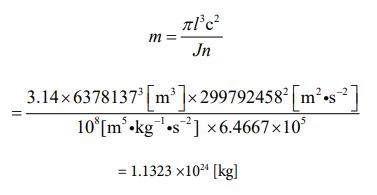
Since the value of the mass has been clarified, the volume value can be obtained. Since it is a sphere, let’s calculate it by the following process using equation ⑪.
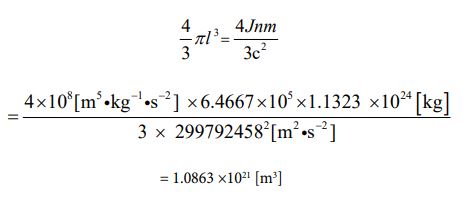
As described above, a solution which would be correct was derived.
Next, I want to treat the moon [25] as a subject. The radius value has already been given. It’s 1738000 [m]. Based on that, let’s find the circumference length, and determine the rotation speed from there. The rotation cycle is 27.322 days. Calculations can be performed in the following process
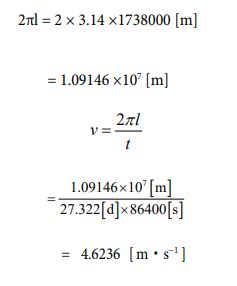
Since the speed is known, the number of parties can be clarified using equation ③. The calculated value can be obtained by the following process.
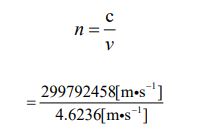
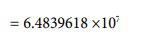
Because the number of parties has been determined, the value of “J ” is also automatically determined by equation ⑯ and ⑰. It’s “106”
Then, I want to apply each numerical value to equation ⑩ and produce the mass value of the moon. It is the following process.
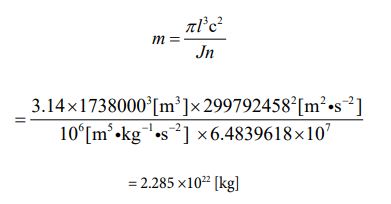
Since the mass value has been clarified, the volume value can be obtained. Since it is a sphere, let’s calculate using equation ⑪. It is the following process.
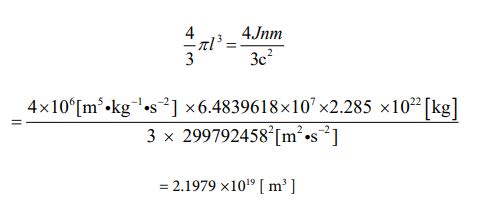
As mentioned above, the solution which would be correct was derived.
Next, I want to treat the sun as a subject. The radius value has already been given. It’s 6.96 ×108[m] [26]. Based on that, let’s find the circumference length and determine the rotation speed from there. The rotation cycle is 27 days [27]. Let’s calculate it in the following process
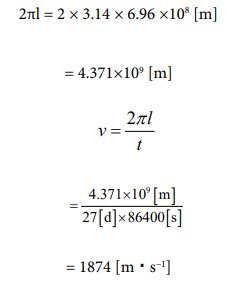
Since the speed is known, the number of parties can be clarified using equation ③. The calculated value can be obtained by the following process.
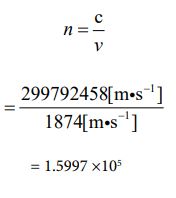
Now, that the number of parties has been determined, equations ⑯ and ⑰ automatically determine the value of “J ”. It’s “108
Then, I want to assign each numerical value to equation ⑩ and find the mass value of the sun. It is the following process.
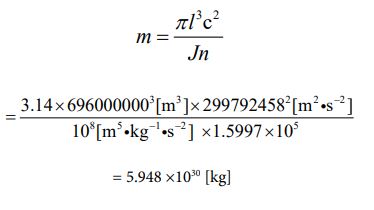
Since the mass value has been clarified, the volume value can be obtained. Since it is a sphere, let’s calculate using equation ⑪. It is the following process
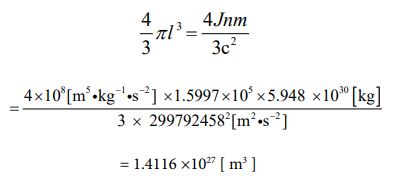
As mentioned above, the solution which would be correct was derived.
Next, I want to treat Venus [28] as a subject. The radius value has already been given. It’s 6052000 [m]. Based on that, let’s find the circumference length and determine the rotation speed from there. The rotation cycle is 243.02 days. Let’s calculate it in the following process.
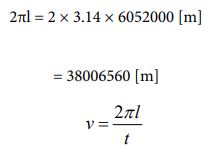
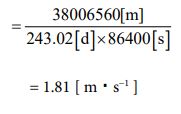
Since the speed is known, the number of parties can be clarified using equation ③. The calculated value can be obtained by the following process.
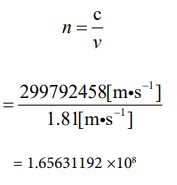
Now, that the number of parties has been determined, equations ⑯ and ⑰ automatically determine the value of “J ”. It’s “105”.
Let’s assign each numerical value to equation ⑩ and find the mass value of Venus. The calculation value is given in the following process
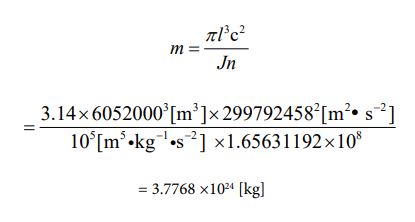
Since the mass value has been clarified, the volume value can be obtained. It is the following process.
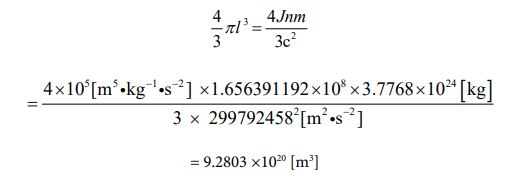
As mentioned above, the solution which would be correct was derived.
Finally, I want to treat Jupiter [29] as a subject. The radius value has already been given. It’s 71492000 [m]. based on that, let’s find the circumference length and determine the rotation speed from there. The rotation cycle is 0.414 days. Let’s calculate it in the following process
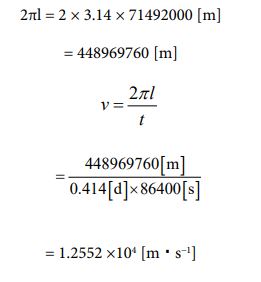
Since the speed is known, the number of parties can be clarified using equation ③. The calculated value can be obtained by following process.
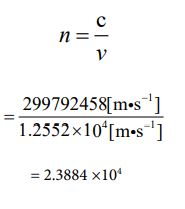
Because the number of parties has been determined, the value of “J” is automatically determined by equations ⑯ and ⑰. It’s “109”
Then, I want to assign each numerical value to equation ⑩ and find the mass value of Jupiter. It is the following process.
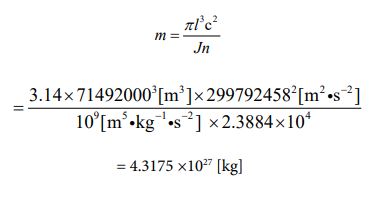
Since the mass value has been clarified, the volume value can be obtained. Since it is a sphere, let’s calculate using equation ⑪. It is the following process
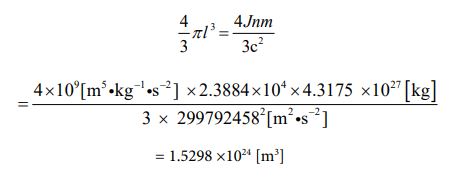
As mentioned above, the solution which would be correct was derived.
Then, let’s cut into the maximum conundrum in modern physics from there
The question is to what extent we can accurately predict the fate of an object. Can we know how an object’s current position and velocity will change by applying existing laws? In this regard, physics has succeeded in predicting the behavior of objects in the macro world. However, physics was powerless about grasping the movement of the particle in the micro world. The reason is simply in the point light and electrons have a strange feature of duality in the double-slit experiment. The processing of duality in which physics describes the behavior of micro-particles means that it has given up predicting the fate of objects as deterministic.
It is clear from the fact that quantum theory makes certain predictions impossible in principle through the idea of uncertainty principles [30]. Even though there is always only one trace of particles on the screen behind the double-slit [31]. In that case, it is scientifically obedient attitude to always interpret only as a particle about the real image of the electron.
Certainly, if you repeat a lot of experiments to fire a single electron from an electron gun, it is no wonder that you want to as- sociate it with interference of the waves. Because it will eventually form stripes on the screen. But nothing, it’s just because we overlook the initial conditions that must be found first in looking at a series of experimental process.
In the first place, I entered the world of physics research when two original ideas flashed in my head. One of them is the idea of energy, and the other is the idea of the real image of an object. The former has already been explained by the model “relationship”. I will explain the latter from now on.
When the object is subdivided into the root level, it ultimately arrives at the particle. Up to this point, it is a common recognition that everyone has. I think so, but what’s unique is the basic form of existence for a particle. It is a picture that is described as “object expansion and contraction” in my coined word. The content is that individual objects will constantly change shape and size within that range as long as their volume remains the same. And, the “expansion and contraction” has a peculiar feature for each object.
I would like to explain electronic information as an example. The model for describing the volume of an object has already been introduced in equations ⑪ and ⑫. It was described above that the former is a model of the sphere type, and latter is a model of the cylindrical type. Here, let’s think about the pattern of “expansion and contraction” of shape and size between the sphere type and the newly assumed cube type.
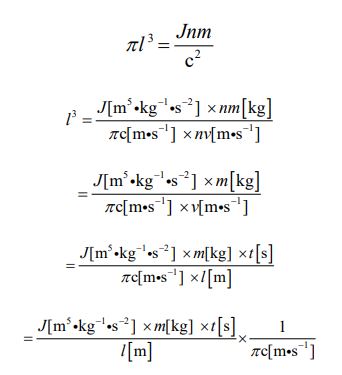
First of all, let’s transform equation ⑪, which is a model of the sphere type. I want to assign equation ③ to the right side. It is the following process.
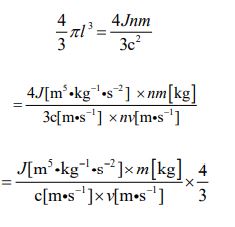
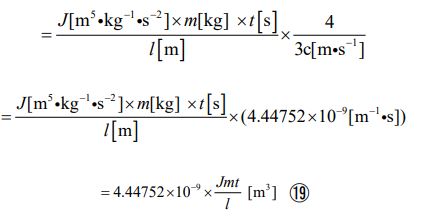
The volume value of electron has already been calculated. It is 1.3514 ×10−34 [m3] . After assigning it to the left side of the upper expression, for each numerical value, let’s assign the value already calculated to the above equation. When calculated, the time value is given in the following shape (it is called “potential time” in my coined word).
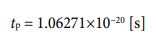
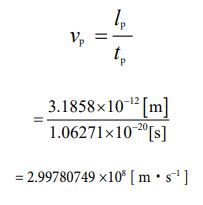
This is the potential speed value inherent in one electron. It can be found that it almost matches the rotation speed calculated using equation ③.
Next, let’s derive the expression which can describe the object of the cube type. Let’s assign equation ③ to transform equation ⑫. It is the following process.
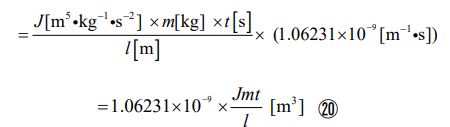
Then, let’s assign the volume value of the electron to the left side. And let’s assign the radius value, the mass value, and the proportional coefficient to the right side. By doing so, the potential time value is given in the following shape.,
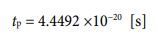
Since the time value has been clarified, the potential speed value can be obtained. Before that, I want to derive the potential radius value of the cube type electron. It can be calculated by the following process.
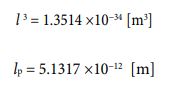
Using these values, the potential speed value is given in the following process.
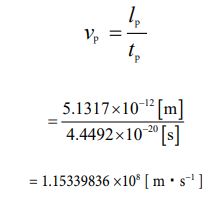
This is the potential speed value inherent in a single cube electron. Compared to that of the sphere type, it can be seen that it decelerates to less than half. Let’s express that by the acceleration. Since “expansion and contraction” consists of both “expansion action” and “contraction action”, it is necessary to determine the acceleration for each. First, the acceleration value for the expansion action is given in the following calculation process,
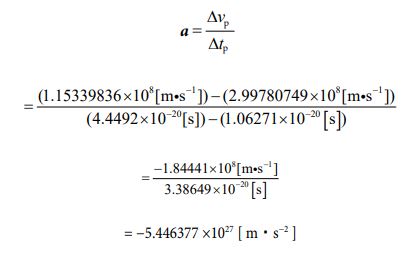
Next, let’s calculate the acceleration value for the contraction action by following process.
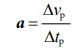
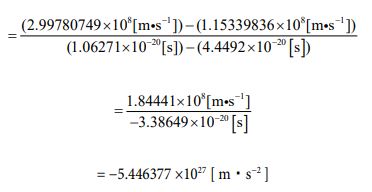
As described above, in both the expansion and contraction action, it is considered that one electron changes shape and size while significantly decelerating. And, as long as friction and external force are not applied, one electron repeats such expansion and contraction forever. That is, it keeps transforming alternately in the sphere, the cube, the sphere, and the cube
This is an overview of my original particle image, “object expansion and contraction”. Thus, given the process of transformation from sphere to cube, it would be possible for us to calculate the fate of the electron deterministically. The important thing is to consider what happen when it interacts with a macroscopic object. In other words, we should examine how the angle of launch, direction of travel, velocity, and position are determined by what shape and how large the object is. What I mean is that my relational theory does not stand in the position of thinking of electronic movements as indeterminate in principle unlike quantum theory. An electron is a particle itself. It’s not a wave.
The particle only changes its shape and size as particle, and does not change to a physical existence other than a particle. That’s why when we do a double-slit experiment, it always leaves a trace as a single particle on the screen. Each shot fired from an electron gun should interact with other objects, such as the muzzle and air molecules floating in space. And they should form various angles depending on the timing and fly in different directions. So, the passing slit and landing points on the screen are also different each time. Therefore, if we repeat many launch experiments, the total result will be a stripe pattern that looks like interference
It is true that stripes do form. However, it is too early to interpret this as an indication that single electron is a wave and non-existent. This is because, as mentioned earlier, we will miss the essence of things if we do not seriously consider the initial conditions further back than the screen or the double-slit.
The “initial conditions” are “the essence of things that should be the starting point of thought” and “the basic image of matter and energy that scientists should stand on”. The most important thing in overcoming a difficult problem is to be keenly aware of this
What is required here is the discovery of such a view of matter and particles. The concrete manifestation of this view is the new concept of “object expansion and contraction”. Since the action takes place within the same volume and mass, it would be acceptable way of thinking about physics. Of course, it may not be a strange idea to think that a single electron always maintains a fixed shape and size. However, there is a profound reason why I dared to introduce the idea of “expansion and contraction” into it. I would like to discuss it in detail. The world is an aggregate or complex made up of many parties. All members have an irreplaceable individuality. When they come face to face with other parties, they create energy (relationship). And individuality is inversely proportional to the number of parties.
The more parties there are, the weaker the individuality becomes. For example, if you roll the dice a huge number of times, you will always have a 50% chance of getting an even number [32]
If you throw the dice just once, it is difficult to predict exactly which number of eyes will appear on the dice. But if you throw the dice 10000 times, you can predict with certainly that an even number of eyes will make up 50% of the total. The reason why this is so is easy to understand if we think about it from the angle of “individuality”. The dice are regular hexahedron with one eye each from “1” to “6”. Each eye is a unique and irreplaceable number. This is nothing less than individuality. If you roll the dice once and once you get some kind of an eye, it means that it is the only unique eye. Being unique also means being unstable, difficult to handle by others, and difficult to predict how one will behave. It is also a troublesome subject that is not straightforward to deal with. However, when a large number of individuality come together to form an aggregate or complex, each individuality cancels each other out. And they turn into a featureless, ordinary, and commonplace existence. As the number of parties increase, each member loses its individuality and becomes more level and homogenized. The reason why 10000 dice rolls are more predictable is that the increased number of throws loses the individuality of each throw, making it a more manageable target. In other words, not being unique can be seen as being stable. Classical physics was able to describe the motion of macroscopic objects. Because these objects were stable and tractable objects that formed aggregates. However, microscopic particles are difficult to predict
Because they have large individuality, small number of parties, and unstable behavior.
The idea of “expansion and contraction” was newly created to express this unpredictability and unwieldiness.
From the perspective of the entire universe, one electron is an element that constitutes it. The universe is the “whole”, and one electron is a “part”. The “whole” and a “part” should be in harmony. Heracratos, an ancient Greek philosopher, said “Everything flows”. As the universe continues to change, it is natural that one electron continues to change accordingly. Only the result derived logically from there is a picture “expansion and contraction”
At the beginning of this paper, I stated that this universe is an “ clockwork organism”. One electron is a “part” that constitutes it. So, it is necessary to think by linking “space image as a whole” and “particle image as part”. They should always be treated in harmony. In other words, it is impossible to capture the essence even if we focus only on electrons. It is necessary to consider their behavior in the balance with the universe as a whole.
While considering the contrasting structure of such “whole” and “part”, the viewpoint of contrast is born. They are as follows. “Macro” and “micro”, “aggregate” and “single”, “stable” and “unstable”, “non-individual” and “individual”, for example. They lead to the discovery of a new view of materials such as “non-telescopic object” and “telescopic object”. Fortunately, such images seem to be a very compatible idea in theoretically explaining the results obtained in the double-slit experiment. Moreover, it is possible to explain the reason why the light velocity slows down from “ꝏ” to “c”. It was only with the introduction of the concept of “object expansion and contraction”. This is a big advancement for physics. It can be said that it is an image opposite to the uncertainty principle of Heisenberg.
The argument is that when we hit light to determine the position of electrons, it becomes indeterminate. But in the theory of “object expansion and contraction”, it is only that it becomes difficult for us to determine the position. Because electrons hit light while expanding. At that time, there is not always one electron that goes toward. Let’s remember Fizeau’s experiment. The parties there have reached a large number of light source, half mirror, reflector, lenses, gear, and observation device. The light fired should interact with all of it. I would like to consider the interaction with one of them, a reflector. The moment when light hits the mirror surface is the moment of interaction. A mirror as a macro object is a complex of many micro objects. As mentioned above, such objects are stable by losing individuality, even though they are inherent individual atoms and electrons. However, by touching the energy of light, those objects regain individuality. And all particles within the range that interacted with light revive “expansion and contraction”. Individual particles have their own rhythm. But depending on the timing, two or more parties may synchronize “expansion and contraction”. If multiple particles expand and lunge into light and immediately turn into shrinkage, they can drag into the material constituting the mirror surface as if grabbing light. The reflection of light is slightly delayed by the action. Therefore, the light speed which was originally infinite slows down to the level of “c” with a finite value
“Interaction between matter and energy” is literally a “mutual” action. In other words, energy also affects objects, but objects also affect energy. The reason why light slows down from “ꝏ” to “c” and becomes a wave or becomes a particle according to the type of experiment is because it was all influenced by objects. In relational physics, energy and force are considered to be “the relationship between objects”. So as objects change, energy and force also change. The individuality of an object is a source of force and energy.
Force and energy are also sources that make objects “individuality”. Objects that are “individualized” by force and energy transition from “stable” to “unstable”. Specifically, it shifts from a “non-telescopic object” to a “telescopic object”. It means that because it was separated from the surrounding objects, it was liberated from counteracting “individuality” and was able to move freely. Since a single micro particle is extremely “unique” and “unstable”, it is difficult to predict how it will move. Quantum theory has denied the existence of objects because of this (uncertainty principle). However, it is not “indeterminate” but only “unstable”. If the substance of the particle is even seen as a “telescopic object”, there is room which can be predicted by calculation how it behaves for the future. Of course, calculations are complex and will not be easily answered. But unlike quantum theory, it does not mean that it is impossible in principle. For the almighty God, in principle, the future can be predicted. In a word, the law which determines the movement of the particle which is not easy to read at first glance in the place hidden from man’s view exists in this world undeniably. This is synonymous with the theory of hidden parameters [33] of David Bohm. And, “hidden parameter” is nothing but a model corresponding to “expansion and contraction” that I derived. Take beta decay (weak interactions) [34] as an example. If we don’t understand such hidden mechanisms that are not visible to the human eye, we will misunderstand the real image of nature. In other words, a quantum theory that does not focus on this is not a faithful description of the laws of nature. It is true that it is not easy to detect hidden messages from nature that are not apparent in experimental results. But it’s not entirely without clues. It is possible to arrive at the idea of “object expansion and contraction” by induction. Because the size of an object can change if its volumes is the same, and the physical laws of this universe are that the “whole” and the “parts” are in harmony
Now, let’s apply this picture of “expansion and contraction” to the type of beta decay. In this case, the imbalance between the number of neutrons and protons in an atomic nucleus causes the bonds between the nucleons to become unstable. And in an attempt to stabilize the nucleus, the number of parties in the nucleus is increased, resulting in the release ofradioactivity. However, the number of parties will only increase for a moment immediately after the collapse, and will soon return to the original number of parties again. So, the unstable state (imbalance in quantity) will not be resolved. Hence, the decay and radioactive release will continue until it is completely resolved. In other words, the weak force is the force that keeps the nucleus decaying until it reaches a sufficient number of parties to stabilize the nucleus
However, increasing the number of parties is not the only way to achieve stability. As long as they can be stabilized, it does not matter how they do it. Here, I would like to consider the “expansion and contraction” of particles. Every particle in a nucleus has a unique “expansion and contraction” rhythm. Protons have their own rhythms, neutrons have their own rhythms, and whole nucleons have their own rhythms. These rhythms are being played together like a concerto.
If each “expansion and contraction” rhythm is in harmony with each other, then the nucleus is in a stable state. So, there is no need to mobilize energy to collapse it. However, if each rhythm is dissonant, it can never be stable. That is why it tries to stabilize itself by disintegrating its nucleus and emitting radioactivity. And the only way radioactive materials can be stabilized is through decay.
According to quantum theory, it is impossible in principle to predict with certainty when radioactivity will be released. And it can only be described as a superposition of “released” and “not released” states. It is true that it seems difficult to find some regularity in the individual decays and radiations. However, as mentioned earlier, if we treat radioactive materials as an aggregate of a large number of particles, rather than as a single unit, we will be able to handle them more easily. And we will be able to predict their half-lives [35]. This is due to the loss of “individuality” caused by the increase in the number of parties.
However, even if we look at each particle individually, the same can be said for predictability. We need information on the total number of members in the nucleus, their types, and their “expansion and contraction” rhythms. If only we had it all, we can in principle calculate the timing of decay and radiation from the viewpoint of the combination of these factors. In other words, in this way of thinking, the overlapping of states does not occur in the first place. It’s not that they are unpredictable, it’s just that prediction is complicated.
In this section, I would like to consider whether there is any common regularity in the phenomenon of “expansion and contrac- tion”. Even if it has different characteristics for each object. I have already introduced a “expansion and contraction” image (poten- tial speed, potential time, potential distance, acceleration) of one electron using equations ⑲ and ⑳. In addition there, I would like to explain the “expansion and contraction” width when one electron are transformed from spherical to cubic. In the following calculation process it is described.
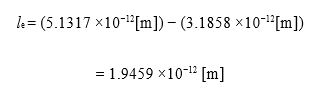
One electron stretches and shrinks between this width.
In addition, let’s think about the circumference length when the electron is seen here as a sphere. It can be calculated in the fol- lowing process.

The above values have come out, but what we are concerned about is the relationship between the two. Let’s derive the ratio of the circumference length and the expansion and contraction width. It is given in the following relation.
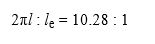
It was found that the circumference length was about 10 times the expansion and contraction width. That is, one lap of one electron corresponds to the total (10 times) of the expansion action and the contraction action.
The detailed calculation process is omitted, but the expansion and contraction data of hydrogen atoms and the sun will be put up. Let’s express each quantity symbol. The spherical potential time is as “tp1”. The cube-type potential time is as “tp2”. The spherical potential speed is as “vp1”. The cube-type potential speed is as “vp2”. The acceleration is as “a”. The spherical circumference length is as “2πl”. The expansion and contraction width is as “le”. The circumference length/expansion and contraction width ratio is as “2πl: le”. The models used for the calculation are equation ⑲ and ⑳.
First, I would like to list each numerical value for hydrogen atoms. It is as follows.

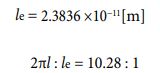
Next, I would like to enumerate each numerical value for the sun. It is as follows.
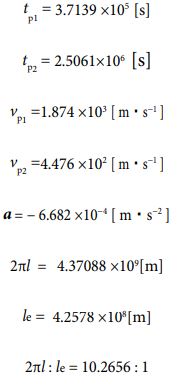
The above calculation results were derived
What can we see from these results ? One thing I can say is the circumference length/expansion and contraction width ratio is always “10 : 1” for any object, such as one electron, hydrogen atom, or sun. From here, this ratio probably applies to all objects.
If so, a new hypothesis will be derived with a logical leap. The content is as follows. The potential speed of the object will become the rotation speed or the “expansion and contraction” speed depending on the situation. In other words, it should no longer be sublimated into one law. It will be expressed as follows.
“Equivalence between rotation and expansion and contraction”. It is this.
In both the macro world and the micro world, the following can be said. How many parties are around, how far they are facing each other, and how much interaction occurs determine whether each object will rotate, stretch, or not. It can be thought that all objects are moving in such a mechanism.
As mentioned above, the “expansion and contraction” width of the sun is large, but such a movement of sun has not been ob- served. Only rotation has been observed. From this, it can be inferred that the sun is rotating by choosing rotation by interacting with other planets.
Because rotation and “expansion and contraction” are equivalent.
As mentioned above, I have roughly explained the outline of “object expansion and contraction”. When the radioactive material causes the beta collapse and the radioactivity is put out should be entirely thought by the balance with such an action. If even it can be succeeded, it does not fail into a strange explanation of coexistence of the state.
For example, let’s take “Schrodinger’s cat” [36] as an example and explore the root of the strangeness. This is a thought experiment created by physicist Schrodinger to criticize the idea of coexistence of states in quantum theory (probability interpretation) [37]. It is a major challenge that has not yet been given a unified view among scholars.
From here, I would like to discuss the reality and non-existence of objects in relation to their resolution. Expanding from there, I will once again highlight the differences between the traditional theory (classical physics and quantum mechanics) and the new theory (relational physics).
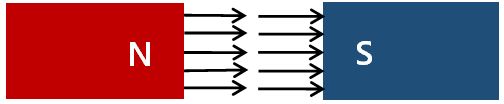
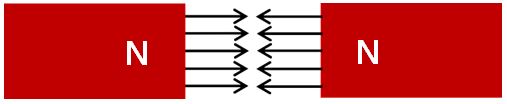
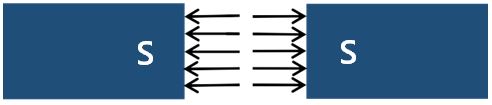
The original natural system is based on a “remote action” or “relationship model” as I advocate. Forces and energies act between objects in a single strand, like a red thread of fate. In contrast, the old theory understands nature in a model in which forces and energies arise from the edges and travel to the edges at high speed between objects. This is the “Proximity theory” and “movement model”. In reality, however, this is not the way the world works. For example, Faraday devised a model of electric and magnetic lines of force. He thereby theorized how force leaves one pole and enters the other [38]. However, that model has already failed logically. Because that would not explain why S-poles (or negative poles) repel each other (Figure 8-10).
In fact, if you look through all the textbooks, technical books, and general books, you will not find any pictures of S-poles (or negative poles) facing each other. Why?
According to the Faraday model, both S-poles would be the recipient of the tip of the line of force. Therefore, the arrow (the point- ed part of the force line) is piercing the wall of the magnet. In other words, in this model, the two arrows are not composed against each other. They are turned away from each other. The arrows are not colliding head-on with each other. This is not a successful explanation of the repulsion phenomenon.
In the case of Figure 8 and 9, Faraday’s concept can be used as an explanatory method. However, in the case of Figure 10, the logic of force lines does not apply. A photo of the S-poles facing each other is not convenient for Faraday supporters. Because they must illustrate that the lines of force are not colliding with each other. This is the reason why all the photos of S-pole (or negative pole) confrontation are covered up.
In the first place, we must analyze more sharply the experiment on which the idea of force lines was based. Faraday sprinkled iron sand around two facing magnets. Then iron sand was distributed as if it were a line. In response, Faraday devised a model of force line.
Relational physics, however, has a different interpretation. The results of that experiment were expressed by the large number of parties involved in the relationship. The experiment involves a multitude of parties: magnets, iron sand, a desk, and the earth. The gravity from the earth is also working there. Not only the electromagnetic force between two magnets is represented. If we want to know exactly what it is, we would have to park two magnets in space and scatter iron sand around it.
Let’s look at another example. In an atomic structure, it is about the case when an electron orbits around a nucleon. As electrons do so, they gradually lose momentum as energy escapes by radiation. Then they will eventually be sucked into the nucleon, col- lide, and collapse. That is the conclusion of electromagnetism to interpret it that way [39].
But, again, nature is not really like that. The fact that atoms, matter, and this world are able to survive without breaking is solid evidence of this.
Thus, it can be said that classical physics does not capture the mechanisms of nature with 100% fidelity, nor is it a perfect model. Quantum mechanics is a theoretical system built on the premise of proximity theory with such weaknesses. It means that when flawed classical physics is modified and theorized to fit the real picture of nature, it becomes quantum mechanics.
As long as the atomic structure is based on classical theory, it can never be stable. Hence, it is necessary to adjust the model so that the atomic structure can be stabilized. The resulting idea is quantum theory. For example, by treating electrons as waves rather than real ones, the scenario of energy reduction by radiation and collisions with nucleons is avoided. In this way, classical physics can survive as a model dedicated to the macroscopic world. And quantum mechanics can be made into a new explanatory tool as a model exclusively for the micro-world.
However, if we create such a strange model, we will not be able to reconcile it with other theories (e.g., relativity). And it would be impossible to reconcile micro-world events with macro-world events. The contradictions that arises in the hypothetical exper- iment “Schrodinger’s Cat” are a perfect example. This speaks ironically to the fact that micro and macro are not well connected. I will briefly describe this experiment.
A box is prepared. A cat is locked in it. Radioactive materials are put in it. A Geiger counter to detect it and a poison bottle opener connected to the Geiger counter are placed in the box. Radioactive materials have a 50% chance of spontaneously disintegrating within an hour, emitting radioactivity in the process. The detection device then reacts and opens the lid of the poison bottle. If it does, the cat is poisoned and dies. If it does not, the cat is safe.
The emission and non-emission of radioactivity is expressed in terms of the concept of coexistence of states based on quantum theory. This is because it is an event in the microscopic world. Hence, it is described in the form of overlapping “radioactive” and “non-radioactive” state. So, it and the macro-world phenomena are linked, and the “cat is alive” and “cat is dead” are coexisting in an overlapping state. Such a coexisting state is determined to be one or the other only when the observer opens the box and looks at the contents (called wave packet contraction).
Conversely, as long as the contents of the box are not seen, the overlap will continue. It is often described as a “half-life, half-dead cat”. A cat that is both alive and dead at the same time. A cat that lives in the macro world but is forced to participate in an exper-iment that leads to the micro world at the whim of a scientist. Because of this, the cat is forced into a halfway, strange existence. This would not help the cat.
How, then, can such inconsistencies be resolved?
I would like to consider it from now on. But even though it is a thought experiment, it is pitiful to put a cat at risk of death. So instead, let’s experiment with curry rice as a material. Its name is “Schrodinger’s Curry”. The content is as follows.
A box is prepared. Radioactive elements are put in it. It has a 50% chance of radioactivity within an hour. Then, a detector for detecting it is put. Furthermore, rice served on a plate, retort curry, and the heating and opening device are put together. If radio- activity is detected in the detector, curry is applied to rice. If the device does not detected it, the rice will remain as it is. In doing so, if we stand in the idea of quantum theory, since radioactivity emission is a phenomenon in the micro world, it becomes a prob- abilistic behavior. So, it is treated as a coexistence of the “release state” and “unreleased state”. And it is linked to the macro world, so it is considered that the “rice state” and “curry rice state” overlap. In other words, it can be said that it is in the state of “half-rice, half-curry”. However, that does not mean half-serving rice or curry, which is often found in restaurants and cafes. It is “Something quantum theory which is neither rice nor curry rice”. Such a superposition condition is not determined until the observer opens the box and sees the contents. And only after visualizing the box does the wave bundle shrinks and is confirmed in one state.
This is a very strange reason. Strange events in the micro world are reflected in the macro world, and phenomena in the macro world are also strange. To break this strangeness, the interpretation of the micro-particle must be modified to begin with. It is natural to think that the phenomenon of coexistence of the state in the micro world cannot fundamentally occur. Unless the eye mask patron who met the quantum theory “half-rice, half-curry” in the macro world actually eats it.
Then, I devised a new particle image “object expansion and contraction”. This is a different image from De Broglie’s material wave [40]. Material wave are a way of thinking that an object is both a particle and a wave. But “object expansion and contraction” is a way of thinking that particles change shape and size but do not become waves. Since it is not regarded as a wave, it is not necessary to bring the theory of coexistence of the state there in the first place. So, the radioactivity release from the radioactive material can be understood deterministically. Therefore, in “Schrodinger’s Curry”, we can develop logic from the stage where the future of radiation is determined. And then, the success or failure of curry rice only has to be treated definitively according to that.
Nature is a system in which forces and energies act remotely between objects with such realities. This is the relationship model. That being so, the micro and macro can be reconciled without contradiction. If we assume this model, it would be easy to explain the stability of the atomic structure without special workmanship. In other words, nucleons and electrons originally have a rela- tionship that is stable at a certain distance. That is the relationship between two. Therefore, there is no need to play with techniques such as regarding electrons as waves or denying their existence in the first place. It can cut straight to the atomic structure and face it straight on.
So it’s not at all odd. Beautiful. Simple. Easy to understand.
It is thanks to it that the fate of an object can be tracked deterministically.
On the other hand, the proximity theory (quantum theory) denies such reality and therefore cannot predict the fate of objects (non-determinism). Hence, it becomes necessary to bring up a strange logic.
Moreover, the mathematics used in the calculations has become extremely complex. I call it “formula positivism”. In general, physicists tend to think of everything in term of mathematical formulas. Indeed, the language of science that talks about physical phenomena is mathematics. But it is only one means of describing truth.
What is important is not the means, but the end: a deeper understanding of nature. If we have a strong passion for it, we should first focus on carefully observing and analyzing all the experimental facts and natural phenomena under study. Interestingly, when modeling is attempted after sufficient such analysis, it can be explained with simple mathematical formulas. Even a junior high school student could understand that. As I mentioned around the beginning of this paper, such a way of thinking is called “formula negativism”.
On the other hand, the “Formula Replacementists” rush into modeling (mathematical formulation) before sufficient analysis of the observed object has been completed. Then, ironically, the content of the expression becomes more complex. Hence, they are forced to use higher mathematics to provide acrobatic explanations. Then, due to its complexity, it becomes difficult to reconcile it with other theories. The inability to unify quantum mechanics and relativity, the inability to unify the four forces, is all due to a lack of prior analysis and the complexity of the mathematics. To use an analogy, it is like pottery. If the clay is thoroughly kneaded in advance, then molded and fired, a durable piece can be produced. However, if the work is suddenly baked without sufficient advance kneading, it may crack. The same is true for scientific research.
By nature, learning should be simple enough to be understood by children.
Fortunately, today, we have computers and calculators. This is no longer the era in which Newton and Descartes lived. Newton created the differential and integral calculus, and Descartes created Cartesian coordinates. They are designed to break down dif- ficult concepts and large numbers into bite-size pieces for people. However, these were methodologies that were required only at that time. They may not be essential in the present day, when conditions are different. The time has come when anyone can easily solve scientific laws using convenient tools such as PCs and smart-phones.
Nowadays, what is most necessary for successful research is not mathematics, but a “formula negativism” attitude that puts ev- erything into “kneading”.
Mathematics should be kept to a minimum.
In this section, based on such a stance, I would like to clarify universal laws common to both the micro and macro worlds through some observed facts and calculations. The subject matter that is best suited to achieve this is the discussion of light. That is, to solve two mysteries: what are the criteria for sorting out “light” and “darkness” and what are the criteria for sorting out “light” and “attraction”?
Let’s discuss the former first. The perfect subject for relational physics to solve astronomical mysteries is the black hole. In this theory, “light” is considered to be a “relationship”.
Therefore, if we assume a state in which such a “relationship” does not exist, it is a “dark state”. Using this model, it is very easy to explain the mechanism of a black hole being a dark celestial body.
“Light” and “Darkness”. There is only simple criterion that separates the two. As mentioned earlier, it is an original concept I in- vented, called a “light pillar”. Please take a look at Figure 11.
The “light” (relationship) between the two objects is well represented as if they are connected by a single line. That’s what it means when an object glows. The “light” is the “light pillar” itself. Whether or not an object becomes a black hole depends on whether or not a “light pillar” is formed. If one or more “light pillars” exist in a celestial body, the object will glow and will not be a black hole. On the other hand, if there is no it there at all, it becomes a black hole. For a black hole to form, the “number of light pillars” must be N = 0.5. I call it the “black hole constant”. The value is always 0.5. This is a universal constant that applies to all black holes in this universe. Whatever the black hole, this number must always be assigned when calculating in relational physics. In the case of the “light pillar” in Figure 11, the “relationship” between the two objects is complete and the “number of light pillars” is N = 1. Hence, the black hole constant is not satisfied. Therefore, the object glows. If it glows, it cannot be called a black hole. In order to be able to call it so, the “number of light pillars” must be N = 0.5. Because “one line (relationship) not being formed” is what it takes to not shine. What “N = 0.5” means is that the “relationship” between objects is cut off in the middle.
Once we have that down, the rest is easy. This constant identifies all of the black holes. If you want to know its true face, all you need is a simple formula at the middle school level.
Now, let’s take a real black hole as an example and calculate it concretely. Let’s focus on Q2237, one of five quasars located approx- imately 10 billion light-years from Earth. At its center is believed to be a black hole [41]. The models used in the calculations are equation ① and ③ already introduced. Let’s assign the former to the latter, and then transform it. The following form is given.
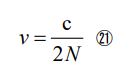
Since the number of light pillars of a black hole is 0.5 as a constant, the rotation speed can be obtained by substituting it into the above equation. The values are as follows.
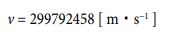
Thus, it was found to have reached the speed of light.
Now, let’s use the same method to calculate each data for quasars.
Quasars are the brightest objects in the universe. Its brilliance is, on average, 10 trillion times that of the sun. It is equivalent to the total brightness of all the stars in our Milky Way galaxy multiplied by a thousand [42].
The “number of light pillars” of the quasar is “N = 1”. If we work backward from the “number of light pillars” of a black hole, we will understand why this is so. The smaller the value of the “number of light pillars”, the more energy the light has and the more brilliant it is. Therefore, “1” is the smallest possible value in the universe.
As long as quasars are the brightest in the universe, the theoretical value of the “number of light pillars” is always “N = 1”. The quantity that represents the “strength of the universe’s number one relationship” is “N = 1”. This is the “quasar constant”, so to speak. Substituting it into equation ㉑ and calculating, we can obtain the following rotation speed values.
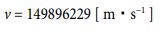
Thus, the value is half the speed of light. These are consistent with observations, including the calculated values for the black holes mentioned earlier [43]. The importance of the concept of the “number of light pillars” in understanding the essential parts of a celestial body can be seen from this.
However, the factor that produces the best light in the universe from quasars is not only the small number of “light pillars”. In fact, the minuteness of the distance between objects is also an essential factor. It is a concept I coined called “light pillar prime length”. It is most sought after, along with “light pillar number”, in explaining the nature of shining celestial bodies such as the sun and quasars. “Light” is a “relationship”. “Relationships” are “energy”. If so, in order to generate the greatest radiant energy in the universe, the strength of the “relationship” must also be the greatest in the universe. Therefore, the distance between objects to make it up must be inversely proportional to the smallest level in the universe. I independently named the tiny distance that is the source of such ultra-microscopic light as “light pillar prime length”.
How, then, can we clarify the actual figures? To do so, it is necessary to put “light” and “attraction” in the same framework. As mentioned earlier, in this paper, the inter-individuality (inter-object) image (Figure 4 and 5) is brought to fruition in the form of formulas ④ and ⑦. What was used there was “light”. In other words, with the completion of equation ④ and equation ⑦, “light” and “attraction” (electromagnetic force) were integrated under the same model. If so, then the opposite logical development would be possible. In other words, since we were able to derive the model of “attraction” (electromagnetism) using the image of “light”, we can also derive the image of “light” using the model of “attraction” (electromagnetism).
Now, let’s move on to the actual, concrete calculations. The brightness of a celestial body is quantified by the amount of radiant en- ergy emitted from it. To calculate the radiant energy from a quasar, the model of attraction (electromagnetic force) cannot be used as is. Therefore, it is necessary to transform equation ⑦ into a model that can cover the radiant energy. The process is as follows.
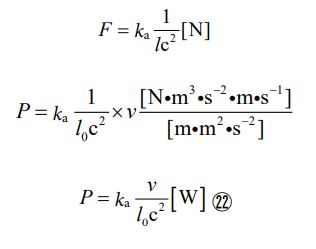
“P” is the quantity symbol for radiant energy. The “W” is the unit for the degree of it, “watt”. And “l0” is a quantity symbol for the “light pillar prime length”.
Now, let’s do the math.
I chose the brightest quasar in the universe, discovered by NASA in 2015. Its brightness is 350 trillion times brighter than the sun’s brightness, P =3.8271026 [W][44]. It is located within the galaxy known as WISE J224607. 57-052635. 0 [45]. The rotation veloc- ity can be thought of as follows. Since the quasar constant applies to all quasars, the velocity calculated from it is also a universal velocity common to all quasars. Hence, the value can be determined to be v = 149896229 [ m・s−1 ]. Now, let’s substitute each value into equation ㉒ for the calculation. The process is as follows.
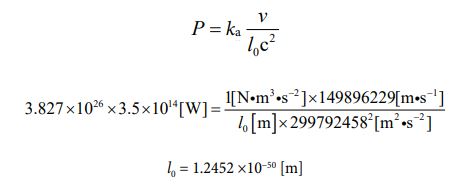
This is the value of the “light pillar prime length” that forms the strongest “relationship” in the universe. This is where the brightest light in the universe is generated. The smaller the distance between individuals, the more intense the “relationship” will be.
Thus, the value of the quasar’s “light pillar prime length” is given. Now that this has been clarified, what can we see?
It is as follows. First, based on the already existing radiant energy values from the sun, we can determine the “light pillar prime length” of the sun as in the previous section. Then, the ratio of the solar radius to the light pillar prime length can be determined. Hence, by applying the model to quasars, the radius of the quasar can also be derived. First, let’s calculate the “light pillar prime length” of the sun. The process is as follows.
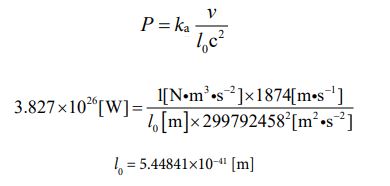
Next, let’s formulate the equation assuming that the ratio of the radius to the light pillar prime length is the same for both celestial bodies. It takes the following form.
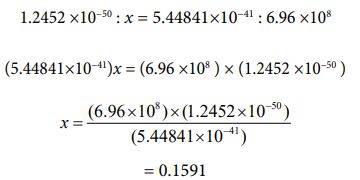
From the above comparison, the radius value of the quasar was found to be, l = 0.1591[m].
Now that the radius value has been obtained, the mass and volume can also be calculated. Let’s calculate the former using equation ⑩ and the latter using the general formula for volume, V = 4/3πl 3 [ m3 ]. Each value to be substituted is as follows. For the number of parties, the value “n = 2” is derived from equation ① based on quasar constant. Accordingly, for the proportionality coefficient, the value “ J = 1013 ” is derived from equation ⑯ and ⑰.
Let’s make a substitution for each of them. The process is as follows.
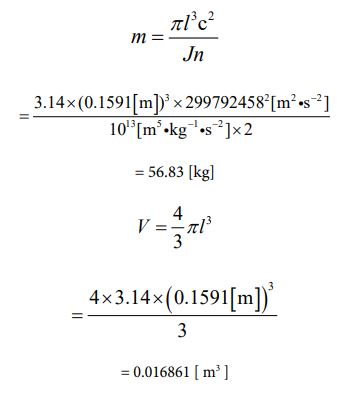
The above results were obtained.
Fortunately, my riddle to the laws of nature through my research has been successful. The reason for this is that I have always been conscious of deriving the global optimum solution, rather than getting caught up in partially optimum solutions. Indeed, a partially optimum solution may be the correct answer to a specific phenomenon or experiment.
However, they are not necessarily the universal correct answer that runs through the entire natural law. Newton derived the law of universal gravitation from Kepler’s planetary law [46]. Niels Bohr derived the atomic model from the spectrum of light emitted from hydrogen gas [47]. Einstein derived the light quantum hypothesis from experiments on the photoelectric effect [48].
Indeed, they were outstanding achievements that left their mark on the history of science. However, they could not be an all-en- compassing global optimum solution. It could be said that narrow-mindedness was the cause of the problem.
Certainly, it will be important to add new work on top of the foundation accomplished by our predecessors.
However, the researcher’s best ground for unraveling the mechanisms of nature is the organic and autonomous nature of the natural world.
What interested me the most was such as an essential part, that is to say, the global optimum solution.
In this paper, I set up a different norm from conventional physics by considering forces and energies to be “relationships” between objects.
I have also led to several new discoveries by doing calculations on specific natural phenomena and experimental facts. The world’s first calculation of the electron radius and quasar radius is an example of this.
And by devising a pervasive system of relational models, I have also succeeded in capturing “light” and the “four forces in nature” within a single framework. The following is a summary of the results.
The number of parties and the distance between them differ. However, “force” and “light” are exactly the same in that they are “relationships” between objects (individuality).
In other words, this paper confirmed the finding that all light, force, and energy are the same (Table 2).
This would apply not only to physics, but also to chemistry, biology, medicine, art-related studies, economics, philosophy, and all other fields.
The era of energy science has arrived.
Then, let’s proceed to the conclusion of this paper.
This universe is, so to speak, a “clockwork organism”. The emphasis on concepts such as “relationship” and “number of parties” in my physical research is based on such a view of nature (organism model). The reason I created relational physics was that the “unification of the four force” by the proximity theory was at a standstill. But the biggest opportunity for it was that such a view of the universe was always in me.