Diabetic Retinopathy, Classification and Clinical Impact
Diabetes mellitus is an increasingly prevalent disease in modern society. Type 1 diabetes mellitus is an autoimmune disorder in which immune system destroys insulin secreting pancreatic islets of Langerhans, hence type 1 diabetic patients are treatable with insulin injection and they are collectively called insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM), whereas, type 2 diabetes is not responsive to insulin injection, so they are called non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM). Except for those patients with insulin resistance, insulin administration remains the best therapy for diabetic patients. However, insulin is a peptide hormone which cannot be administered through oral ingestion but has to be through subcutaneously administration to avoid the proteolytic digestion in the gastrointestinal track. Therefore, an alternative oral therapy for diabetes mellitus is highly desirable. α-glucosidase inhibitors and sulfonylureas are two older oral therapies, but since 1997, pharmaceutical companies have rolled out a series of pharmaceutical agents that target different parts of glucose metabolism. This article will review briefly the mechanisms associated with those recent hypoglycemic agents.
Keywords: Diabetes Mellitus; Orally Active Hypoglycemic Agents
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a chronic disease in which peripheral tissues/organs show blunted responses to insulin stimulation (insulin resistance) and persistent hyperglycemia. T2DM makes up 90-95% of all diabetic cases and the chronic hyperglycemia can lead to non-enzymatic glycation of proteins that eventually causes kidney failure [1], cataract, cardiovascular damages [2], and amputation of extremities due to hypoxia caused by higher oxygen affinity of glycated thymoglobulin [3].
The glucose homeostasis is maintained by balancing between 1) the glucose influx (the rise of blood glucose) through carbohydrate ingestion or gluconeogenesis by liver and kidneys versus 2) the glucose uptake (utilization of blood glucose) by peripheral tissues/organs. Pancreatic insulin is the natural hypoglycemic (blood glucose lowering) hormone in the body that stimulates the uptake and utilization of blood glucose, but its exogenous form has to be administered hypodermically to preserve its peptide constituents and biological activity. Therefore, oral hypoglycemic agents other than reconstituted insulin would provide much desirable convenience for diabetic patients who need to control of his/her blood glucose levels. The review will focus on traditional and recent oral hypoglycemic compounds and how their hypoglycemic mechanisms are achieved.
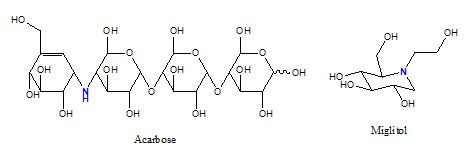
Carbohydrates of polysaccharides require intestinal α-glucosidase digestion (hydrolysis) before releasing free glucose for absorption. The enzyme (EC 3.2.1.20, α-1,4-glucosidase or maltase) cleaves away the terminal glucose that has an α-1,4 linkage to its next glucose. An inhibitor specific for intestinal α-1,4-glucosidase can be used to suppress the postprandial rise of blood glucose in diabetic patients [4]. Common α-glucosidase inhibitors include Acarbose and Miglitol (figure 1). Acarbose is a tetrasaccharide analogue which may also inhibit pancreatic α-amylase, whereas Miglitol is an iminosugar (1-dexoynojirimycin) derivative that resembles a monosaccharide. The most common side-effects of α-glucosidase inhibitors are flatulence and diarrhea, because unabsorbed carbohydrates fuel the growth of intestinal microorganisms.
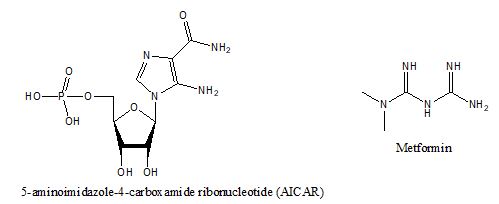
AMPK is an enzyme (E.C. 2.7.11.31) and master switch for energy metabolism [5]. It is activated when ATP is depleted with concurrent increase of cellular AMP. Increased AMP concentrations turn on catabolic pathways for energy production, e.g., glucose uptake, lipid oxidation but shut down anabolic pathways like protein and lipid syntheses [6]. AICAR (5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide, figure 2) is an intermediate in the synthesis of inosine monophosphate (IMP) which resembles AMP and is capable of activating AMPK. Biguanides are another class of compounds that can activate AMPK. Metformin (N, N-dimethylbiguanide, figure 2) is a simple biguanide which is consisted of two guanidine molecules condensed at an ammonia molecule. Metformin is capable of alleviating hyperglycemia through reduced hepatic gluconeogenesis [7] and activation of AMPK[8]. The administration of metformin can lead to reduced appetite and weight loss but may result in diarrhea. Metformin is not metabolized in the body and excreted in the urine without modification. The challenge in developing an activator for AMPK is that AMPK is a heterotrimer and each subunit has multiple isotypes (α1, α2, β1, β2, γ1, γ2, γ3). Since the location and function of each isotype is complicated [9], it is difficult to pinpoint an isotype to develop an effective activator. However, the use of metformin is very common, particularly as an augmenting agent in addition to gliptin (DP-4 inhibitors) [10] or glifozin (SGLT-2 inhibitor) compounds [11].
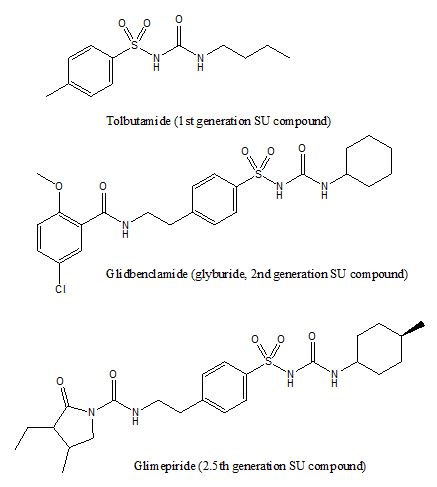
The sulfonylurea compounds are typically consisted of an arylsulfonylurea moiety at the center with substitutions at either end (figure 3). This class of compounds can stimulate insulin release from β-cells within the pancreatic islets of Langerhans, and therefore they are insulin secretagogues. The sulfonylurea compounds engage sulfonylurea receptors (SUR), an integral part of an ATP sensitive potassium channel that is formed by tetrameric Kir 6.1 or 6.2 with tetrameric SUR on the β-cell surface [12]. The engagement of sulfonylurea on the SUR or ATP on the Kir subunits blocks the efflux of cellular potasium and causes a membrane potential depolarization and an influx of calcium and thus leading to the exocytosis of insulin granules [12]. Since sulfonylurea compounds trigger insulin release mechanistically, an overdose (similar to an overdose of insulin) can cause a hypoglycemia which may lead to unconsciousness or even death [13]. Many sulfonylurea compounds have been developed e.g., tolbutamine (1st generation), glibenclamide (2nd generation), and glimepiride (3rd generation, but some consider it 2nd generation).
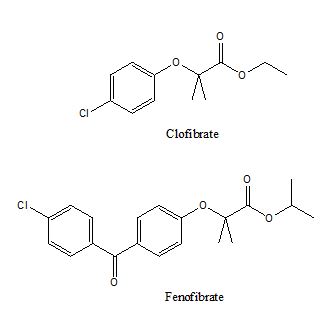
Peroxisome proliferator activated receptors (PPAR) are a group of nuclear receptors that require forming a heterodimer with retinoid X receptor (RXR) to be functionally active at regulating the synthesis/storage/oxidization of adipose lipids [14]. Three major subgroups of PPAR are PPARα, PPARγ, and PPARδ. PPARα is responsible for fatty acid uptake and oxidation. The natural ligand for PPARα is not clear but they can be activated by synthetic fibrates compounds, e.g., fenofibrate, clofibrate (figure 4).
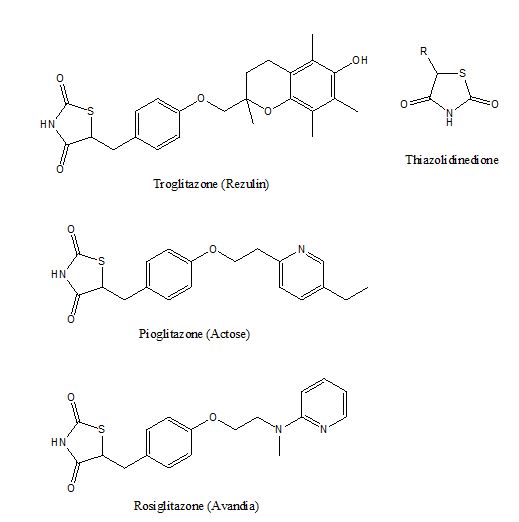
Activation of PPARγ by glitazones with a thiozolidinedione (TZD) pharmacophore, illustrated in figure 5, potentiates adipocytes differenctiation in adipose tissues[15] and resensitize insulin sitmulation[15]. The use of TZD compounds often lead to a side effect of truncal obesity [16] because the activation of PPARγ promotes adipocyte differentiation and down-regulates inflammation in adipose tissues[17]. Troglitazone (Rezulin) was the first glitazone marketed by Warner-Lambert in 1997, but it was withdrawn from the market in late 1990s due to hepatitis side effect (liver toxicity). Rrosiglitazone (Avandia) was released by GlaxoSmithKline in 1999 but its side effect of heart attack had lead to a restriction of use in the US during 2011 to 2013 while it was withdrawn from the European market since 2010. Pioglitazone (Actose) was introduced by Takeda in 1999. It does not have the side effects like those of Rezulin or Avandia, but Takeda admitted that Actose has a propensity of causing fracture among female users. Originally PPARγ agonists are considered a breakthrough as an insulin sensitizer for treating type 2 diabetes, but the rare liver toxicity associated with thiozolidinedione has made them less attractive as an antidiabetic pharmaceutical agent.
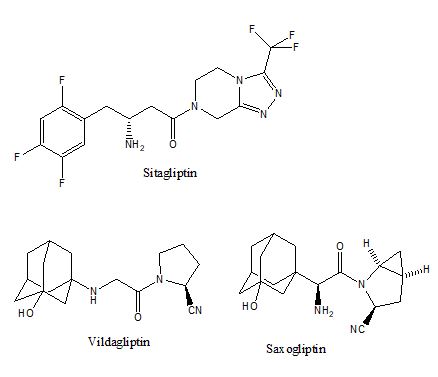
Dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DP-4, EC 3.4.14.5) is a protease domain of the CD26 surface protein on lymphocytes. The protease domain on CD26 can be cleaved off and becomes soluble DP-4 in the circulation. Upon ingestion of food, the L-type enterocytes can secret glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) incretin to synergize the effect of insulin but it is degraded quickly by DP-4 or CD26. Therefore, an inhibition on DP-4 protease activity has been suggested as a new approach to control the postprandial rise of glucose in diabetic patients[18]. The development of DP-4 inhibitor was validated with the CD-26 knocked out mice[19,20], which demonstrated normal physiological phenotypes but resilient to weight gain despite being put on high fat diet[19]. Since DP-4 cleaves off the N-terminal dipeptide from its substrate, many pharmaceutical compounds modelled this dipeptidyl product as a competitive inhibitor, illustrated in figure 6. These compounds are called gliptins collectively, e.g., Sitagliptin, Vildagliptin, Saxogliptin. The hypoglycemic effect of DP-4 inhibitors relies on the action of endogenous GLP-1 through its incretin hormone receptor; therefore, another related class of hypoglycemic agent is GLP-1 analogue, e.g. exenatide.
Exenatide is a 39 amino acid peptide derived from the saliva of a lizard, Gila monster. Exenatide acts as a GLP-1 agonist and bears 50% homology to GLP-1 (30 or 31 amino acid peptide) and has a longer half life (2.4 hr) in vivo, i.e., slower turnover rate. Like insulin, it has to be administered hypodermically to preserve its efficacy. However, some long-lasting formula (weekly [21], and monthly [22]) have been developed. Because the leading sequence of GLP-1, comprised of 6 residues are cleaved off before secretion, circulating GLP-1 starts with residue 7 and penultimate residue 8 of gly or ala are susceptible to dipeptidyl peptidase IV cleavage. Liraglutide and semaglutide are peptide derivatives of GLP-1 but with a few modifications: 1) the last 3 residues of GLP-1, KGR, are replace by RGRG; 2) a fatty acid is attached to residue Lys26 to preserve its half-life by attaching to circultating albumins; 3) the penultimate residue of semqglutide, Ala, is replace by an amino-isobutyric acid (designated as X) to resist DP-4 degradation. Recently orally active semaglutide, has been approved by FDA [23]. Semaglutide adopts several strategies to achieve oral activity, which includes substituting Ala 8 with aminoisobutyric acid (2-methylated alanine) to avoid DP-4 cleavage and attaching a long chain fatty acid to Lys 26, so semaglutide avoids the cleavage of trypsin and enhances its affinity to circulating albumin to elongate its half-life. Peptide sequence of GLP-1 and its analogues are listed in table 1.
A major advantage of prescribing glyptins compounds or GLP-1 analogues is that they avoid the danger of hypoglycemia if overdosed, because GLP-1 activation is not directly tied to blood glucose levels. GLP-1 does not contribute to the rise or drop of blood glucose directly [24].
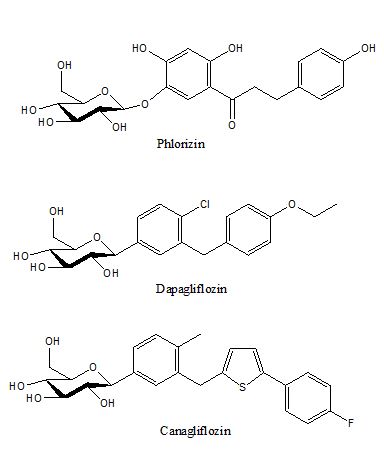
One latest hypoglycemic target is the glucose reabsorption in the kidneys. The kidneys filter through our blood fluid daily, it is estimated that approximately 180 g of glucose is filtered through the kidneys everyday and 90% of the filtered glucose is reabsorbed by sodium glucose cotransporter-2, SGLT-2, in the proximal tubules in the kidneys. Almost all of the remaining glucose is reabsorbed by SGLT-1, less than 100 mg of glucose is lost in the urine of a non-diabetic individual. The mechanism is by hindering the renal reabsorption of glucose, so a significant portion of blood glucose is lost in the urine, and thus the blood glucose level is lowered. Because the glucose level in blood is lowered, long term use of Canagliflozin is reported to have lower hemoglobulin A1c[25], reduced body weight[25,26] and both the systolic and diastolic blood pressures [26]. The earliest SGLT inhibitor is phlorizin (first isolated in 1835), illustrated in figure 7, which is a natural glucoside with strong SGLT-1 and SGLT-2 inhibition capabilities that lead to glucosuria. Because phlorizin is not a selective inhibitor for SGLT-1 or SGLT-2, its clinical application was not developed. Since 90% of urinary glucose is reabsorbed by SGLT-2 in kidneys, selective SGLT-2 inhibitors were developed, illustrated in figure 7. Dapagliflozin was the first SGLT-2 inhibitor by Bristol-Myers Squibb and AstraZeneca. It was approved by the Eauropean Union in 2011, and by FDA in the US in 2014. Canagliflozin was approved by FDA in 2013.
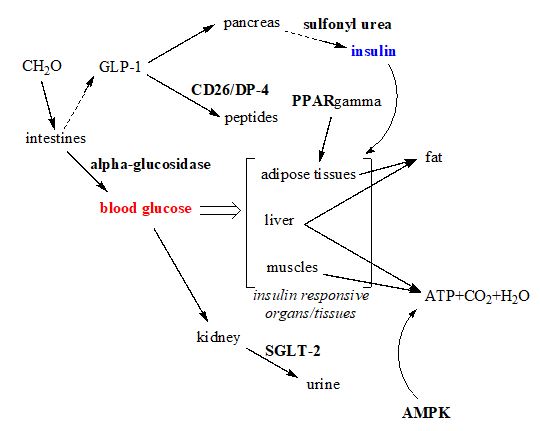
The overall mechanisms of those abovementioned oral hypoglycemic agents are conceptualized in figure 8. The pharmacokinetic parameters of those oral therapies are summarized in table 2. Chronic hyperglycemia is detrimental to protein structure and function at the cellular level, because glucose is an aldose which is readily to react with any amine group exposed on the proteins surface and brings glycation adducts to cells that need to have those nonenzymatic adducts removed before restoring protein’s functions. The latest class of hypoglycemic agent, the sodium glucose transporter inhibitor which forces eliminating blood glucose through urine, is particularly interesting with amazing end-results, which include 1) lowering blood pressures, by eliminating the osmotic pressure of glucose; 2) lowering body weight that signals a negative net energy balance through the loss of glucose in the urine. The loss of body weight and accompanied by lower blood pressures will not only alleviate diabetic stress but also renal stress as well.
Funding: This work was supported by Asia University/China Medical University Hospital joint grant [ASIA-105-CMUH-21], and Asia University/Asia University Hospital/China Medical University Hospital grant [ASIA-106-CMUH-27].
Contributions: JDT contributes to the revision of the manuscript; CCC contributes the latest therapeutic agents; YTC contribute the experiences in emergency care for diabetic patients; HJT is responsible for drafting the manuscript.
Acknowledgement: All authors have no conflict of interests and agreed to publish the manuscript.