Bibliometric and Visualized Analysis of Ampelopsin Researches
Objective: Ampelopsin is the most potent bioactive agent in vine tea. The past thirty years have seen increasingly advances in the field of ampelopsin research. However, there have been no bibliometric studies examining this field as a whole. It would be interesting to assess the prevailing topics and citation performances of its research works.
Methods: The currently analyzed bibliometrics data were extracted from the Web of Science Core Collection database using the search string TOPIC= ("ampelopsin*" OR “dihydromyricetin*”) and analyzed using the VOSviewer software.
Results: The literature search resulted in 566 manuscripts. Nearly more than 75% of them were published since the 2012s. The most contributing country is China, which account for more than half of all manuscripts. These publications were mainly published in journals representing such scientific disciplines as biology, agriculture, food chemistry, nutrition, and medicine. Then it analyzes the recurring keywords and the recurring terms from the title and abstract. Chemicals that were frequently mentioned in the keywords of evaluated ampelopsin publications included ε-viniferin, resveratrol and flavonoids.
Conclusion: Compared with other fields, the field of ampelopsin is still in infancy. The distribution of researches is imbalanced and cooperation between countries, organization and institutions remains to be strengthened. Furthermore, basic food chemistry research occupies an absolute dominant position, and the exploration of the clinical application of ampelopsin may become a key point in the future. These results can serve as a quick baseline for researchers or the general public members.
2. Keywords: Ampelopsin; Bibliometrics; Biochemistry; Cancer; Citation Analysis; VOSviewer; Web of Science
List of abbreviations: AMP: Ampelopsin; DMY: Dihydromyricetin; WoS: web of Science; NC: Normalized citation
Ampelopsin (AMP), also called dihydromyricetin (DMY or DHM), is an important flavonoid compound, which is found with high content in vine tea (also known as rattan tea, mildewed tea). Vine tea widely distributes in Guangxi, Yunnan, Guizhou, Hunan, Hubei, Fujian and other southern mountainous areas in China. The Zhuang and Yao ethnic minorities have used the young stem and leaf of rattan tea for health benefits since ancient times, and its safety is well established. Analysis of the phytochemicals revealed that dihydromyricetin and myricetin were two major flavonoids in rattan tea. In addition, ampelopsin (20-30%, w/ w) was much higher than myricetin (1.5-3.0%, w/ w) [1].
Flavonoids perform a variety of health functions, such as scavenging free radicals, anti-thrombosis, anti-inflammatory, and anti-tumor activities [2]. In addition to these health functions of flavonoids, ampelopsin also appears to effective at influencing the risk of other diseases including atherosclerosis [3], myocardial injury [4], chemical liver injury [5], neurodegeneration [6] and some types of cancers [7,8]. Ampelopsin can effectively inhibit tyrosinase activity, reduce melanin content in cells, inhibit the growth of melanoma, and prevent skin damage caused by ultraviolet rays [9].
With the increase in phytochemical research and published articles on ampelopsin and health, understanding the trends and research advances is essential. A bibliometric study could serve as a useful tool for this purpose. Similar research has been conducted in other areas such as ethnopharmacology [10], neuropharmacology [11], nutraceuticals [12], and oncology [13]. However, the current states of ampelopsin research and major research topics change have not been summarized. The purpose of the current study is to identify and analyze publications on ampelopsin to outline the major contributors in terms of author affiliations, countries/regions, and journals. The results may help to reveal the major research themes present in the literature about ampelopsin, based on the publication and citation data. The information is helpful for researchers to quickly have a general overview of the ampelopsin literature landscape, including prominent authors, major output countries, and prevailing major research topics and trends. The provided information can also be used to identify potentially promising research directions and possible collaboration partners, and to give initial orientation to direct further more in-depth searches for the identification of relevant publications or research opportunities.
All data were acquired from the Clarivate Analytics-owned Web of Science (WoS) Core Collection online database in September 2020. To identify ampelopsin publications, the following search string was used: TOPIC= (“ampelopsin*” OR “dihydromyricetin*”). This search string identified publications that mentioned the word “ampelopsin” or its derivatives in the title, abstract, or keywords. We did not place additional restriction on the search strategy, such as publication year, publication type, or language.
The publications identified from the search were evaluated by: (1) publication year; (2) author affiliations; (3) countries/regions of the affiliations; (4) journal title; (5) WoS category; (6) publication type; (7) language; and (8) total citation count. The full records and cited references of these publications were downloaded and loaded into VOSviewer for further bibliometric analyses.
The VOSviewer software (v.1.6.15, 2020) is capable of extracting and analyzing the semantic contents of the titles, abstracts, and keywords of publications, relating them to the citation count data and generating a bubble map to visualize the results [14]. Default parameters were used for the analyses and creation of bubble maps. The font size of the words in the bubble map indicates their frequency of occurrence (multiple appearances in a single publication count as one). Two words are nearer to each other if they co-occurred in the evaluated publications more frequently. For the keyword map, full counting method was used, meaning that each co-occurrence link carried the same weight. The default “association strength method” was used for normalization of the co-occurrence matrix with default values of attraction and repulsion.
To better explain the potential, confound of publication date on the citation count, we further analyzed the normalized citation (NC) counts, which are expressed with values starting from 0 with no upper limit. When a term has NC = 1, it means that the publications in which the term occurs, either in the title or abstract, have received the same number of citations as the average number of citations of all ampelopsin publications from the same period (the same year of publication). Similarly, if NC = 2, the term has twice the number of citations than the average citation count of the publications from the same period. This corresponds to the concept of average NC impact in the VOSviewer.
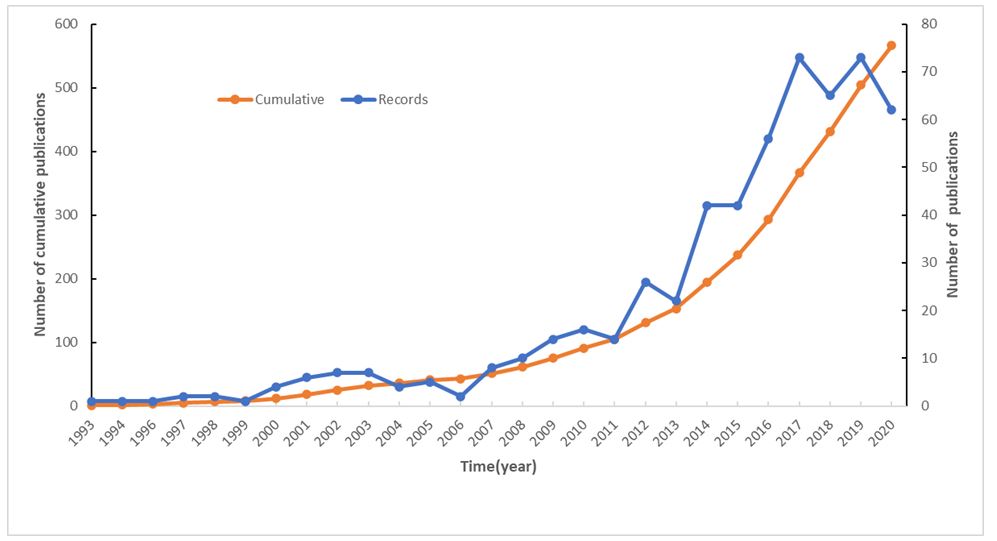
A total of 566 publications were acquired through the primary literature search. The annual trend of ampelopsin publications was shown in Figure 1. The first article was published in 1993, and a very slow increase was found in the following 20 years. More than three quarters of the analyzed papers have been published since the year 2012. The increasing trend led to a jump in the number of publications in 2017 (n=72). As the quantity of publications was rapidly increased, the number of cumulative publications has reached 505 in 2019. In September 2020, there are 62 publications on ampelopsin, revealing that the ampelopsin-related research is receiving more and more attention.
The top five contributors with regard to country/territory, organization, and journal are listed in Table 1. These countries or regions had 13.04–26.30 citations per manuscript. The majority of the publications were contributed by China (n = 345, 60.95%). Moreover, we found that the top 5 organizations were all from China. Among them, The Third Military Medical University contributed the most publications on ampelopsin (24 papers), followed by Chinese Academy of Sciences, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. Meanwhile, the top 5 most prolific organizations have 11.88-25.73 citations per manuscript. Among them, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences had the highest average citation rate. Further normalized citation count analyzes showed that manuscripts contributed by the Third Military Medical University had higher NC counts (NC=1.86) than other organizations. Contributions came from 672 organizations (author affiliations) from 55 countries/territories and were published in 288 academic journals. The top 5 journals of citation per manuscript were those dealing either with food science or plant science. Phytochemistry is a leading international journal publishing studies of plant chemistry, which belongs to the biology industry. In this table, when NC was considered, manuscripts published in food chemistry were 2.14 times higher than the average published in the same year.
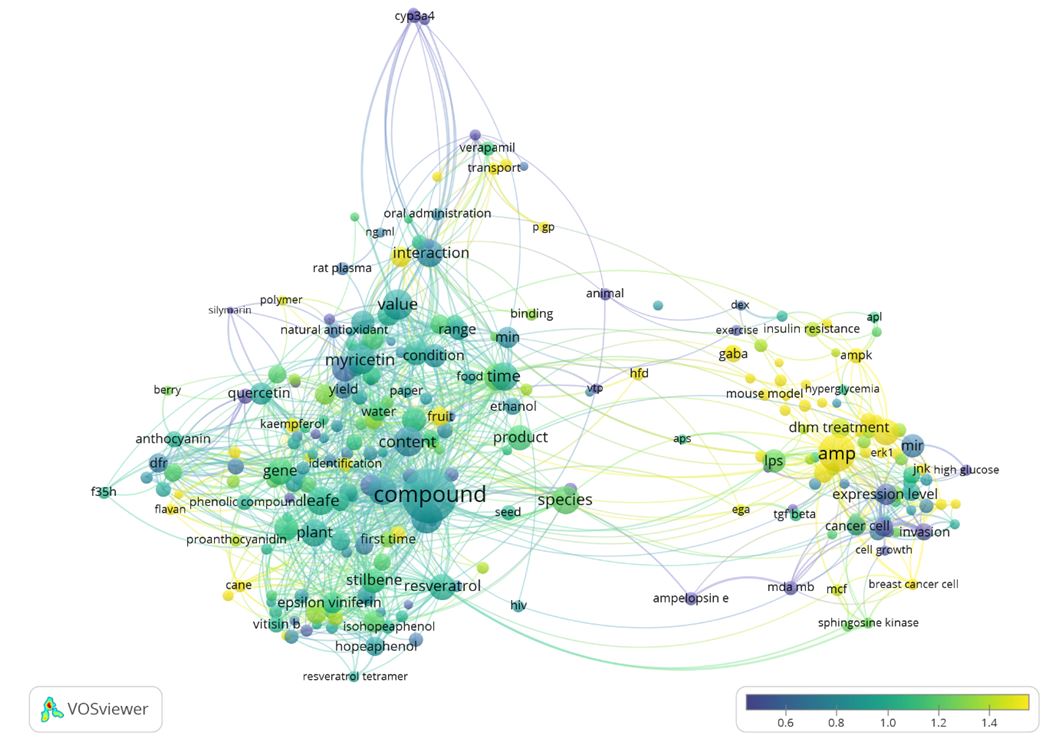
There were 433 terms that met the threshold of the evaluated publications. By analyzing these words in the titles and abstracts of the 566 publications, we observed that compound (n = 318, citations per publication =15.03, NC=0.88) is repeated most often in the data (Figure 2). The second highly repeated term is ampelopsin (n = 149, citations per publication =20.45, NC=1.65). NC data showed that articles with the top 20 recurring terms from titles and abstracts generally had higher citations than average. Other words such as “structure”,”extract”, ”species”, ”vine tea”, ”leaves” and “plant” were also included in the top 20 recurring terms, revealing that ampelopsin is an important active ingredient of vine tea leaves.
VOSviewer software was used to analyze and visualize recurring terms. Only words that appeared in at minimum number (10) of occurrence of a term were analyzed and visualized. There were 260 terms that met the threshold of the evaluated publications. The word size indicates the appearance frequency of the words (multiple appearances in a single manuscript counted as one). Two words are closer to each other if they co-occurred more frequently in the evaluated publications. Bubble colors represent the normalized citation of the terms.
Moreover, we observed that ampelopsin co-occurred with other notable highly cited themes of the publications. These terms were resveratrol (n = 72, citations per publication = 20.90, NC=0.98) and myricetin (n = 88, citations per publication = 13.16, NC=0.89). The top 20 recurring terms are listed in Table 2.
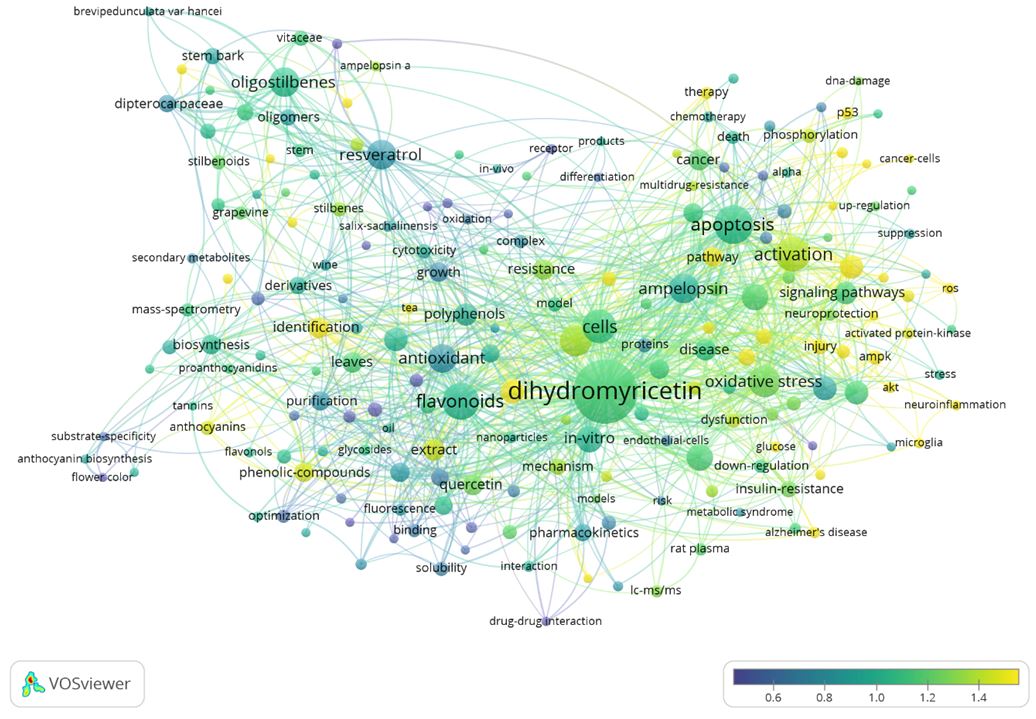
Subsequently, we analyzed the keywords included into publications. As we know keywords are important for document searching and retrieval, authors usually carefully consider keyword selection for relevance, and a higher frequency of keywords use could indicate their importance. Only the keywords that appeared in at minimum number (5) of keyword occurrence of the publications were analyzed and visualized. There were 204 keywords that met the threshold of the evaluated publications. In the bubble map presented in Figure 3, the size of the text/bubble is reflecting the frequency with which the keywords were used, and the color of the bubble is reflecting the citation frequency of the manuscripts in which the keywords were occurring. Therefore, a bigger size of the text/bubble might indicate a higher number of papers dealing with the respective topic, and a higher “intensity” of the color (according to the presented “color scale”) reflects higher impact (more citations obtained) of the manuscripts. The major themes were similar as reported above (Figure 2) for the words in the titles and abstracts of the 566 publications. Here, as evident from Figure 3, we can see the visualized research hotspots. "Dihydromyricetin"(n = 207, citations per publication = 11.49, NC=1.14) and "apoptosis" (n = 74, citations per publication = 12.92, NC=1.05) turned out to be the core keywords. The closest relationships between "dihydromyricetin" and "apoptosis" implied the research hotspot was the apoptosis mechanism of cells. In addition, the keyword of “oxidative stress” (n = 49, citations per publication = 12.22, NC=1.29) suggests that AMP possesses high antioxidant capacity.
We used VOSviewer software to analyze and visualize recurring keywords added to the publications by the authors and by Web of Science. Only keywords that appeared in at minimum number (5) of occurrence of a keyword of the publications were analyzed and visualized. There were 204 keywords that met the threshold of the evaluated publications. The word size indicates the appearance frequency of the words (multiple appearances in a single manuscript count as one). Two words are closer to each other if they co-occurred more frequently in the evaluated publications. Bubble colors represent the normalized citation of the terms.
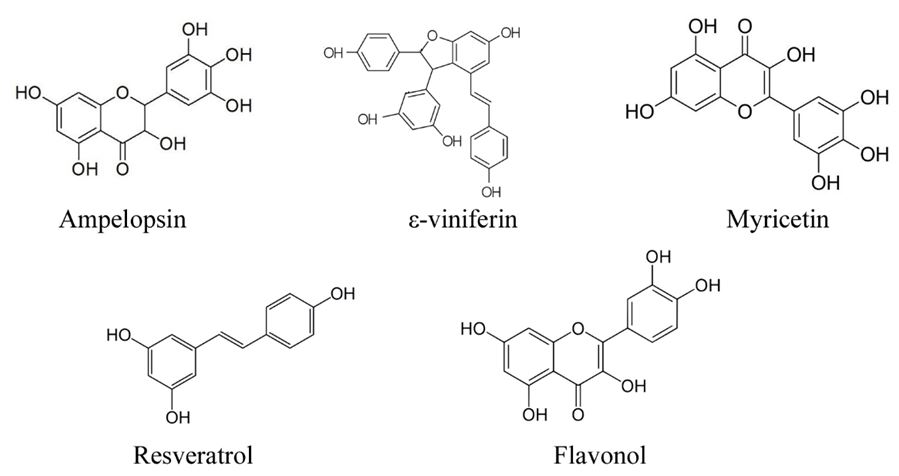
Meanwhile, several compounds were frequently mentioned in the keywords of evaluated ampelopsin publications, such as flavonoids (n = 69, citations per publication = 16.65, NC=1.00), oligostilbenes (n = 42, citations per publication = 28.5), resveratrol (n = 38, citations per publication =16.5), and myricetin (n = 19, citations per publication = 11.3). Their chemical structures are shown in Figure 4. It can be seen from the chemical structure of these compounds that they all have the structure of phenolic hydroxyl group and possess strong antioxidant properties.
Bibliometric analysis is a useful tool to describe knowledge structure and development trends in a particular area [15]. Studying the characteristics of highly cited research in journals enables to provide a comprehensive view of research development and dynamic changes of topic hotspots. For this reason, we performed a bibliometric analysis of publications in ampelopsin research from 1990s to present.
In our study, the result showed a rise in the number of articles published on ampelopsin in recent years. This trend indicates that ampelopsin research has been improved greatly and attracted more attention in the global researchers. But the number of publications or citations on ampelopsin is relatively small compared with other research fields, indicating this research field is still in infancy and needs further exploration.
Visual analysis of titles and abstracts indicates that single phytochemical does not work as well as compounds combination. For example, anti-proliferation effects of ampelopsin C were enhanced when combined with luteolin and chrysin when compared with either two or a single agent in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells [16]. Dihydromyricetin can significantly reduce the serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), creatine kinase MB (CKMB) activity of doxorubicin-induced myocardial apoptosis injury and abnormal cardiac electrophysiological activity [17]. Furthermore, studies have found that dihydromyricetin combined with nedaplatin can significantly improve the sensitivity of liver cancer cells to chemotherapy and reduce the cytotoxicity of the latter, suggesting that dihydromyricetin may have the potentials to be developed as an anti-liver cancer or adjuvant drug [18].
Among the keywords, oligostilbenes (citations per publication = 31.42) had the highest average citation. Oligostilbenes are polyphenol oligomers derived from resveratrol and are commonly produced by members of the Gnetaceae family. The current basic studies on oligostilbenes were mostly focused on their anti-inflammatory activities [19]. Naturally occurring-viniferin, an oligomer of resveratrol usually found in Carex pumila and C. Lactiflora extracts, displays antibiotic activities against Gram-negative bacteria such as Escherichia (E. coli) [20]. Resveratrol is a polyphenolic nutrient that has shown pleiotropic activity in human subjects. It is reported that resveratrol can improve the therapeutic outcome in patients suffering from diabetes mellitus, obesity, colorectal cancer, breast cancer, multiple myeloma, metabolic syndrome, hypertension, Alzheimer's disease, stroke, cardiovascular diseases, kidney diseases, inflammatory diseases, and rhinopharyngitis [21].
Meanwhile, we observed that several cancer-related themes were frequently mentioned, such as apoptosis (n = 74, citations per publication = 12.92, NC=1.05), autophagy (n = 29, citations per publication = 18.07, NC=1.61), and oxidative stress (n = 49, citations per publication = 12.22, NC=1.29). Frequently mentioned components for the potential mechanisms included nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB, n = 28, citations per publication = 14.5, NC=1.14). Among them, those with higher citations per publication but fewer occurrences were AMPK (n = 10, citations per publication = 15.2, NC=3.18), P53 (n = 8, citations per publication = 12.75, NC=1.62) and AKT (n = 7, citations per publication = 34.86, NC=1.78). Previous researches show that dihydromyricetin may inhibit tumor growth by inhibiting NF-κB [22], AKT [23], P53 [24] and AMPK pathways [25]. The keywords suggested that many of the studies were conducted in vitro using (cancer) cells, however in vivo studies using animals and clinical studies in humans are insufficient.
The present bibliometric analysis outlines mainstream publications and citation trends on ampelopsin, however, several limitations need to be acknowledged. Firstly, the current study only used a single database (WoS) to collect publications. In the future, adding other scientific databases can expand the scope of the dataset. Secondly, the analysis is retroactive and may remain undetected due to recent trends (which still do not produce a large number of publications due to their novelty). Thirdly, due to a large number of Chinese authors who have similar initials that will cause inaccurate counting, we did not analyze the authorship of ampelopsin publications [26]. Lastly, the readers should keep in mind that some highly cited articles might skew the results when interpreting the citation data for each manuscript. Even though geometric or truncated methods could better explain this, it is not possible to use the geometry or truncation methods of the VOSviewer. Besides, we report that the performance of NC citations is compared with the average number of citations in all relevant ampelopsin publications (within the dataset) for the same period (year). Despite all these limitations, these findings provide insights and research opportunities for researchers and executives in ampelopsin and other closely related phytochemicals so as to investigate its future applications in disease prevention and treatment. Furthermore, it is hoped that more experimental and clinical studies are needed to promote the clinical application of ampelopsin.
In conclusion,a bibliometric analysis was conducted to evaluate manuscripts concerned with ampelopsin. So far, although not many manuscripts have been published about ampelopsin, the available data show that China is a major contributor to ampelopsin research areas, with the top five most prolific institutions all from China. The most prolific journals were mainly specialized in food chemistry. More than three quarters of the publications were published since 2012, which mainly focused on food chemistry. Further research is needed on the clinical application of ampelopsin. Third Military Medical University contributed the most publications on ampelopsin, especially on its biochemical and therapeutic properties, such as tumor prevention and lipid metabolism regulation. Manuscripts involving myricetin, resveratrol, oligostilbenes and flavonol have provided references for the development of ampelopsin research.This work was funded by the Open Project of Key Laboratory of Electromagnetic Radiation Medical Protection of Ministry of Education, Army Medical University (2017DCKF002) to ZHOU Yong. We would like to thank Irakoze Laurent for his careful reading and editorial corrections for this manuscript.