Development and Ex-vivo Evaluation of a Novel Device to Facilitate and Standardize Intravitreal Injections in Rabbits
Rabbits are frequently used to study the pharmacokinetics and toxicology of compounds delivered into the eye as they are a translatable animal model. The aim of this study was to develop a device which facilitates and standardizes intravitreal injections in rabbits. Similar devices for intravitreal injections in humans already exist and have shown to prevent damage to the retina and lens. We hypothesized use of the new device would increase the precision of injections and results would be comparable between experienced and novice operators. Prototype devices were produced using 3-dimensional (3D) printing and trailed using a 3D-model of the eye. The final device was produced using injection-molding. Two aspects were investigated using ex-vivo rabbit eyes; (1) Location of contrast-agent-deposition within the vitreus following device-guided and freehand injections by a novice operator was analysed by magnetic-resonance-imaging (MRI). (2) The anatomical location of the needle-penetration-point following device-guided and freehand injections by one experienced and three novice operators was evaluated using histology. Our results indicate that the device can successfully be used to deliver compounds into a favourable mid-vitreal location. Following device-guided injection the contrast-agent was never located in direct proximity to the lens while this was the case in over half of freehand injections. We interpret this as a safety benefit of the device as it consistently directs the injection away from the lens. Contrary to our hypothesis the device did not lead to increased precision nor did it allow novices to achieve comparable results to an experienced operator. In conclusion, the device facilitates intravitreal injection to rabbit eyes and might offer a safety benefit as it directs the needle away from the lens. Further in vivo studies are required to evaluate the device’s effects on the safety and pharmacokinetics of intravitreal injections.
Keywords: Device; Drug Delivery; Eye; Injection; Intravitreal; Methods; Rabbit; 3R’s; Vitreous
Rabbits are often used to establish the safety of compounds delivered via intravitreal injection and they are a clinically translatable animal model for intravitreal pharmacokinetics [1,2]. The rabbit eye is large enough to perform accurate intraocular injections but certain anatomical features - namely the structure of the vitreous humor, the relatively large lens and the small pars plana – create specific challenges with regards to standardizing the procedure and ensuring good quality data.
Standardization of the exact location of compound delivery into the vitreous is of particular interest for pharmacological evaluations of novel compounds owing to the structure of the vitreous humor [3]. The precise location will have a marked effect on the distribution of a drug and its elimination from the vitreous [4]. A central mid-vitreal drug deposition has been suggested to reduce unwanted vitreal reflux [5].
The rabbit eye also contains a relatively large lens and damage to the lens, resulting from an inappropriate injection angle, invariably leads to early termination of an animal and loss of data.
The optimal location of the needle-penetration-point when injecting into the vitreous is the pars plana which is located between the retina and ciliary body [6-8]. This injection location ensures sensitive tissues such as the retina and choroid are avoided [9]. In the rabbit, the pars plana measures only approximately 1 mm and the only external feature that can be used to estimate its location is the distance from the limbus [10].
In a human patient, intravitreal injections are performed by specialized ophthalmic surgeons, who perform multiple procedures every day and achieve high levels of expertise and dexterity. However, in preclinical animal studies, intravitreal injections are usually performed by academic or technical staff who are trained “on the job” by either experienced ophthalmic specialists or other competent staff but without the in-depth expertise of an ophthalmic surgeon who regularly carries out the technique. Acquisition and maintenance of the required dexterity to perform intravitreal injections accurately and safely can be impeded by low numbers of procedures and long gaps between studies. Various operators with a range of dexterity and experience will inevitably introduce inter-operator variability with regards to the injection and drug deposition site which could further impact on the results of pharmacokinetic studies.
Devices designed for intravitreal injections in humans such as the InVitrea or the Doi-Uematsu Intravitreal Injection Guide have been shown to prevent damage to the retina and lens. They stabilize both the eyeball and the needle and make the procedure easier and safer owing to the reduced number of procedural steps required [11-13]. Further benefits include a statistically significant reduction in pain perception, shortened procedure time, cost savings and standardization of needle-penetration-point [13].
While Miura, et al. used the instrument designed for humans in a preclinical study with rabbits, a device specifically designed for the anatomy of the rabbit (taking into consideration the large lens and small pars plana) does not yet exist to the author’s knowledge [11]. In the pre-clinical setting a device with the properties mentioned above could offer considerable 3Rs benefits: More consistent results could lead to a reduction of animal numbers needed to support pharmacokinetic studies. Any reduction in pain perception would lead to a refinement of the procedure for the animal. Standardization of the location of drug deposition, the needle-penetration-point and a reduced risk of damage to the lens would improve data quality. Additionally, a device to guide intravitreal injections could potentially allow less experienced staff to perform standardized injections. This would be especially valuable in an early discovery or academic setting where intravitreal injections are not performed routinely, or where intravitreal injections are new to the group and access to experienced ophthalmic surgeons is limited.
The purpose of this study was therefore to design and develop a device specifically designed for the anatomy of the rabbit eye which facilitates intravitreal injections in this species.
We hypothesized that - by fixating the needle to enter the eye to a predetermined depth, angle and needle-penetration-point - use of the device would lead to increased consistency regarding the location of drug deposition and needle-penetration-point. We further hypothesised that the device would enable novice operators to achieve comparable results to an experienced operator.
Only rabbits that had previously been euthanized at the end of unrelated scientific procedures were used to support this study and all work was conducted ex vivo. All animal studies had been scientifically and ethically reviewed and approved by GSK internal ethical review committees and were carried out in accordance with the Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act 1986 and the internal GSK Policy on the Care, Welfare, and Treatment of Animals. Further information on the strain, husbandry and health status of the animals can be found in Supplementary Information (Animals). All experimental procedures described below were carried out within 5 minutes of death, with the eyes remaining in situ.
To gain a better understanding of the required dimensions and specific measurements of the intravitreal injection device the vertical and horizontal diameter of the orbit and the cornea were measured in 90 New Zealand White (NZW) and 156 Chinchilla Bastard rabbit eyes using calipers (Fisher Scientific Traceable®). A literature search was performed for additional anatomical data of the rabbit eye. To better understand the location of the pars plana in relation to the externally visible limbus, histology was carried out on cross sections of enucleated eyes of nine NZW rabbits. Slides were digitally scanned with Hamamatsu Nanozoomer scanner and examined using Hamamatsu’s NDP. view software. The mean distance of the limbus to pars plana/retina junction (in mm) was measured in two positions per eye (Supplementary Information Figure 1).
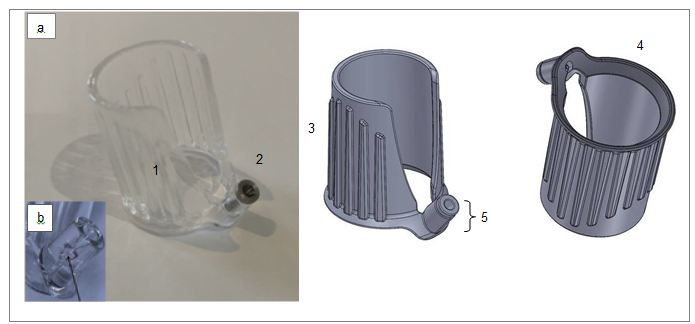
Origin Product Design Ltd. used the anatomical data to create a computer-generated 3-dimensional (3D) computer-aided design (CAD) simulated eye model using Solid works design software. From this 3D-CAD model, an anatomical model of the rabbit eye was produced using 3D printing technology incorporating three different hardness polyurethane materials (Supplementary Information Figure 2). These materials were semi-opaque and of a consistency that was suitable to insert a needle. The position of the needle within the rabbit-eye-model in relation to the lens and the vitreous could be assessed visually. Four alternative device prototype designs were developed and produced using Origins Object 3D printer. These prototypes were trialed for their practical aspects including ergonomics, ease of placement on the anatomical rabbit-eye-model and ease of insertion of the needle into the injection guide. Using the feedback from these trials the designs were refined and further prototypes were produced. These were evaluated with regards to the needle-penetration-point using histology in an ex vivo study (data not shown). A final design was agreed and the intravitreal injection device produced using injection molding. As an unexpected and undesirable effect of the production process the injection guide contained an air bubble, which hindered smooth needle insertion. To mitigate this problem a stainless-steel-insert was placed in the injection guide as a final modification.
Randomisation and Blinding
The experimental unit was the eye. Left and right eyes were randomly distributed to treatment groups using Microsoft Excel software. The MRI and Histology image analysts were blinded to the treatment groups.
Location of Contrast-Agent-Deposition within the Vitreus
To evaluate the location of drug deposition within the vitreous and its location in relation to the lens a suitable contrast agent (10 μL of dextran-coated iron oxide nanoparticles, Endorem®, Guerbet S.A. 0.112mg Fe per ml) was injected by a novice operator. A total of 24 eyes were injected with 2 different needle types attached to a Hamilton MicroliterTM syringe. There were three treatment groups (1) Freehand injection, n = 9 and (2) device-guided injection both using a 30G 13-mm-needle (BD MicrolanceTM 3, 30G
x ½‘’, 0.3-mm x 13-mm), n = 9. (3) Device-guided injection using a 19-mm-needle (30G x ¾’’, 0.3-mm x 19-mm, Cooper’s Needle Works LTD), n = 6.
Device-guided injections were performed by placing the device on the eye after slightly lifting the eyelids. The device was centered by checking that the pupil was central and an equal amount of sclera was visible within the circumference of the device. A mild downward pressure was applied and the device was turned to move the injection guide into the supero-temporal quadrant of the eye. The needle was inserted into the injection guide and advanced to its full length until the hub touched the injection guide. This lead to a fixed injection depth of 6 mm when used with a 13-mm-needle and 12 mm when used with a 19-mm-needle.
Freehand intravitreal injections were performed using an eyelid speculum (FST # 17000-03) to retract the eyelids. The eye was stabilized with conjunctival forceps (Katena J12, K5-182). The needle was inserted into the supero-temporal quadrant of the eye as deep as possible without touching the eye with the hub (ca. 10 mm), approximately 4-5 mm away from the limbus and at an angle which avoided hitting the lens (approximately 40˚).
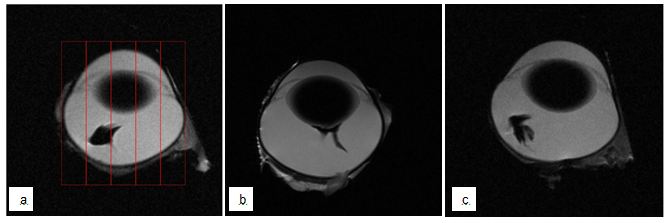
Immediately after the injection eyes were removed from the orbit and placed in the middle of a 4.7T Bruker MRI system with a 35-mm RF send/receive volume coil. Scans were acquired using T2-weighted Turbo RARE scan (Field of View – 30-mm. Voxel size (x,y,z) – 0.15625, 0.15625, 1 mm). Iron oxide nanoparticles appear as areas of no signal (black). Contrast-agent-deposition was scored by analyzing three planes of the eye (lateral, vertical, rostral) and dividing each plane into 5 segments. Contrast-agent that was present in the central segment was scored 0 (closest to desired mid-vitreal location), middle segments were scored 1 and the peripheral segment was scored 3 (furthest from the desired location). If contrast-agent was present in more than one segment the mean was calculated. Scores from all three planes were added to achieve the contrast-agent-deposition score. Additionally, images were assessed as to whether the contrast-agent was deposited in a location touching the lens.
Anatomical Location of the Needle-Penetration-Point
To evaluate the anatomical location of the needle-penetration-point and assess the effect of the experience level, 48 eyes of NZW rabbits were randomly allocated to four operators (one experienced and three novices). Each operator performed six device-guided and six freehand injections as described above.
Novice operators had not previously performed intravitreal injections and were trained solely for the purpose of this study. They were shown a semi-schematic drawing of the rabbit eye and an image comparing the primate eye with the rabbit eye to illustrate the anatomy of the rabbit eye and in particular to point out the large lens and small pars plana [10,14]. The pars plana was pointed out as the preferred anatomical location for the needle to penetrate the eye. The importance of choosing an appropriate injection angle to avoid damage to the lens was stressed. Following the theoretical training novice operators performed both device-guided and freehand ex-vivo intravitreal injections until deemed proficient by the supervising veterinary surgeon.
The experienced operator had conducted extensive freehand intravitreal injections in live animals successfully. All injections were performed using a 30G, 13-mm-needle (BD Micro lanceTM 3, 30G x ½‘’, 0.3-mm x 13-mm) attached to a 1-ml syringe and 50 μL of sterile saline was injected.
Immediately after the injections eyes were removed and prepared for histology as described in the Supplementary Information (Histology Protocol). The junction between the retina and the pars plana, the needle-penetration-point and the junction between the ciliary body and the pars plana were marked using Hamamatsu NPD. view software. The distance between the needle-penetration-point and the retina/pars plana junction was measured (μm). The numbers of injections which penetrated the pars plana, retina and the ciliary body were counted.
Given a primary objective to compare precision rather than average position, a 2-sided F-Test for equality of variance was used to compare needle-penetration points rather than a standard t-test or ANOVA. ANOVA (Fishers LSD test) was however used to compare MRI-agent-deposition scores and Person’s chi-squared test for penetration counts. Measured data was square root transformed before analysis to allow for deviations in variation across the measurement scale, with standard deviations (SDs) used to describe variability between measurements and standard errors (SEs) where differences between means are compared. Statistical significance was set at *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01. A formal power calculation to determine sample size was not possible due to the unavailability of comparable prior data. Group sizes were largely determined by practical constraints but are thought to be reasonable for this type of initial evaluation study. Data were analysed with commercial software (SAS, JMP® 12.2.0).
The aim of this study was to design and develop a device which can be used to inject into the vitreous of rabbits and this aim has been achieved. Design features of the final intravitreal injection device include a transparent body to allow visibility of the needle-penetration-point, vertical grips for easy manipulation and a stainless-steel-insert with a large lead in angle within the needle guide to facilitate needle insertion (Figure 1). During the initial manufacturing process an air-bubble was noted within the injection guide (Figure 1b) and this problem was mitigated by inserting the stainless-steel-insert for the final device.
Further specifications of the device can be found in Table 1. Anatomical data used to design the device are presented in the Supplementary Information Table 1.
The production costs of the device including sterilisation (autoclave or ethylene oxide) are anticipated to be reasonably low so that the device can be used as a single-use item and be discarded after each animal. Comparing the cost of a single-use device versus a conventional pack used for intravitreal injection (containing lid speculum, callipers, conjunctiva forceps etc.) Ratnarajan, et al. have found that the single-use device was more cost efficient, leading to a saving of £7.70 per patient [13]. Additional to a potential cost saving the new single-use device could augment aseptic technique and improve the safety of the procedure in facilities were supply of sterile instruments or access to autoclave or ethylene oxide is limited. Any queries regarding purchasing of the novel device should be directed to Origin Product Design Ltd.
Operators commented favourably about the stabilization of the eye achieved with the device compared with using the speculum and conjunctiva forceps during freehand injections. Additional results are presented in the Supplementary Files.
The depth and angle of injection and therefore the location of drug deposition within the vitreous and its location in relation to the lens are important aspects with regards to pharmacokinetic studies [6, 7, 15, 16]. Injection angles must be chosen appropriately to avoid the risk of damaging the lens, as damage to the lens inevitably results in exclusion of the animal from the study and loss of data [6, 7]. The injection angle of the device was fixed at 40˚ and this angle has proven to reliably miss the lens in the computer model and the printed eye model during the development phase. Commonly reported injection angles for freehand intravitreal injections in rabbits are approximately 45˚ or are described as directed into the mid-vitreous under direct visualization [17-19]. Our results show that none (0/11) of the injections made with the device (either with a 13-mm or 19-mm-needle) led to contrast-agent-deposition touching the lens (see Figure 2c for representative image), while this was the case in 67% (6/9) of freehand injections (see Figure 2b for representative image). This difference was statistically significant (P = 0.0053, Pearson’s Chi-square test, n = 20) (Figure 2).
Although the present study did not directly evaluate the lens itself, we interpret our results as a safety advantage of the device as it consistently deposits contrast-agent in a location not touching the lens.
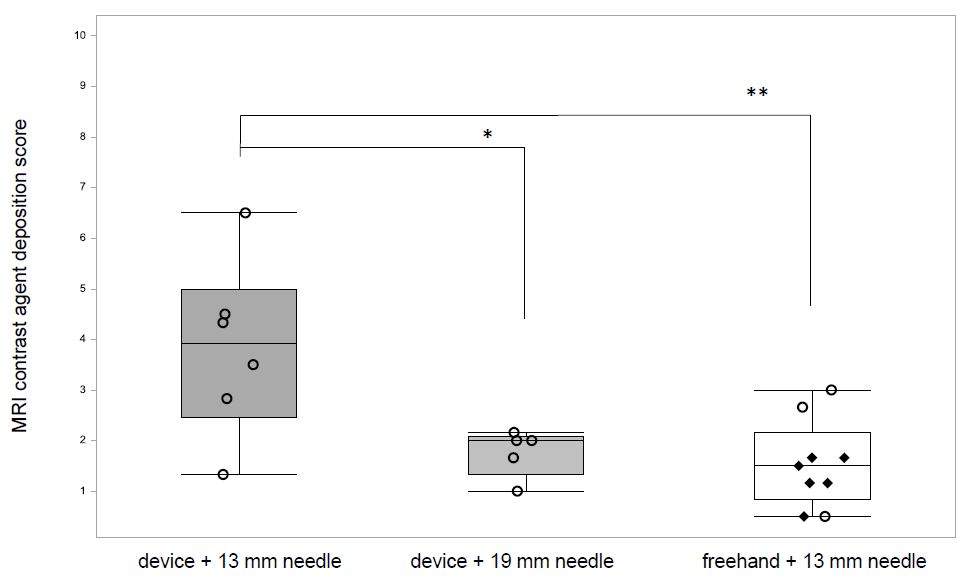
The depth of injection will determine the location of drug deposition within the vitreous. The rabbit vitreous is organized into three distinct layers with variable consistency and the injection location has a substantial effect on material distribution and elimination in the vitreous [15,20, 21]. A study has shown that depending on the injection location the mean concentration of drug remaining in the vitreous after 24 hours varied by up to a factor of 3.8 [16]. We had anticipated that device-guided injections would lead to a higher precision of drug deposition compared with freehand injections, but found that both freehand and device-guided injection (with a 19-mm-needle) resulted in comparable precision and low scores which translate to a mid-vitreal contrast-agent-deposition (SE 1.53 ± 0.86, n = 9 and 1.76 ± 0.46, n = 5, respectively) (Figure 3). In contrast, the device used with a 13-mm-needle did not lead to comparable precision and mid-vitreal injections (SE 3.83 ± 1.74, n = 6) and the difference in mean scores was statistically significant (device 13-mm vs. device 19-mm, P = 0.0156; device 13-mm vs. freehand, P = 0.0016, ANOVA Fisher’s LSD test) (Figure 3).
Our results show that there is no difference in the precision of the location of contrast-agent-deposition within the vitreous between freehand and device-guided injections. Future PK studies will be required to verify this result in-vivo
Contrast-agent was detected in 100% (9/9) of freehand-injections, 83% (5/6) of device guided injections using a 19-mm-needle (which leads to an injection depth of 12 mm) and only 67% (6/9) of device-guided injections using a 13-mm-needle (which limits the injection depth of 6 mm). We had anticipated that the 6-mm injection depth of the device, when used with a 13-mm-needle, would be sufficient; A device used to deliver compounds into the vitreous of humans (who have a larger eyeball than the rabbit) limits the injection depth to 6 mm and most commonly 13-mm-needles which are inserted into the eye to an approximate depth of 10 mm are used for intravitreal injections in rabbits [13,18,22]. The most likely explanation for the missed doses is incorrect positioning of the device. If during the procedure, the device was moved and lifted from its correct position, the needle might not have been long enough to enter the vitreous. Another explanation is that the Hamilton syringe had not been loaded with the contrast-agent or that the very small injection volume of 10 μL might have been expelled from the syringe before injection into the vitreous. In conclusion, we recommend using the device with a needle of a sufficient length to ensure equivalent injection depths to the routinely used 13-mm-needle. When using the device, the operator must pay great attention to the correct positioning, both during initial placement and during the procedure itself.
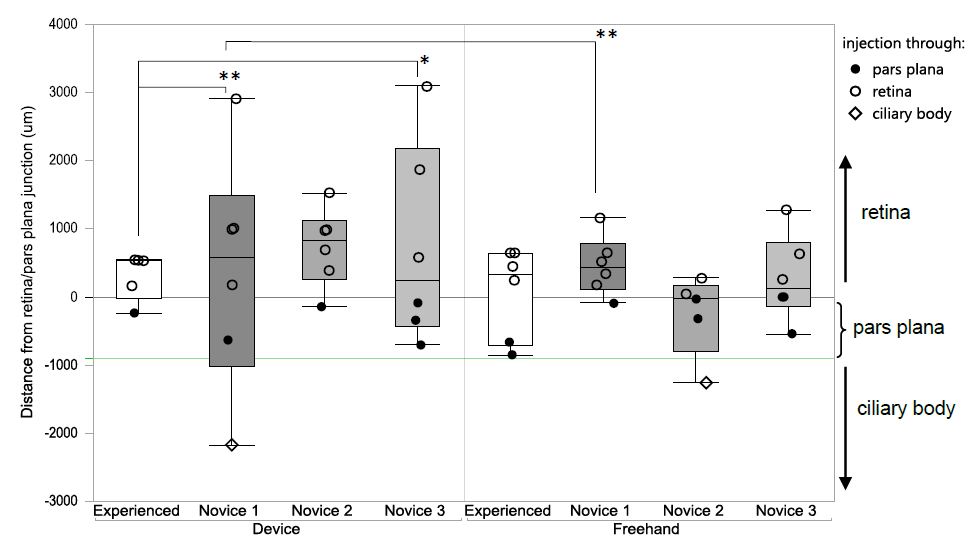
We had anticipated that the device would allow novice operators to achieve comparable results to an experienced operator. However, contrary to our hypothesis, use of the device did not lead to more precise needle-penetration-points in the hand of novices (Figure 4). In fact, the device appeared to increase the variability of needle-penetration-points in the hand of novices and device-guided injections by Novice 1 were significantly less precise than the freehand injections (Novice 1 device: SD 381.2 ± 1716.99 μm, n = 6 vs. Novice 1 freehand: SD 458.7 ± 430.97 μm, n = 6; P = 0.0087, two sided F-test). The experienced operator achieved precise results using both techniques and compared with Novice 1 and Novice 3 the device-guided injections of the experienced operator were significantly more precise (experienced operator with device: SD 308.6 ± 344.64 μm, n = 5 vs. Novice 1 with device: SD 1467.44 ± 1163.64 μm, n = 6; P = 0.015 and Novice 3 with device SD 381.17 ± 1716.99 μm, n = 6, P = 0.0083, two sided F-test) (Figure 4).
It is known that acquisition and retention of surgical skills involve repeated practice and performing a high volume of surgery is associated with improved patient outcomes and clinical results [23-25]. The three novice operators had been trained and demonstrated proficiency but did not perform the procedure routinely. It appears that the device, which had to be positioned correctly and maintained in this position for the duration of the procedure overburdened the novice operators who were still learning the procedure.
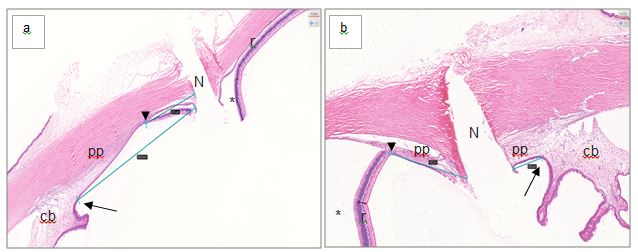
Further analysis of the anatomical location of the needle-penetration-point revealed that most of the injections (device-guided and freehand) penetrated the retina and not as anticipated the pars plana (see Figure 5 for a representative histological image). Only 6/23 (26%) device-guided and 8/23 (34%) freehand injections penetrated the pars plana. The ciliary body was penetrated once (1/23, 0.04%) following device-guided and once (1/23, 0.04%) following freehand injections (Figure 5).
The needle-penetration-point chosen for freehand injections in this study was in line with recently published data [17, 18]. The needle-penetration-point of the device was fixed at 3.2 mm posterior to the limbus. This decision was based on histological images of NZW rabbit eyes which measured the limbus to pars plana distance as 2.25 mm (see Supplementary Information) and the anticipation that the fixation process of the eye would result in a certain degree of shrinkage [26]. One aspect which most likely contributed to the low success rate of penetrating the pars plana was its small size (1 mm) in the rabbit, which in itself is challenging (see Supplementary Information Table 1) [10]. Furthermore, it can be concluded that the needle-penetration-point distance to limbus chosen in this study was too big as most injections penetrated the retina. The shrinkage effect of the histological fixation process was likely overestimated. Other authors have chosen a needle-penetration-point of 1.5 mm and 2-3 mm posterior the limbus and it can be concluded that a higher success rate of penetrating the pars plana in the rabbit could potentially be achieved by choosing similar needle-penetration-points [19,27]. It is noteworthy, that while the pars plana is recognized to be the ideal location for the needle to penetrate during intravitreal injections, adverse events directly related to penetrating the retina and choroid such as retinal tears, retinal detachment or intravitreal haemorrhage in the clinic are rare and believed to be more commonly attributable to underlying pathologic condition and not the intravitreal injection procedure itself [7, 28, 29]. Therefore, it is unlikely that injections through the retina of the eye of a healthy rabbit will cause detrimental effects to animal welfare or study data. We conclude, that while the device is safe to use in the hands of novice operators further extensive hand-on training and experience are required to allow novices to achieve comparable results to an experienced operator.
Limitations of the study include the fact that all data were gathered from cadavers. Information on the safety of the new device was therefore not generated in live animals. However, it is unlikely that this limitation impacts the validity of the data in respect of the anatomical location of the needle-penetration-point and contrast-agent-deposition. All injections were performed within 5 minutes of confirmation of death and while the intraocular pressure will drop immediately after death, other factors which determine the size, shape, and firmness of the eye remain constant [30]. Another limitation was the fact that shortly after planning the development and evaluation of the device, ocular work using rabbits in the authors’ facility was no longer conducted and the supply of rabbits was low and sporadic. This meant that each operator could only perform limited numbers of injections. Group sizes were largely determined by the low supply of rabbits but are thought to be reasonable for a first evaluation study. Ideally, data from more than one experienced operator should have been collected but only one experienced operator was available for the study. A potential limitation for the practical usefulness of the novel device is the fact that it should be used with a needle that is longer than the commonly available 13-mm-needle and custom-made needles had to be ordered for the purpose of this study.
The novel intravitreal injection device can be used to inject into the vitreous of rabbits and operators commented favourably about the superior stabilization of the eye compared with using the conjunctiva-forceps and eyelid-speculum during freehand injections.
Contrast-agent-deposition following device-guided injection by a novice operator was never in the near vicinity of the lens and we interpret this finding as a safety benefit of the device over freehand injections. To achieve contrast-agent-deposition comparable to freehand injections the device had to be used with a 19-mm-needle.
Contrary to our hypothesis, the device did not lead to an increased precision and it did not allow novice operators to achieve comparable results to an experienced operator with regards to the needle-penetration-point. We conclude that while the device is likely to be safe when used by novices, thorough and continuous hands-on-training and practice is required to achieve the same precision as an experienced operator.
Further in vivo studies are necessary to evaluate the device’s effects on the safety and pharmacokinetics of intravitreal injections. Experienced ophthalmic surgeons will be able to evaluate its practical utility and benefits.
The authors thank Terence Ballard, Amanda Buxton and Hugh Edgar for study support, Stephanie Webb for identification of a suitable MRI contrast agent, David Willé for statistical support and Nienke Fishwick for valuable input and thorough review of the manuscript.