Medullary Sponge Kidney with Distal Renal Tubular Acidosis: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Medullary sponge kidney (MSK) is a rare disease, with a prevalence of 0.0002 – 0.0005%, characterized by cystic dilations of the collecting ducts. Patients with MSK have the propensity for recurrent formation of kidney stones, nephrocalcinosis and urinary tract infections (UTIs). Unfamiliar to many practitioners and commonly asymptomatic, MSK patients often remain undiagnosed. In addition to a comprehensive review of the literature published to date, we report a case of how we diagnosed MSK coexisting with distal renal tubular acidosis (dRTA) in an adult patient who presented with severe hypokalemia and hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis.
Keywords: Renal Tubular Acidosis; Nephrocalcinosis; Medullary Sponge Kidney; Hypokalemia; Metabolic Acidosis
Medullary sponge kidney (MSK) is a rare disorder, usually congenital, defined by cystic dilations of the precalyceal collecting ducts within the medullary pyramids of the kidney [1-3]. The prevalence of MSK is reported to be 0.0002 – 0.0005%, with twice the frequency in females than males [2,3]. Often asymptomatic, MSK is underdiagnosed. The disease is usually discovered during evaluation of a urinary tract infection (UTI), renal colic or hematuria [4]. The pathophysiology of MSK is unknown, but it is associated with impaired acidification of the urine and most commonly distal renal tubular acidosis (dRTA).
While no longer commonly performed, intravenous urogram (IVU) is believed to be the gold standard for MSK diagnosis. IVU reveals linear striation and accumulation of contrast in small cysts within the papillae giving a “brush-like” or “bouquet of flowers” appearance to the renal papillae [4]. There is no specific therapy that can treat the cysts of MSK, but preventing hypercalciuria and alkalization of the urine can help prevent stone formation. Due to its rarity and under diagnosis, there have not been many recent reported cases of MSK in adults in the literature. We report a case of MSK in an adult patient, with no history of kidney stones or UTI, who presented with severe asymptomatic hypokalemia due distal renal tubular acidosis, nephrocalcinosis and a UTI.
A previously healthy 37-year-old Caucasian female, with a past medical history of mild asthma and controlled epilepsy on levetiracetam, presented for hospital admission from her primary care facility due to hypokalemia with a potassium level of 2.5 mEq/L. Her home medications included levetiracetam and montelucast. At triage, review of systems was positive only for intermittent, non-radiating, substernal chest pain lasting less than 30 minutes. She denied associated shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting or recent diarrhea. Her vital signs were within normal limits. On admission, her laboratory investigations revealed hypokalemia and hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis. Her laboratory test results, including plasma and urine electrolytes are shown in Table 1. As she was not in acute respiratory distress, a blood gas analysis was not obtained. Due to reported chest pain, her EKG and cardiac enzymes were trended and deemed not indicative of cardiac ischemia.
To determine the cause of her hypokalemia we performed a series of calculations shown in Table 2. Her transtubular potassium gradient was determined to be 9.78, suggesting renal potassium loss. Her serum anion gap was normal with decreased bicarbonate and elevated chloride concentration. Her urine anion gap was +11 mEq/L, suggesting failure of renal secretion of ammonium and bicarbonate. Given her adequate renal function, hypokalemia, and probable normal anion gap hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis, the diagnosis of dRTA was established. The patient’s initial phosphorus was 1.6 mg/dL. We attributed this to malnutrition as it quickly corrected to 2.9 mg/dL with administration of phosphorus and has remained stable over the past year without any intervention. While hypophasphatemia is unusual in dRTA, it is common in Fanconi syndrome; however, she displayed no other features of Fanconi syndrome.
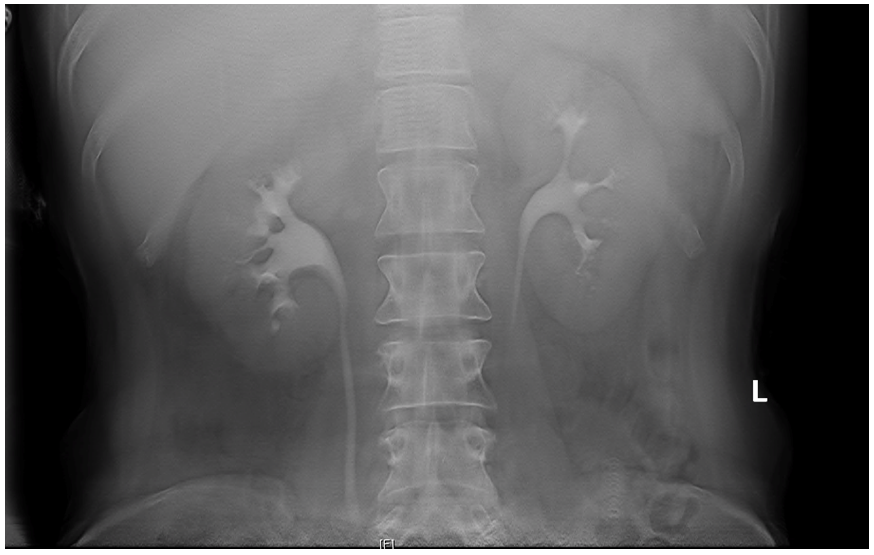
On the second day of admission, she complained bilateral flank pain and her physical exam revealed bilateral costovertebral angle tenderness. As such, a urinalysis and urine culture was performed, revealing a urine dipstick pH of five with occult blood noted (Table 3). The urine culture grew E.coli. Due to the patient’s pain and urine culture, a renal ultrasound was obtained. The ultrasound revealed significant bilateral nephrocalcinosis (Figure 1). The finding of such significant bilateral nephrocalcinosis in a young healthy patient prompted further work-up. An intravenous urogram (IVU) tomogram revealed dilated contrast-filled tubules within the renal medulla appearing like a “bouquet of flowers,” characteristic of medullary sponge kidney (Figure 2) [4].
The patient’s hospital course was uncomplicated. After her potassium was corrected, she was discharged on potassium citrate 40 mEq three times daily, sodium bicarbonate 1300 mg twice daily, and eplerenone 50 mg daily for 2 weeks. At 2 weeks hospital follow up, her labs were within normal limits and she was prescribed to only take potassium citrate 30 mEq three times daily. It has been one year, and her potassium remains within normal limits, taking potassium citrate 30 mEq three times daily.
Medullary sponge kidney is also known as Cacchi-Richi disease since it it was first described in the 1930s by Cacchi (a urologist) and Ricci (a pathologist) and Lenarduzzi (a radiologist) [5]. It is characterized by dilation of the terminal collecting ducts of the renal tubules, leading to formation of cysts in precalyceal collecting ducts within the medullary pyramids of the kidney [1-3,6]. Most commonly it is seen bilaterally; however, it has been reported to occur unilaterally in approximately 30% of cases [6,7]. With diameters ranging from 1.0 -7.5 mm, the cysts make the renal medulla appear like a sponge, hence the name “medullary sponge kidney” [4]. Although there have been few case reports of childhood diagnosis in the literature, symptoms usually appear in the third decade of life or after, most likely as a result of delayed expression of the genes that cause this congenital anomaly [3,8,9]. Most cases have not been linked to family history; however, a rare autosomal dominant form has been reported [7,8]. MSK has also been observed in several patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) [10].
Although the pathogenesis is not clearly understood, MSK is thought to be associated with hyperparathyroidism or parathyroid adenomas, as either a complication of prolonged hypercalciuria or a renal anatomical complication of primary hyperparathyroidism [11]. Interestingly, the RET proto-oncogene mutation is associated with multiple endocrine neoplasia type IIA (MEN-2A), a familial cancer syndrome, well known to be associated with parathyroid adenomas or hyperplasia; and MSK in a patient who had this syndrome has been previously reported [12]. Measuring serum parathyroid hormone (PTH) in patients who present with MSK could be beneficial. Our patient’s serum PTH was within normal limits.
It has been reported that close to 90% of patients with MSK have defects in renal acidification and most commonly distal RTA [4]. Distal RTA is defined as a urine pH above 5.5, hypercalciuria, hypocitraturia, hyperkaluria, hyperchloremic, hypokalemic normal anion gap metabolic acidosis, and normal renal function tests [2,3]. RTA may be accompanied by clinically significant hypokalemia due to renal potassium wasting [3]. Our patient’s diagnostic workup for the cause of her hypokalemia was compatible with dRTA and her urine was acidic most likely due to the concurrent urinary tract infection with E.Coli. The H+- ATPase pump is expressed in the alpha-intercalated cells localized in the late distal tubules and in the cortical collecting ducts, the same anatomical regions involved in MSK [2]. It has been suggested that dysfunction of this proton pump can trigger ectasia and dilation of the collecting ducts as metabolic acidosis can manipulate gene expression of proteins, thereby changing metabolic and signaling processes, including those involved in cell proliferation and apoptosis [2]. As such, metabolic acidosis can cause cell hypertrophy, hyperplasia and transdifferentiation, resulting in remodeling of the nephron [2,13]. Our patient was taking levetiracetam for seizure control, a drug known to induce acute interstitial nephritis and renal failure [14]. However, there have been no reports of levetiracetam causing dRTA as a side effect. Whether our patient acquired dilation of her distal collecting ducts secondary to dysfunction of H+- ATPase pumps versus whether she had congenital MSK resulting in dysfunction of her H+- ATPase pump remains unknown.
Although most commonly asymptomatic, 50% of patients with MSK have the propensity to develop renal calculi, most commonly comprised of calcium oxalate and calcium phosphate [4]. It has been known that hypercalciuria and distal tubular acidification defects play a role in the pathogenesis of kidney stones formation and nephrocalcinosis [4,15]. While there is no hypercalciuria associated with MSK, the dilated collecting tubules contribute to urinary stasis, which allows the urine to crystalize and subsequently pass the ductal stones into the renal pelvis where they may serve as foci for further stone formation [4,16]. Stones are a medium for growth of bacteria. Thus, like our patient, MSK patients can present with frequent UTIs and pyelonephritis, which can increase their risk for chronic kidney disease [4,6].
MSK is diagnosed via radiographic imaging. Both computer tomography (CT) scan and plain X-ray (the IVU scout image) can be used to visualize renal calculi. IVU is believed to be the gold standard for MSK diagnosis. IVU reveals linear striation and accumulation of contrast in small cysts within the papillae giving a “brush-like” or “bouquet of flowers” appearance to the renal papillae [4]. However, it is no longer commonly performed when suspecting renal calculi, due to the prevalence of computer tomography (CT) scans. Our patient’s bilateral nephrocalcinosis seen on the ultrasound was the first sign that prompted us to consider a diagnosis of medullary sponge kidney, which we verified by performing an IVU. A similar sequence of events was reported in another MSK case report [3].
As long as nephrolithiasis and UTIs are prevented, the expected renal outcome in patients with MSK is excellent [4,6]. To date, there is no specific therapy that can treat the cysts of MSK, but preventing hypercalciuria and alkalization of the urine can help prevent stone formation. Patients are commonly treated with potassium citrate to alkalinize the urine, and thus reduce the urinary saturation of calcium salts. Moreover, to reduce the risk of stone and UTI development, patients are encouraged to keep their urine output greater than 3 liters per day by increasing their fluid intake. Finally, thiazide diuretics can lower urinary calcium, and therefore decrease the risk of calcium stone formation [6].
Medullary sponge kidney is a rare and underdiagnosed disease. Due to hypercalciuria, urinary stasis in dilated collected tubules and distal tubular acidification defect, patients with MSK have the propensity for recurrent formation of kidney stones, nephrocalcinosis and urinary tract infections (UTIs). Our case illustrates a presentation of MSK diagnosed in an adult presenting with hypokalemia and hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis.

.PNG)
.PNG)