Variety X Nitrogen Fertilizer Interaction on Striga Control, Yield and Yield Related Attributes of Sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] Under Striga Infestation Conditions Area of Abergelle District, Northern Ethiopia
Sorghum [Sorghum Bicolor (L.) Moench] is an important food crop in Ethiopia, and is ranked second for “injera” quality next to tef. However, the productivity of sorghum is limited by several biotic and abiotic constraints amongst striga hermonthica (Del.) Benth is the greatest specialized parasitic weed causing serious injury by depriving water, minerals and photosynthesis from the host. Striga hermonthica is becoming the major epidemic in most of sorghum growing areas in the country including Abergelle. Thus, a field experiment was conducted in 2013/14 cropping season to assess the interaction effect of variety by nitrogen fertilizer rates on striga control, yield and yield related attributes as well as to determine optimum nitrogen fertilizer rate to enhance the productivity of sorghum under natural striga infestation areas of Abergelle district, Northern Ethiopia. The treatment combination comprised of two striga resistant and early maturing sorghum varieties (Gobye and Abshir) and three nitrogen fertilizer levels (0, 50 and 100 kg N ha-1) in 2x3 factorial arrangement in randomized complete block design (RCBD) with three replications. The analysis of variance result showed highly significant (P≤0.01) differences due to nitrogen, variety and variety by nitrogen interaction for number of striga count per plot. The lowest number of striga count per plot was obtained from the combination of Gobye+100 kg N ha-1, whereas, the highest number of striga count per plot was recorded from Abshir+0 kg N ha-1. Thus, Gobye exhibited resistance to striga hermonthica by supporting the lowest number of striga plants germination with increasing fertilizer levels from zero to 100 kg N ha-1. Besides, the analyzed result indicated that grain yield of sorghum was significantly influenced (P≤0.01) by variety x nitrogen interaction effect. The highest grain yield of sorghum (1743 kg ha-1) was obtained from the combination of Gobye+100 kg N ha-1 while the lowest grain yield (1086 kg ha-1) was recorded from Abshir+0 kg N ha-1. However, days to physiological maturity and growth traits like plant height and panicle length were not significantly affected by variety x nitrogen interaction effect. Moreover, the partial budget analysis revealed that the highest net benefit was recorded from the combination of Gobye+100 kg N ha-1. Therefore, farmers in the study area could control striga and enhance sorghum productivity through combination use of the early matured and striga resistant variety Gobye+100 kg N ha-1 under natural striga infestation.
Keywords: Variety x Nitrogen Interaction; Sorghum; Striga hermonthica; Yield and yield related traits
Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench) is a drought and heat tolerant C4 tropical crop with wide agro-ecological adaptations. The crop is mostly cultivated in the semiarid regions of the world where drought and poor soil conditions make the production of cereals difficult. It is unique to adapt to environmental extremes of abiotic and biotic stresses and an essential crop to diets of poor people in the semi-arid tropics where droughts cause frequent failures of other crops [1]. It is a major food and nutritional security crop to more than 100 million people in horn of Africa, owing to its resilience to drought and other production constrains [2]. Sorghum has four features which make it one of the most drought resistant crops of all i.e., i) it has a very large root to leaf surface area ii) in times of drought it will roll its leaves to reduce water loss by transpiration iii) if drought continues, it will go into dormancy rather than dying, and iv) its leaves are protected by a waxy cuticle.
Sorghum plays an important role in the economy of Ethiopia and is carried out by small-scale and resource poor farmers. Especially in the lowlands of eastern, north and north-eastern parts of the country where the climate is characterized by unpredictable drought and erratic rainfall, sorghum is one of the most important cereal crops planted as food insurance [3]. Sorghum is grown in almost all regions that adapted to a wide range of environments between 400 m to 2500 m altitude, therefore, can be cultivated in the high lands, medium altitude and lowland areas of Ethiopia. It is the third important crop in terms of area coverage and volume of production and second to tef in ‘injera’ making in the country. In the year 2015/16, 4.32 m tons annual harvest from 1.85 m ha was obtained [4]. However, sorghum productivity in the world in general and Ethiopia in particular (2.31 t/ha) is by far below its potential due to biotic and edaphic factors affecting directly and indirectly sorghum production [5].
The major constraints that account for this low productivity are drought (moisture stress), low soil fertility (nutrient deficiency) and pest damages. Among the pests, the parasitic weed; Striga has long been recognized as the utmost biotic factor to sorghum production especially in northern Ethiopa [6]. Striga is a Latin word which stands for ‘Witch’. It is known as witch weed because it causes stunted growth and early discoloration of crop leaves before its emergence (Fischer, 2006). There are many striga species which are economically important, but S. hermonthica (Striga hermonthica (Del.) Benth.) is the most harmful and serious threat of sorghum production in Abergelle area, northern Ethiopia. S. hermonthica is believed to be originated around the border of Sudan and Ethiopia now-a-days Nuba and where it causes severe losses in most cultivated crops thereby the lives and livelihoods of over 100 million of the African people adversely affected in the region. This region is also the birthplace of domesticated sorghum [7,8]. Though, it’s endemic in the African savanna currently, and striga constrained the production of sorghum worldwide [9,10]. Ejeta (2007) estimated that striga causes 65-70% loss in sorghum fields. But, if intensity of infestation is excessively high and the variety used is susceptible, losses could reach up to 100%. Striga could be controlled by using resistant variety, fertilizer and tied ridges on farms which had long been abandoned due to Striga infestation, whereas the local cultivars had severe infestation [10].
The use of resistant varieties for striga control would probably be the most feasible and practical method particularly for the subsistence farmers in the striga endemic regions of Ethiopia. In the country, there are three striga resistant varieties of sorghum released by the national sorghum improvement program in collaboration with Purdue University, namely, Gobiye, Abshir and Birhan. Those varieties have been found to be promising to reduce yield losses due to striga. Severity of infestation of Striga is reported to correlate negatively with soil fertility and the critical element among the nutrients is widely believed to be nitrogen. The advantageous effect of fertilizers include increasing soil N and other nutrients, replacing the soil organic matter and increasing soil moisture holding capacity [11]. The suppressive effects of N on Striga infestation are attributed to delayed germination; reduced radical elongation, reduced stimulants production and reduction of seeds response to the stimulants [12]. Kaudi and Abdulsalam (2008) also reported that Striga spreads rapidly in areas of low fertility and decreasing plant diversity, conditions often experienced by poor farmers in dry land zones including the study area [13]. Accordingly, this study was undertaken with the following objectives:
1. To assess the interaction effect of variety by nitrogen fertilizer rates on striga control and yield and yield related traits of sorghum
2. To determine optimum nitrogen fertilizer rate with improved integrated striga control packages to enhance the productivity of sorghum under natural striga infestation areas.
The field experiment was conducted under rain-fed conditions in the Central part of Tigray region, northern Ethiopia specifically at Abergelle on station in 2013/2014 cropping season. Geographically the experimental site lies between 13014’06” N latitude and 38058’50” E longitudes. The area is agro-ecologically characterized as hot warm sub-moist lowland (SMl-4b) located below an elevation of 1500 meter above sea level. The average annual rainfall and temperature status of the study area ranges from 350 – 650 mm and 21 – 41°c, respectively. The agricultural sector of the study area is highly susceptible to climate variability, seasonal shifts in rain fall, resulting in drought [14]. Drought is frequent due to abnormally low and ultimately rain fall dawn. Almost every year, the study area experiences localized droughts and devastated by striga infestation causing crop failure and risking development activities. Thus, early maturing and striga tolerant /resistant sorghum varieties to highly infested areas are of great interest to the farmers.
The treatments were consisted of a combination of two striga resistant and early maturing sorghum varieties (Gobye and Abshir) and three Nitrogen levels (0, 50 and 100 kg N ha-1). The seed was obtained from Melkasa Agricultural Research Center. Triple super phosphate (TSP) applied as source of P sowing at the recommended rate (46% P2O5 kg ha-1) was sourced from Mekelle Soil Laboratory Center. Urea (46% N) was used as source of N.
The two striga resistant and early maturing sorghum varieties and three rates of N were laid out in 2 x 3 factorial arrangements in randomized complete block design (RCBD) with three replications. Each experimental plot have had an area of 18 m2 with 3.75 m width and 5 m length, separated by a spacing of 1 m between blocks and 0.5 m between plots within a block. A spacing of 75 cm between rows within a plot and 20 cm between plants within a row was maintained. There were five rows of 5 m length in each plot. The outer most rows at both sides of the plots were considered as a border. Therefore, three rows of 5 m length (2.25 m x 5 m) were considered as a net harvested experimental plot.
The land was ploughed properly with an ox and a ridge of 30 cm height and a furrow width of 0.45 m was being made manually using hand hoes 10 days prior to planting. Ridges were cross tied with soil bunds across the ridges of 25 cm height at 2 m intervals. After leveling the land, rows were made. Two to three sorghum seeds were sown at a depth of 4-5 cm deep and then thinned to one per hill three weeks after planting to maintain the requisite plant population. All plots were fertilized uniformly with 46% of TSP at planting time. All other necessary field management practices such as thinning, weeding and crop protection control measures were applied uniformly (except the different N rates to be studied) for each treatment based on the recommendations for sorghum in dry lowlands.
Soil sample at a depth of 0-30 cm was taken from five random spots diagonally across the experimental field using auger before planting. The collected soil samples were composited to one sample. The bulked soil samples collected before planting were air dried, thoroughly mixed and ground to pass 2 mm sieve size before laboratory analysis [15]. Then the samples were properly labeled, packed and transported to the laboratory. Then soil analysis had performed in Mekelle Research Center soil laboratory for physico-chemical properties mainly for soil pH, organic matter, total nitrogen, available phosphorus, soil texture (silt, clay and sand) and cation exchange capacity (CEC) following the standard procedures [15].
The soil pH was determined using potentio metrically in 1:2.5 soil-water suspensions with standard glass electrode pH meter [16]. The Walkley and Black (1934) method was used to determine the organic matter content and the result was obtained by multiplying percent organic carbon by a conversion factor of 1.724 [17]. The total nitrogen content of the sample soil was also determined following Kjeldahl digestion, distillation and titration procedure as described by Bremner and Mulvaney (1982) [18]. Besides, available phosphorus was determined by Olsen, et al. (1954), Cation Exchange Capacity and, the particle size distribution was determined by the hydrometer method (differential settling within a water column) according to FAO (2006) using particles less than 2 mm diameter [19-21]. The procedure measured percentage of sand (0.05 - 2.0 mm diameter), silt (0.002 - 0.05 mm diameter) and clay (<0.002 mm diameter) fractions in soils [22].
Data recorded on S. hermonthica weed
1. Striga count at flowering: It was recorded as the number of striga count per each plot at flowering of sorghum and pulled out during weeding.
2. Striga count at harvesting: This was recorded as the number of striga count per each plot at harvesting of sorghum.
Data recorded on Sorghum components
Phenological trait
3. Days to 90% maturity (DM): This was recorded as the number of days from sowing to the stage when 90% of the plants in a plot have reached physiological maturity.
Growth traits
4. Plant height (cm): This was determined as the average plant height (cm) measured from the central rows of each net plot at 90% physiological maturity from the soil surface to the tip of head.
5. Panicle length (cm): It was recorded as the average panicle length (cm) measured from the flag leaf to the tip of the head (at physiologically matured).
Yield and yield related traits
6. Grain yield (g/plot): It was determined as grain yield in grams obtained from the net plot area of each plot and converted to kilograms per hectare at 12.5% moisture level.
7. Above ground biomass (g/plot): It was measured after the plants from the net plot area were harvested and sun dried till constant dry weight yield attained and converted to kilograms per hectare.
8. Harvest index: It was calculated as the ratio of dried grain yield to the dried above ground biomass.
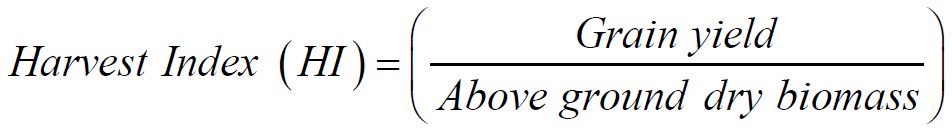
Economic analysis was executed to assess the economic feasibility of the treatments using partial budget and marginal analyses. Starting from the lowest level of fertilizer, the change in yield was multiplied by the sorghum price to develop the marginal revenue for each additional kg of soil nitrate N. Partial budget was estimated using the farm gate prices of the various inputs. The partial budget analysis was made using the predominant inputs at planting and for outputs at the time the crop was harvested. Market prices of urea, TSP in May 2013 and sorghum grain in January 2014, were 11.50, 25.00 EB kg-1 and 8.00 EB kg-1, respectively. All costs and benefits were calculated on hectare basis in Ethiopian Birr (Birr ha-1). The economic analysis was based on the formula developed by CIMMYT (1988) and is shown as follows: Average grain yield: was the average yield (kg ha-1) of each treatment. Gross field benefit (GFB): was the product of field price (EB ha-1) of sorghum and the average grain yield for each treatment. Total variable costs (TVC): was the sum of field cost (EB ha-1) of fertilizer and the cost of fertilizer application. Net benefit (NB): was calculated by subtracting the total costs from the gross field benefit for each treatment. NB = GFB – TVC. CIMMYT (1988) reported that the % MRR between any pair of treatments denotes the return per unit of investment in fertilizer expressed as a percentage. Marginal rate of return (MRR %): was calculated by dividing change in benefit by change in cost [23].
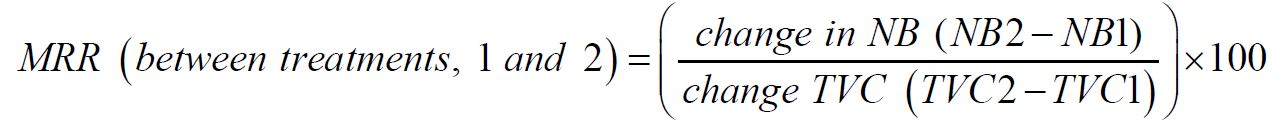
Where: NB1=net benefit at level one, NB2= net benefit at level two, TVC1=total variable cost at level one and TVC2= total variable cost at level two, MRR= Marginal Rate of Return. Thus, marginal rate of return (MRR) of 100% implies a return of one Birr on every Birr of expenditure in the given variable input.
The collected data (phenological, morphological, yield and yield attributes and sriga count) were subjected to analysis of variance (ANOVA) using GenStat 16th edition (GenStat, 2014) software following a procedure appropriate to RCBD (Gomez and Gomez, 1984) [24]. Mean separation was done using Fisher’s least significant difference (LSD) test at 5% level of significance.
The analytical results of the experimental soil revealed that the soil textural class of Abergelle testing site is sandy clay with a particle size distribution of 61% sand, 26% clay and 1% silt (Table 1). Therefore, the soil of the study site was sandy clay in texture with high proportion of sand followed by clay. This implies that the basic cations such as Ca, K, Na and Mg would be leached more easily as texture determines the degree of retention or ease of leaching of basic cat ions.
The study site had neutral nature with soil pH 7.18, which is in agreement with the reports of Bruce and Rayment (1982) who generally classified soil pH as very strongly acidic (4.5-5.0), strongly acidic (5.1- 5.5), moderately acidic (5.6-6.0), slightly acidic (6.1-6.5), neutral (6.6-7.3), mildly alkaline (7.4-7.8), moderately alkaline (7.9-8.4), strongly alkaline (8.5-9.0), and very strongly alkaline (>9.0) (Table 1) [25]. Soil organic matter of the experimental site was 0.72% which fall into very low category according Fisher (1974) and Westerman (1990) rating who categorized organic matter content of soil is very low (<1%), low (1.0 to 2.0), medium (2.1 to 4.2), high (4.3 to 6), and very high (>6) [26,27]. The low organic matter might be attributed to the intensive cultivation and continuous removal of crop residue. Thus, the experimental site needs supplement or addition of materials that increase the organic matter in the soil.
The soil analysis further indicated that the experimental site had very low total nitrogen (0.08%) according to Tekalign, et al. (1991) and Havlin, et al. (1999) who rated total N (%) as very low (<0.1), low (0.1 to 0.15), medium (0.15 to 0.25) and high (>0.25) [28,29]. The low nitrogen content could be accompanied with the low soil organic matter content in the soil; a limiting factor for optimum crop growth. Therefore, the soils need amendment with organic fertilizers. The available phosphorus content of the study site was within high range with the value of 13.82 ppm as presented in Table 1. In line with this result, Olsen, et al. (1954) rating, P (mg kg-1) content is: (< 3) very low, (4 to 7) low, (8 to 11) medium, (>11) high and Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC) of the site was 22.60 cmol (+) kg-1 which is high according to Tucker (1974) classification (10-20 cmol (+) kg-1) is medium and >20 cmol (+) kg-1 is high [19]. This showed high capacity of the soil to retain cations in exchangeable form for the plant. According to Hazelton and Murphy (2007), the EC of the soil (0.18 ds m-1) also indicated that the experimental soil was non-saline.
The analysis of variance result indicated that the main effect of variety, nitrogen and variety by nitrogen interaction significantly (P≤0.01) influenced for number of Striga hermonthica per plot at flowering and harvesting of sorghum (Table 2). The smallest number of the striga count per plot at flowering (1.5) and harvesting (0.98) of sorghum was observed from combination of Gobye+ 100 kg N ha-1 while the highest number of Striga count per plot at flowering (8.67) and harvesting (5) of sorghum was noted from the combination of Abshir+ zero kg N ha-1 (Table 2). This confirmed the fact that increasing nitrogen rates from zero to 100 kg N ha-1 in combination with Gobye significantly reduced the number of Striga population. Possible reason for this could be due to the positive interaction between resistant sorghum variety and nitrogen fertilizer at high application levels supports significantly fewer emerged S. hermonthica plants, hence suppressed striga and increases grain yield of sorghum. Besides, this study confirms with the findings of Tesso, et al. (2003) who reported that resistant varieties effectively reduced the Striga with and without other options indicating that host plant resistance alone can be used in situations where integration of all options is impossible [30]. Similarly, Ejeta, et al. (2000); Haussmann, et al. (2000); an Omanya (2001) also suggested that host plant resistance would probably be the most feasible and potential method for parasitic weed control [31-33].
Phenological and Growth Traits
Days to 90% maturity:
Analysis of variance result showed non significance difference due to variety, nitrogen and variety by nitrogen interaction effects for days to 90% physiological maturity (Table 3). The result indicated that there was no genetic variation between test varieties for earliness. It could be also providing sufficient nitrogen permits crop to grow to full maturity rather than delaying it.
Phenological and Growth Traits
Plant height:
The analysis of variance illustrated that the main effect of nitrogen significantly (P≤0.05) influenced sorghum plant height whereas variety and nitrogen by variety interaction had no significant effects on plant height of the crop (Table 5). The highest plant height (132.5 cm) was recorded from the application of 100 kg N ha-1 while the shortest (125 cm) was recorded from control (0 kg N ha-1 ) (Table 3). Similarly, Bilal, et al. (2000) who reported that plant height increased progressively up to harvest over control with the application of nitrogen fertilizer [34].
Panicle length:
Analysis of variance result revealed that the main effect of nitrogen significantly (P≤0.05) influenced panicle length whereas variety and nitrogen by variety interaction had no significant effects on panicle length of the crop (Table 5). The tallest panicle length (30 cm) was recorded from 100 kg N ha-1 while the shortest (28 cm) was recorded from control (Table 3). But, there was no genetic difference among the test varieties. The result of this study disagreed with that of Zerihun, et al. (2016) who reported that under the competition for water and nutrients with Striga hermonthica, the plant height and panicle length of uninfected sorghum was significantly different from that of infected plants due to genetic difference of varieties [35].
Yield and yield related traits
The analysis of variance result as presented in Table 4 revealed that the main effect of variety, nitrogen and variety by nitrogen interaction significantly (P≤0.01) affected for both grain yield and biomass yield of the crop. The highest grain yield (1743 kg ha-1) and biomass yield (6527 kg ha-1) were attained from application of 100 kg N ha-1 in combination with the striga resistant sorghum variety Gobye, whereas, the lowest grain yield (1086 kg ha-1) and biomass yield (3036 kg ha-1) were attained from zero kg N ha-1 + Abshir. Grain yield increased as N rate increased indicating the possibility of using fertilizer level higher than 100 kg N ha-1 (Table 4). There were also significant differences among each N rate and variety. The grain yield of Gobye variety was significantly higher than Abshir (Table 4).
Besides, the investigated result revealed that the main effect of nitrogen and nitrogen by variety interaction significantly (P≤0.05) influenced harvest index while variety had no significant effects on harvest index of the crop (Table 5). The highest harvest index (0.38) was obtained with application of 50 kg N ha-1 + Abshir variety where the lowest harvest index (0.27) was obtained with application of 100 kg N ha-1 + Gobye variety. This result concurred with the finding of Gebrelibanos (2015) who reported that nitrogen fertilizer showed significant differences on harvest index.
As result of the partial budget (economic) analysis for fertilizer N levels has been presented in Table 6, 158.79% gain from 0 to 50 kg N ha-1 was less than from 50 to 100 kg N ha-1 which is 215.83%. The highest positive gross margin was shown when applying 100 kg N ha-1 at planting with (13,944.00 ETB ha-1). The adoption of this treatment as methods for Striga control, would give an additional gain of 215.83% from every Birr invested in Striga control. Application of 100 kg N ha-1 resulted in the highest average grain yield increase when compared to 0 and 50 kg N ha-1 rates. The 100 kg N ha-1 will be considered as profitable treatment and gave the best in the conditions of the trial. It has the highest returns to the money invested in its production; it maximized profit and output and minimized costs (Table 6). All N rates were economically viable and had positive marginal rate of returns. Generally, the economic analysis showed that the highest net benefit was recorded from the combination of Gobye+100 kg N ha-1 [36]. This finding agrees with that of Tsegay, et al. (2018) who reported that the cultivation of Striga resistant sorghum variety (Gobye) in combination with other integrated striga control packages gave higher gross margin as compared to farmer’s local variety and practices for Striga control.
According to soil analysis for physico-chemical properties of the soil; the soil class of study site was sandy clay in texture with high proportion of sand (61%) followed by clay (26%). Soil of the trial site had neutral nature with soil pH 7.18. Soil nutrients such as OM% and total N falls into very low category, whereas, CEC and available phosphorus falls into high category. There were highly significant (P≤0.01) differences due to nitrogen, variety and variety by nitrogen interaction for number of striga count per plot both at flowering and harvesting of sorghum and application of 100 kg N ha-1 in combination with Gobye variety was best means to control Striga.
Regarding to phenological data of sorghum, analysis of variance result showed non significance difference due to variety, nitrogen and variety by nitrogen interaction effects for days to 90% physiological maturity. The growth traits; plant height and panicle length were significantly (P≤0.05) influenced by nitrogen (100 kg N ha-1), but not due to variety and nitrogen by variety interaction effects. Increased grain yield due to N application also attributed to increased biomass production and increased seed set with N fertilization. The highest grain yield (1743 kg ha-1) and biomass yield (6527 kg ha-1) were obtained from application of 100 kg N ha-1 in combination with the sriga resistant sorghum variety Gobye, whereas, the lowest grain yield (1086 kg ha-1) and biomass yield (3036 kg ha-1) were obtained from zero nitrogen fertilizer application+ Abshir. The partial budget analysis also revealed that the highest net benefit was recorded from the combination of Gobye+100 kg N ha-1. Therefore, the farmers in the study area could sustainably control striga and enhance sorghum productivity through combination use of the early matured and striga resistant variety Gobye+100 kg N ha-1 under natural striga infestation.
The author has not declared any conflict of interest.
The author thanks Abergelle Agricultural Research Center for funding the research work.
