Zinner Syndrome with Dilatation of Vas Deferens with Reflux on Doppler
Zinner syndrome is a triad of Mullerian duct abnormality characterized by ejaculatory duct obstruction, ipsilateral seminal vesicle cyst and unilateral renal agenesis. It is often detected incidentally during cross sectional imaging or during per rectal examination when most of the seminal vesicle cysts are less than 5 cms in size. It usually presents in the third or fourth decade of life due to infertility. We present a case of a 28 - year old male patient who presented with swelling in left hemiscrotum in the region of epididymal tail. Sonography of abdomen revealed left renal agenesis, multiple cysts in left seminal vesicle, dilated left vas deferens showing reflux on Valsalva maneuver and a well-defined slightly echogenic lesion in the left epididymal tail of size approximately 17 x 15 mm with central echoreflective calcification – likely due to epididymal cyst with inspissated secretions. Right megaureter was also seen.
Keywords: Seminal Vesicle; Renal Agenesis; Ejaculatory Duct; Vas Deferens; Zinner Syndrome
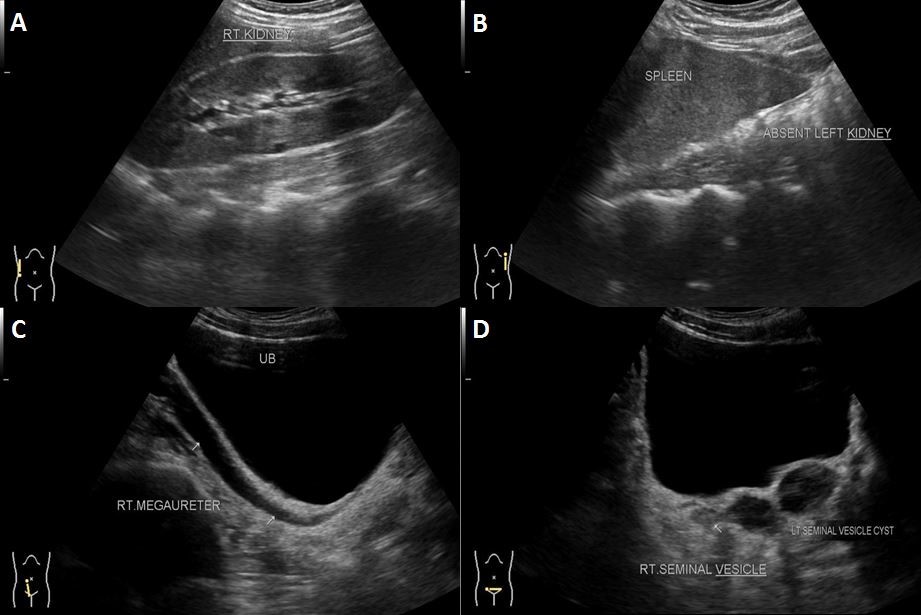
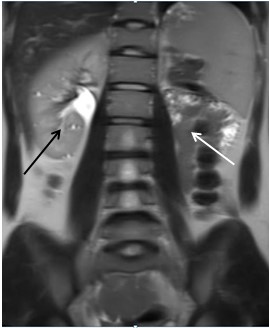
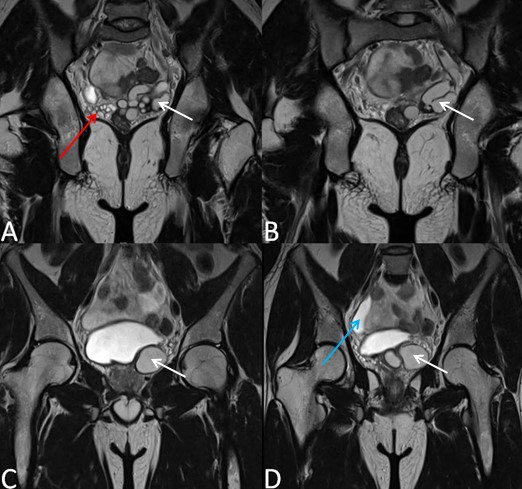
A 28 year old male patient presented with swelling in the left hemi-scrotum since 1 year, which increased since the last two months. There was no history fever, trauma and urinary bladder complaints. Sonography (USG) abdomen and pelvis showed absence of the left kidney in left renal fossa, along its course of ascent and in ectopic location – suggestive of agenesis. Right kidney showed mild compensatory hypertrophy (Figure 1A-B, Figure 2 and Figure 3).
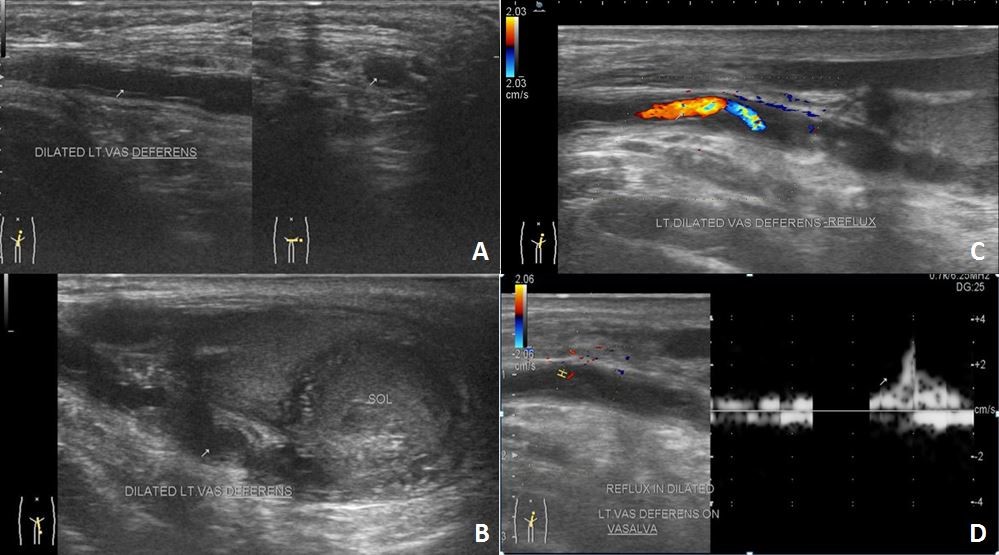
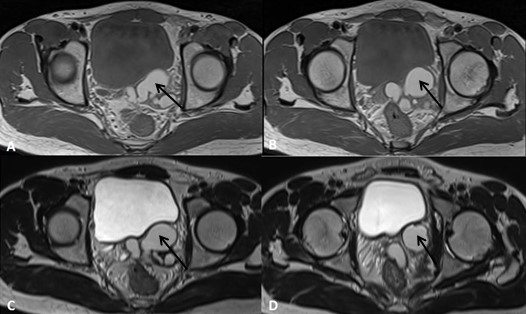
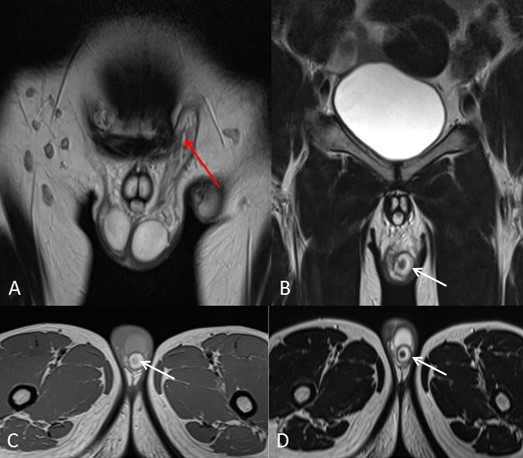
Pelvic portion of right ureter showed mild dilatation with narrowing at right uretero-vesical junction – suggestive of congenital megaureter (Figure 1C). Left seminal vesicle was enlarged due to multiple anechoic cysts of variable sizes (Figure 1D). USG of the inguino-scrotal region showed a well-defined slightly echogenic lesion in the left epididymal tail of size approximately 17 x 15 mm with central echoreflective calcification (Figure 2B). Both the testicles appeared normal. Left vas deferens was dilated in its entire extent (Figure 2A-D). On colour Doppler and pulse Doppler studies, reflux was noted in dilated left vas deferens (Figure 2C-D). MRI of pelvis and inguino-scrotal region was done by obtaining T1 weighted images (T1WI) and T2 weighted images (T2WI) sequences in axial, coronal and sagittal planes. Left seminal vesicle was enlarged due to multiple cysts (Figure 4 and 5). Largest cyst measured approximately 38 x 25 mm. The cyst appeared hyperintense on T1WI and T2WI due to inspissated secretions or high protein content. Right seminal vesicle appeared normal, measuring approximately 22 x 14mm. Pelvic portion of right ureter showed dilatation with narrowing at right uretero-vesical junction – suggestive of congenital megaureter (Figure 5D). Both testicles appeared normal. A well-defined round lesion of size approximately 17 x 15 x 19 mm in Antero-posterior, transverse and cranio-caudal dimensions respectively was noted on left postero-lateral aspect of left testis in the region of epididymal tail. It appeared hyperintense on T1WI and T2WI with no fat suppression on T1 fat saturated images (T1FS) – suggestive of cyst with inspissated secretions or high protein content. The cyst showed a hypointense central focus on T2WI – suggestive of central calcification (Figure 6). Left spermatic cord was thickened. Prostate appeared normal. A diagnosis of Zinner’s syndrome was made in view of seminal vesicle cysts, ipsilateral renal agenesis and ejaculatory duct obstruction.
Zinner syndrome is a triad of Mullerian duct abnormality characterized by ejaculatory duct obstruction, ipsilateral seminal vesicle cyst and unilateral renal agenesis. It usually presents in the third or fourth decade of life due to infertility. It was first described by Zinner in 1914 [1]. Most patients with Zinner’s syndrome are asymptomatic till third or fourth decade of life and manifest during reproductive age group. It is often detected incidentally during cross sectional imaging or during per rectal examination when most of the seminal vesicle cysts are less than 5 cms in size. Giant seminal vesicle cysts are more than 12 cm in size and can cause colonic and bladder obstruction [2]. Malignant transformation in the seminal vesicle cysts is rarely reported [3]. Less than 200 cases have been reported in literature till 2016 [4].
During embryogenesis, mesonephric (Wolffian duct) is a paired organ found in humans. Under the influence of testosterone and anti-Mullerian hormones in males, it develops into seminal vesicle, vas deferens, hemitrigone, and bladder neck, urethra proximal to the external sphincter, epididymis, paraepididymis, appendix epididymis and efferent ducts. Insult occurring during the first trimester affects the embryogenesis of seminal vesicle, vas deferens, kidney and ureter. Due to insult, there is maldevelopment of distal part of mesonephric duct leading to atresia of ejaculatory duct and abnormal ureteral budding. Atresia of ejaculatory duct leads to obstruction and cystic dilatation of seminal vesicle due to gradual accumulation of secretions in seminal vesicle with subsequent cyst formation. Abnormal ureteral budding leads to renal agenesis and dysplasia. These pathologies result in azoospermia or oligozoospermia which present as primary infertility [3]. The metanephric blastema during the fourth to sixth week of gestation secretes growth factors. These growth factors induce the growth of the ureteric bud towards it. The ureteric bud also secretes growth factors and proliferates to finally fuse with the metanephric blastema forming the primitive kidney. Disturbance in these inductive events during the fourth to sixth week of embryogenesis (like a mutation of metanephric blastema, disruption of retinoic acid signalling) causes inhibition of ureteric bud growth with resultant failure of fusion of ureteric bud with the metanephric blastema. This results in renal hypoplasia/ agenesis. Failure of ureteric bud to separate from the lower part of metanephric duct leads to atresia of ejaculatory duct and obstruction of the seminal vesicle. There is accumulation of secretions in seminal vesicle with resultant cystic dilatation [5].
On sonography, seminal vesicle cyst appears anechoic with variable wall thickness and may show internal echoes due to previous haemorrhage or infection. Ipsilateral renal agenesis is detected by the absence of kidney in renal fossa, along its course of ascent and in an ectopic location. Intra venous urography confirms renal agenesis and can show smooth extrinsic compression along the infero-lateral surface of urinary bladder due to seminal vesicle cyst. On computed tomography (CT), the seminal vesicle cysts are seen as retro-vesicular lesions of water or near water attenuation just superior to the prostate. The cysts may show thick, irregular walls and hyperdense contents due to previous haemorrhage or increased protein content. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can differentiate a seminal vesicle cyst from other pelvic cystic malformations. The presence of fluid of high signal intensity on T2WI and a convoluted tail connecting cyst to seminal vesicle go in favour of the seminal vesicle origin of cystic lesion [3]. Other cystic pelvic lesions are prostatic utricle cyst, true cyst of prostate gland, bladder diverticula, ureteroceles, Mullerian duct cysts and hydronephrotic pelvic kidneys. These can be differentiated from seminal vesicle cysts based on their location (median, paramedian and lateral) and imaging characteristics like intra-lesional contents and associated findings in urogenital system. Mullerian duct cysts and ejaculatory duct cysts are midline in location. Aspirate from seminal vesicle cyst show spermatozoa, which differentiate it from Mullerian duct cysts. Bladder diverticulum, ectopic ureterocele and diverticulosis of Ampulla of the vas deferens are laterally located. MRI is useful for accurate pre-operative surgical planning for seminal vesicle cyst excision [3]. Surgical excision is indicated in case of large cyst and presence of clinical symptoms. Zinner syndrome usually presents with dysuria, frequency of micturition, perineal pain, epididymitis, infertility, recurrent UTI, prostatitis and painful ejaculation [2]. Giant seminal vesicle cyst can present with bladder outflow obstruction or colonic obstruction [2].
Transrectal sonography is useful in determining size, location and nature of the seminal vesicle cyst. It demonstrates anechoic contents or debris – suggestive of infection/ previous haemorrhage [3].
Casey, et al. reported a pentad of mesonephric duct abnormality on imaging, which included ipsilateral renal agenesis, seminal vesicle cyst, partial hemi-trigonal development, epididymal dilatation and cystic dysplasia of rete testis [6].
Aspiration of cyst fluid with identification of spermatozoa is diagnostic for Zinner’s syndrome, which can be done transperineally [2].
Due to ejaculatory duct atresia, vas deferens can be dilated [7].
There can be dilatation of convoluted structures in the epididymis presenting as a para-testicular mass. These convoluted structures show honeycomb appearance with thickened walls and can show reflux on performing Valsalva maneuver at colour Doppler examination [8]. Unique feature in our case report is dilatation of vas deferens showing reflux during the Valsalva maneuver on colour Doppler examination. The solid lesion seen in epididymal tail is probably due to inspissated secretions due to distal block. Congenital megaureter on the contralateral side in Zinner’s syndrome has not been described yet in literature.
Zinner syndrome is rare and a triad of unilateral renal agenesis, ipsilateral seminal vesicle cysts and ipsilateral ejaculatory duct obstruction. MR is an imaging modality of choice for its diagnosis. It usually presents in third to fourth decade of life with infertility.